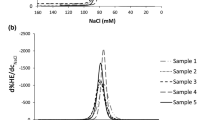
Abstract
Morphology of erythrocyte membrane has been recognized as an alternative biomarker of several patho-physiological states. Numerous attempts have been made to upgrade the existing method of primitive manual counting, particularly exploring the light scattering properties of erythrocyte. All the techniques are at best semi-empirical and heavily rely on the effectiveness of the statistical correlations. Precisely, this is due to the lack of a non-empirical scale of the so-called “morphological scores”. In this article, fractal dimension of erythrocyte membrane has been used to formulate a suitable scoring scale. Subsequently, the rapid experimental output of flow-cytometry has been functionally related to the mean morphological quantifier of the whole cell population via an optimum neural network model (R2 = 0.98). Moreover, the fractal dimension has been further demonstrated to be an important parameter in early detection of an abnormal patho-physiological state, even without any noticeable poikilocytic transformation in micrometric domain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas, N., D. Mohamad, and A. H. Abdullah. Automated erythrocytes counting in microscopic thin blood smear digital images. J. Telemat. Inform. 3:49–59, 2015.
Ahlgrim, C., T. Pottgiesser, T. Sander, Y. O. Schumacher, and M. W. Baumstark. Flow cytometric assessment of erythrocyte shape through analysis of FSC histograms: use of kurtosis and implications for longitudinal evaluation. PLoS ONE 8:e59862, 2013.
Antonio, P. D., M. Lasalvia, G. Perna, and V. Capozzi. Scale-independent roughness value of cell membranes studied by means of AFM technique. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 3141–3148:2012, 1818.
Bessis, M., R. I. Weed, and P. F. Leblond. Red Cell Shape: Physiology, Pathology, Ultrastructure. New York: Springer, p. 180, 1973.
Blank, M. E., and H. Ehmke. Aquaporin-1 and HCO3(-)-Cl(-) transporter-mediated transport of CO2 across the human erythrocyte membrane. J. Physiol. 550:419–429, 2003.
Buys, A. V., M.-J. Van Rooy, P. Soma, D. Van Papendorp, B. Lipinski, and E. Pretorius. Changes in red blood cell membrane structure in type 2 diabetes: a scanning electron and atomic force microscopy study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 12(1):25, 2013.
Cybenko, G. Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Math. Control Signals Syst. 2:303–314, 1989.
Diez-Silva, M., M. Dao, J. Han, C.-T. Lim, and S. Suresh. Shape and biomechanical characteristics of human red blood cells in health and disease. MRS Bull. 35:382–388, 2010.
Fauci, A. S., E. Braunwald, D. L. Kasper, S. L. Hauser, D. L. Longo, J. L. Jameson, and J. Loscalzo. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. New York: Mcgraw-hill, p. 2958, 2008.
Ferrell, J. E., and W. H. Huestis. Phosphoinositide metabolism and the morphology of human erythrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 98:1992–1998, 1984.
Gagnepain, J. J., and C. Roques-Carmes. Fractal approach to two-dimensional and three-dimensional surface roughness. Wear 109:119–126, 1986.
Girasole, M., G. Pompeo, A. Cricenti, A. Congiu-Castellano, F. Andreola, A. Serafino, B. H. Frazer, G. Boumis, and G. Amiconi. Roughness of the plasma membrane as an independent morphological parameter to study RBCs: a quantitative atomic force microscopy investigation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 1768:1268–1276, 2007.
Girasole, M., G. Pompeo, A. Cricenti, G. Longo, G. Boumis, A. Bellelli, and S. Amiconi. The how, when, and why of the aging signals appearing on the human erythrocyte membrane: an atomic force microscopy study of surface roughness. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 6:760–768, 2010.
Goodman, S. R., and K. Shiffer. The spectrin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal human erythrocytes: a review. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 244:121–141, 1983.
Higuchi, T. Approach to an irregular time series on the basis of the fractal theory. Phys. D 31:277–283, 1988.
Ionescu, C., A. Lopes, D. Copot, J. A. T. Machado, and J. H. T. Bates. The role of fractional calculus in modeling biological phenomena: a review. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 51:141–159, 2017.
Jackups, Jr, R. Deep learning makes its way to the clinical laboratory. Clin. Chem. 63:1790–1791, 2017.
Jin, H., X. Xing, H. Zhao, Y. Chen, X. Huang, S. Ma, H. Ye, and J. Cai. Detection of erythrocytes influenced by aging and type 2 diabetes using atomic force microscope. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391:1698–1702, 2010.
Jing, J., P. Feng, S. Wei, H. Zhao, and Y. Liu. Investigation on the surface morphology of Si3N4 ceramics by a new fractal dimension calculation method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 387:812–821, 2016.
Kim, Y., K. Kim, and Y. Park. Measurement techniques for red blood cell deformability: recent advances. In: Blood Cell—An Overview of Studies in Hematology, edited by T. E. Moschandreou. Rijeka: InTech, 2012, pp. 167–194.
Knauf, P. A., F.-Y. Law, T.-W. V. Leung, A. U. Gehret, and M. L. Perez. Substrate-dependent reversal of anion transport site orientation in the human red blood cell anion-exchange protein, AE1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:10861–10864, 2002.
Kubisztal, J., M. Kubisztal, and G. Haneczok. Quantitative characterization of material surface—application to Ni + Mo electrolytic composite coatings. Mater. Charact. 122:45–53, 2016.
