Abstract
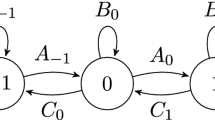
Our initial motivation was to understand links between Wiener-Hopf factorizations for random walks and LU-factorizations for Markov chains as interpreted by Grassman (Eur. J. Oper. Res. 31(1):132–139, 1987). Actually, the first ones are particular cases of the second ones, up to Fourier transforms. To show this, we produce a new proof of LU-factorizations which is valid for any Markov chain with a denumerable state space equipped with a pre-order relation. Factors have nice interpretations in terms of subordinated Markov chains. In particular, the LU-factorization of the potential matrix determines the law of the global minimum of the Markov chain.
For any matrix, there are two main LU-factorizations according as you decide to enter 1 in the diagonal of the first or of the second factor. When we factorize the generator of a Markov chain, one factorization is always valid while the other requires some hypothesis on the graph of the transition matrix. This dissymmetry comes from the fact that the class of sub-stochastic matrices is not stable under transposition. We generalize our work to the class of matrices with spectral radius less than one; this allows us to play with transposition and thus with time-reversal.
We study some particular cases such as: skip-free Markov chains, random walks (this gives the WH-factorization), reversible Markov chains (this gives the Cholesky factorization). We use the LU-factorization to compute invariant measures. We present some pathologies: non-associativity, non-unicity; these can be cured by smooth assumptions (e.g. irreductibility).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barlow, M.T., Rogers, L.C.G., Williams, D.: Wiener-Hopf factorization for matrices. In: Seminar on Probability, XIV (Paris, 1978/1979) (French). Lecture Notes in Math., vol. 784, pp. 324–331. Springer, Berlin (1980)
Bertoin, J.: Lévy Processes. Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics, vol. 121. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1996)
Ciarlet, P.G.: Introduction à L’analyse Numérique Matricielle et à L’optimisation. Collection Mathématiques Appliquées pour la Maîtrise. (Collection of Applied Mathematics for the Master’s Degree). Masson, Paris (1982)
Dellacherie, C., Martinez, S., San Martin, J.: Hadamard functions of inverse M-matrices. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 31(2), 289–315 (2009)
Doney, R.: Fluctuation theory for Lévy processes. In: Lévy Processes, pp. 57–66. Birkhäuser Boston, Boston (2001)
Feller, W.: An Introduction to Probability Theory and Its Applications. Vol. II. Wiley, New York (1966)
Fiedler, M., Pták, V.: On matrices with non-positive off-diagonal elements and positive principal minors. Czechoslov. Math. J. 12(87), 382–400 (1962)
Fourati, S.: Points de croissance des processus de Lévy et théorie générale des processus. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 110(1), 13–49 (1998)
Fourati, S.: Fluctuations of Lévy processes and scattering theory. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 362(1), 441–475 (2010)
Funderlic, R.E., Plemmons, R.J.: LU decomposition of M-matrices by elimination without pivoting. Linear Algebra Appl. 41, 99–110 (1981)
Grassmann, W.: Means and variances of time averages in Markovian environments. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 31(1), 132–139 (1987)
Heyman, D.P.: A decomposition theorem for infinite stochastic matrices. J. Appl. Probab. 32(4), 893–901 (1995)
Kemeny, J.G., Snell, J.L., Knapp, A.W.: Denumerable Markov Chains. Van Nostrand, Princeton (1966)
Kuo, I.W.: A note on factorizations of singular M-matrices. Linear Algebra Appl. 16(3), 217–220 (1977)
Kyprianou, A.E.: Introductory Lectures on Fluctuations of Lévy Processes with Applications. Universitext. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Li, Q.-L.: Constructive Computation in Stochastic Models with Applications. The RG-Factorization. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing (2010)
Li, Q.-L., Cao, J.: Two types of RG-factorizations of quasi-birth-and-death processes and their applications to stochastic integral functionals. Stoch. Models 20(3), 299–340 (2004)
Li, Q.-L., Zhao, Y.: A constructive method for finding β-invariant measures for transition matrices of M/G/1 type. In: Matrix-Analytic Methods, Adelaide, 2002, pp. 237–263. World Scientific, River Edge (2002)
Li, Q.-L., Zhao, Y.Q.: A MAP/G/1 queue with negative customers. Queueing Syst. 47(1–2), 5–43 (2004)
Martínez, S., San Martín, J., Zhang, X.-D.: A new class of inverse M-matrices of tree-like type. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 24(4), 1136–1148 (2003)
Martínez, S., San Martín, J., Zhang, X.-D.: A class of M-matrices whose graphs are trees. Linear Multilinear Algebra 52(5), 303–319 (2004)
McDonald, J.J., Schneider, H.: Block LU factorizations of M-matrices. Numer. Math. 80(1), 109–130 (1998)
Seneta, E.: Non-negative Matrices. An Introduction to Theory and Applications. Halsted, New York (1973)
Varga, R.S., Cai, D.V.: On the LU factorization of M-matrices. Numer. Math. 38(2), 179–192 (1981/1982)
Vigon, V.: Simplifiez vos Lévy en Titillant la Factorisation de Wiener-Hopf. Editions Universitaires Europeennes (2002). Also available on HAL and on my web page
Vigon, V.: Comparaison des deux composantes d’un subordinateur bivarié, puis étude de l’enveloppe supérieure d’un processus de Lévy. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré Probab. Stat. 39(6), 993–1011 (2003)
Vigon, V.: (Homogeneous) Markovian bridges. Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré Probab. Stat. 47(3), 875–916 (2011)
Widom, H.: Wiener-Hopf integral equations. In: The Legacy of Norbert Wiener: A Centennial Symposium, Cambridge, MA, 1994. Proc. Sympos. Pure Math., vol. 60, pp. 391–405. Am. Math. Soc., Providence (1997)
Williams, W.E.: Recognition of some readily “Wiener-Hopf” factorizable matrices. IMA J. Appl. Math. 32(1–3), 367–378 (1984)
Williams, D.: Some aspects of Wiener-Hopf factorization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 335(1639), 593–608 (1991)
Williams, D.: A new look at ‘Markovian’ Wiener-Hopf theory. In: Séminaire de Probabilités XLI. Lecture Notes in Math., vol. 1934, pp. 349–369. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Woess, W.: Random Walks on Infinite Graphs and Groups. Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics, vol. 138. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Zhao, Y.Q., Li, W., Braun, W.J.: On a decomposition for infinite transition matrices. Queueing Syst. 27(1–2), 127–130 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vigon, V. LU-Factorization Versus Wiener-Hopf Factorization for Markov Chains. Acta Appl Math 128, 1–37 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-013-9799-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10440-013-9799-2
Keywords
- Markov chains
- Random walks
- LU-factorization
- Path-decomposition
- Fluctuation theory
- Probabilistic potential theory
- Infinite matrices