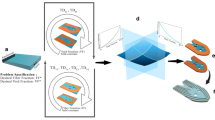
Abstract
For the integrated design of composite material and structures, it is essential to have an effective micromechanical numerical tool to link macroscopic material properties to microstructural configurations. In this paper, 3D computational grains (CGs) with embedded fibers are proposed for the first time, for the direct micromechanical modeling of fiber composites. The microstructure of a unidirectional lamina with random fibers can be assembled by many CGs, and the stiffness matrix of each CG with an embedded fiber can be directly computed by combining two new algorithms. On one hand, a new kind of Trefftz trial displacement field based on scaled cylindrical harmonics is independently assumed, in addition to inter-elemental displacement interpolations with surface nodal degrees of freedom (DoFs). On the other hand, a new kind of multi-field boundary variational principle is proposed to relate independently assumed Trefftz fields to nodal DoFs and to derive the stiffness matrix. Numerical examples demonstrate that without the traditional fine meshing, accurate distribution of micro-stresses in a representative volume element (RVE) with thousands of fibers can be directly computed, and the equivalent orthotropic properties of fiber composites can be predicted. This is also the first time that a three-dimensional finite element with an embedded fiber is developed.

摘要
面向纤维复合材料与结构的优化设计需要, 建立高效准确的纤维复材细观力学仿真工具具有重要意义. 本文首次提出了包含内嵌纤维的三维计算晶粒(computational grains), 用于纤维增强复合材料的直接细观力学建模. 基于所开发的纤维计算晶粒方法, 可以直接构造含有多根随机分布纤维的代表性体积单元(RVE). 此外, 本文提出了一种基于缩放柱调和函数的Papkovich-Neuber解来表征纤维和基体中独立的Trefftz试函数位移场, 并且开发了一种新的多场边界变分原理来计算纤维计算晶粒的刚度矩阵. 数值算例表明, 对于内嵌大量随机分布纤维的RVE, 纤维计算晶粒不需要构造复杂的网格, 即可快速计算RVE的精确应力场, 并预测其有效力学性能. 此外, 这也是内嵌纤维的三维有限元单元的首次提出.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Qiu, X. Zhang, S. Xia, T. Sun, Y. Ling, S. Zhou, H. Guang, Y. Chen, Z. Xu, M. Liang, and H. Zou, Magnetic graphene oxide/carbon fiber composites with improved interfacial properties and electromagnetic interference shielding performance, Compos. Part A-Appl. Sci. Manuf. 155, 106811 (2022).
N. R. J. Hynes, N. J. Vignesh, J. T. W. Jappes, P. S. Velu, C. Barile, M. A. Ali, M. U. Farooq, and C. I. Pruncu, Effect of stacking sequence of fibre metal laminates with carbon fibre reinforced composites on mechanical attributes: Numerical simulations and experimental validation, Compos. Sci. Tech. 221, 109303 (2022).
Z. Huang, K. Fu, Y. Li, and C. Yan, Development of impact resistant 3D printed multi-layer carbon fibre reinforced composites by structural design, Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 121428 (2022).
H. Xin, A. Mosallam, J. A. F. O. Correia, Y. Liu, J. He, and Y. Sun, Material-structure integrated design optimization of GFRP bridge deck on steel girder, Structures 27, 1222 (2020).
R. Hill, Theory of mechanical properties of fibre-strengthened materials: I. Elastic behaviour, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 12, 199 (1964).
Z. Hashin, On elastic behaviour of fibre reinforced materials of arbitrary transverse phase geometry, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 13, 119 (1965).
R. Hill, Theory of mechanical properties of fibre-strengthened materials—III. self-consistent model, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 13, 189 (1965).
Y. Benveniste, G. J. Dvorak, and T. Chen, Stress fields in composites with coated inclusions, Mech. Mater. 7, 305 (1989).
T. Mori, and K. Tanaka, Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions, Acta Metall. 21, 571 (1973).
J. D. Eshelby, The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 241, 376 (1957).
M. Ferrari, Asymmetry and the high concentration limit of the Mori-Tanaka effective medium theory, Mech. Mater. 11, 251 (1991).
Q. Guo, W. Yao, W. Li, and N. Gupta, Constitutive models for the structural analysis of composite materials for the finite element analysis: A review of recent practices, Compos. Struct. 260, 113267 (2021).
S. Bahl, and A. K. Bagha, Finite element modeling and simulation of the fiber-matrix interface in fiber reinforced metal matrix composites, Mater. Today-Proc. 39, 70 (2021).
M. Katouzian, S. Vlase, and M. L. Scutaru, Finite element method-based simulation creep behavior of viscoelastic carbon-fiber composite, Polymers 13, 1017 (2021).
C. Stephen, S. R. Behara, B. Shivamurthy, R. Selvam, S. Kannan, and M. Abbadi, Finite element study on the influence of fiber orientation on the high velocity impact behavior of fiber reinforced polymer composites, Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 16, 459 (2022).
F. Yang, Z. Li, Z. Zhuang, and Z. Liu, Evaluating the blast mitigation performance of hard/soft composite structures through field explosion experiment and numerical analysis, Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 121238 (2022).
A. G. Adeniyi, S. A. Adeoye, D. V. Onifade, and J. O. Ighalo, Multi-scale finite element analysis of effective elastic property of sisal fiber-reinforced polystyrene composites, Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 28, 1245 (2021).