Mandelbrot, B. B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature. New York: W. H. Freeman and Co., 1982.
Melzak, K. A., G. R. Lázaro, A. Hernández-Machado, I. Pagonabarraga, J. M. de Espada, and J. L. Toca-Herrera. AFM measurements and lipid rearrangements: evidence from red blood cell shape changes. Soft Matter 8:7716–7726, 2012.
Méndez-Vilas, A., J. M. Bruque, and M. L. González-Martín. Sensitivity of surface roughness parameters to changes in the density of scanning points in multi-scale AFM studies. Application to a biomaterial surface. Ultramicroscopy 107:617–625, 2007.
Mohandas, N., Y. R. Kim, D. H. Tycko, J. Orlik, J. Wyatt, and W. Groner. Accurate and independent measurement of volume and hemoglobin concentration of individual red cells by laser light scattering. Blood 68:506–513, 1986.
Mosior, M., T. Krawczak-Sadowska, A. Wróbel, W. A. Bialas, and J. Gomulkiewicz. The effect of arsenate and vanadate ions on the critical cell volume of bovine erythrocytes. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 11:337–343, 1992.
Mukherjee, R., K. Chaudhury, and C. Chakraborty. Topological features of erythrocytes in thalassemic patients: quantitative characterization by scanning electron and atomic force microscopy. Anal. Quant. Cytol. Pathol. 36:91–99, 2014.
Mukherjee, R., M. Saha, A. Routray, and C. Chakraborty. Nanoscale surface characterization of human erythrocytes by atomic force microscopy: a critical review. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 14:625–633, 2015.
Pages, G., T. W. Yau, and P. W. Kuchel. Erythrocyte shape reversion from echinocytes to discocytes: kinetics via fast-measurement NMR diffusion-diffraction. Magn. Reson. Med. 64:645–652, 2010.
Piagnerelli, M., K. Z. Boudjeltia, D. Brohee, A. Vereerstraeten, P. Piro, J. L. Vincent, and M. Vanhaeverbeek. Assessment of erythrocyte shape by flow cytometry techniques. J. Clin. Pathol. 60:549–554, 2007.
Pretorius, E., and D. B. Kell. Diagnostic morphology: biophysical indicators for iron-driven inflammatory diseases. Integr. Biol. 6:486–510, 2014.
Pretorius, E., A. C. Swanepoel, A. V. Buys, N. Vermeulen, W. Duim, and D. B. Kell. Eryptosis as a marker of Parkinson’s disease. Aging (Albany NY) 6:788–819, 2014.
Santacruz-Gomez, K., E. Silva-Campa, S. Álvarez-García, V. Mata-Haro, D. Soto-Puebla, and M. Pedroza-Montero. An AFM approach of RBC micro and nanoscale topographic features during storage. Int. J. Med. Health Biomed. Bioeng. Pharm. Eng. 8:478–481, 2014.
Scarabelli, L., F. Giovanardi, E. Gervasi, G. Prati, D. Pezzuolo, and L. Scaltriti. Increased mean corpuscular volume of red blood cells in patients treated with capecitabine for advanced breast and colon cancer. Chemotherapy 59:369–372, 2013.
Steck, T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J. Cell Biol. 62:1–19, 1974.
Takeuchi, M., H. Miyamoto, Y. Sako, H. Komizu, and A. Kusumi. Structure of the erythrocyte membrane skeleton as observed by atomic force microscopy. Biophys. J. 74:2171–2183, 1998.
Ţălu, Ş., S. Stach, V. Sueiras, and N. M. Ziebarth. Fractal analysis of AFM images of the surface of Bowman’s membrane of the human cornea. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 43:906–916, 2015.
Wong, P. A hypothesis of the disc-sphere transformation of the erythrocytes between glass surfaces and of related observations. J. Theor. Biol. 233:127–135, 2005.
Wu, Y., J. Cai, L. Cheng, Y. Xu, Z. Lin, C. Wang, and Y. Chen. Atomic force microscope tracking observation of Chinese hamster ovary cell mitosis. Micron 37:139–145, 2006.
Zhang, Y., W. Zhang, S. Wang, C. Wang, J. Xie, X. Chen, Y. Xu, and P. Mao. Detection of erythrocytes in patients with multiple myeloma using atomic force microscopy. Scanning 34:295–301, 2012.
Zhang, Y., W. Zhang, S. Wang, C. Wang, J. Xie, X. Chen, Y. Xu, and P. Mao. Detection of human erythrocytes influenced by iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia using atomic force microscopy. Micron 43:1287–1292, 2012.
Acknowledgments
The present work has been carried out utilizing the infrastructures developed under the project, entitled “Quantifying morphological alteration of RBC population”, funded by TEQIP, phase-II, University of Calcutta (Vide Sanction Letter No. TEQIP-II/R&D/13/105(4) dated November, 2013). The contribution of TEQIP is gratefully acknowledged. We are also grateful to the Centre for Research in Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (CRNN), IIT Kharagpur and the University of Calcutta for the infrastructural support.
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Umberto Morbiducci oversaw the review of this article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, S., Roy, A., Chakraborty, I. et al. Fractal Dimension of Erythrocyte Membranes: A Highly Useful Precursor for Rapid Morphological Assay. Ann Biomed Eng 46, 1362–1375 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2050-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-2050-6