X. Wang, H. Li, T. Yang, Z. Zhang, C. Zheng, W. Wang, D. Zhang, and K. Qian, Multi-scale strength and buckling analysis of 3D woven composite spherical shells subjected to hydrostatic pressure, J. Industrial Textiles 51, 6236S (2022).
M. Chen, and Q. Liu, Multi-scale modelling of progressive damage and failure behaviour of 2D woven SiC/SiC composites, Ceram. Int. 47, 28821 (2021).
E. Kheng, R. D’Mello, and A. Waas, A multi-scale model for the tensile failure of twill textile composites, Compos. Struct. 307, 116614 (2023).
H. Dang, P. Liu, Y. Zhang, Z. Zhao, L. Tong, C. Zhang, and Y. Li, Theoretical prediction for effective properties and progressive failure of textile composites: A generalized multi-scale approach, Acta Mech. Sin. 37, 1222 (2021).
A. Bhaduri, A. Gupta, and L. Graham-Brady, Stress field prediction in fiber-reinforced composite materials using a deep learning approach, Compos. Part B-Eng. 238, 109879 (2022).
S. A. Tabatabaei, S. V. Lomov, and I. Verpoest, Assessment of embedded element technique in meso-FE modelling of fibre reinforced composites, Compos. Struct. 107, 436 (2014).
M. Mahdi, and L. Zhang, An adaptive three-dimensional finite element algorithm for the orthogonal cutting of composite materials, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 113, 1 (2001).
S. Ghosh, and R. L. Mallett, Voronoi cell finite elements, Comput. Struct. 50, 33 (1994).
S. Ghosh, K. Lee, and S. Moorthy, Multiple scale analysis of heterogeneous elastic structures using homogenization theory and voronoi cell finite element method, Int. J. Solids Struct. 32, 27 (1995).
T. H. H. Pian, Derivation of element stiffness matrices by assumed stress distributions, AIAA J. 2, 1333 (1964).
P. Raghavan, and S. Ghosh, A continuum damage mechanics model for unidirectional composites undergoing interfacial debonding, Mech. Mater. 37, 9 (2005).
S. Ghosh, and S. Moorthy, Three dimensional Voronoi cell finite element model for microstructures with ellipsoidal heterogeneties, Comput. Mech. 34, 510 (2004).
R. Zhang, T. Wang, and R. Guo, Modeling of interphases in multiple heterogeneities reinforced composites using Voronoi cell finite elements, Acta Mech. Sin. 36, 887 (2020).
S. Li, and S. Ghosh, Modeling interfacial debonding and matrix cracking in fiber reinforced composites by the extended Voronoi cell FEM, Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 43, 397 (2007).
L. Dong, and S. N. Atluri, Development of 3D T-Trefftz Voronoi cell finite elements with/without spherical voids &/or elastic/rigid inclusions for micromechanical modeling of heterogeneous materials, CMC-Comput. Mater. Con. 29, 2 (2012).
L. Dong, and S. N. Atluri, Development of 3D Trefftz Voronoi cells with ellipsoidal voids &/or elastic/rigid inclusions for micromechanical modeling of heterogeneous materials, CMC-Comput. Mater. Con. 30, 1 (2012).
J. Wang, P. Yan, L. Dong, and S. N. Atluri, Direct numerical simulation of complex nano-structured composites, considering interface stretching and bending effects, using nano-computational grains, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 122, 1476 (2021).
G. Wang, L. Dong, J. Wang, and S. Atluri, Three-dimensional Trefftz computational grains for the micromechanical modeling of heterogeneous media with coated spherical inclusions, J. Mech. Mater. Struct. 13, 505 (2018).
P. L. Bishay, L. Dong, and S. N. Atluri, Multi-physics computational grains (MPCGs) for direct numerical simulation (DNS) of piezoelectric composite/porous materials and structures, Comput. Mech. 54, 1129 (2014).
Y. Huang, G. Wang, L. Dong, and S. N. Atluri, 3D viscoelastic computational grains with spherical inclusions with or without interphases/coatings for micromechanical modeling of heterogeneous materials, Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 122, 4966 (2021).
L. Ai, Theory of Elasticity, 4th ed., translated by Belyaev (Springer, Berlin, 2005).
J. D. Eshelby, The elastic field outside an ellipsoidal inclusion, Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 252, 561 (1959).
Z. H. Tong, S. H. Lo, C. P. Jiang, and Y. K. Cheung, An exact solution for the three-phase thermo-electro-magneto-elastic cylinder model and its application to piezoelectric-magnetic fiber composites, Int. J. Solids Struct. 45, 5205 (2008).
C. P. Jiang, Y. L. Xu, Y. K. Cheung, and S. H. Lo, A rigorous analytical method for doubly periodic cylindrical inclusions under longitudinal shear and its application, Mech. Mater. 36, 3 (2004).
P. M. No, Finite Element Method: Simulation, Numerical Analysis and Solution Techniques (IntechOpen, London, 2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12072011 and 12102023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yezeng Huang designed the research. Yezeng Huang and Junbo Wang wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Yezeng Huang and Guannan Wang provided the computer code and the supporting algorithms. Mingjing Li and Guannan Wang helped organize the manuscript. Leiting Dong and Satya N. Atluri revised and edited the final version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Wang, J., Li, M. et al. 3D computational grains with embedded fibers for the direct micromechanical modeling of fiber composites. Acta Mech. Sin. 39, 423179 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-023-23179-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-023-23179-x