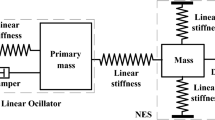
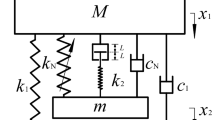
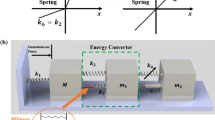
Abstract
The nonlinear energy sink (NES) is outstanding in vibration control for the well-known character of energy targeted transmitting and resonance automatically capturing. To enhance the practicability, this paper proposes a ground-limited NES. The novel design can be encapsulated in a certain box. However, as the vibration region of NES is limited, the control efficiency of it must be considered seriously. Hence, the ground-limited NES is discussed via the analytical method, the simulation method, and especially the experiment in forced vibration. All parameters involved in this study are obtained through the parameter identification based on the experimental platform. The piecewise nonlinearity is fitted into the continuous nonlinearity by the hyperbolic tangent function. Then the harmonic balance method (HBM) is used during the analytical processing to promote the accuracy of the solution. The direct numerical method produces results to verify the analytical method together with the experimental records. The discussion on the control parameters shows that a proper limiting spring can effectively reduce the vibration of the NES while the cost of the control efficiency is small. In a word, this work provides a simple and reliable approach for restricting the NES, which is beneficial to the design of the NES and broadens the application of the NES in engineering.
摘要
非线性能量汇(NES)以能量定向传输和共振自动捕获的特性在被动振动控制方面表现突出. 为了提高实用性, 本文提出了一种接地限幅型NES. 该设计可以封装在一个盒子里. 然而, 由于NES的振动区域有限, 需要考虑其控制效率. 因此, 通过近似解析方法、 数值仿真方法, 特别是强迫振动实验, 研究接地限幅型NES的动力学特性. 本研究中涉及的所有参数均通过基于实验平台的参数辨识得到. 通过双曲正切函数将分段非线性拟合成连续非线性. 然后在分析处理过程中使用谐波平衡法(HBM)来提高解的准确性. 直接数值方法产生的结果与实验记录一起验证了解析方法. 对控制参数的分析表明, 适当的限位弹簧可以有效地降低NES的振动, 同时控制效率的代价很小. 总之, 这项工作为NES的约束提供了一种简单可靠的方法, 有利于NES的设计, 拓宽了NES在工程中的应用.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Z. H. He, Y. Z. Wang, and Y. S. Wang, Active feedback control of sound radiation in elastic wave metamaterials immersed in water with fluid-solid coupling, Acta Mech. Sin. 37, 803 (2021).
P. Zhao, K. Zhang, C. Zhao, and Z. Deng, Multi-resonator coupled metamaterials for broadband vibration suppression, Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 53 (2021).
J. C. Ji, Design of a nonlinear vibration absorber using three-to-one internal resonances, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 42, 236 (2014).
X. Geng, H. Ding, K. Wei, and L. Chen, Suppression of multiple modal resonances of a cantilever beam by an impact damper, Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 41, 383 (2020).
F. Xie, and A. M. Aly, Structural control and vibration issues in wind turbines: a review, Eng. Struct. 210, 110087 (2020).
J. C. Ji, and N. Zhang, Suppression of the primary resonance vibrations of a forced nonlinear system using a dynamic vibration absorber, J. Sound Vib. 329, 2044 (2010).
X. Shui, and S. Wang, Investigation on a mechanical vibration absorber with tunable piecewise-linear stiffness, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 100, 330 (2018).
K. Wang, J. Zhou, C. Cai, D. Xu, S. Xia, and G. Wen, Bidirectional deep-subwavelength band gap induced by negative stiffness, J. Sound Vib. 515, 116474 (2021).
M. Farid, and O. V. Gendelman, Response regimes in equivalent mechanical model of moderately nonlinear liquid sloshing, Nonlinear Dyn. 92, 1517 (2018).
Z. N. Ahmadabadi, Nonlinear energy transfer from an engine crankshaft to an essentially nonlinear attachment, J. Sound Vib. 443, 139 (2019).
A. F. Vakakis, Inducing passive nonlinear energy sinks in vibrating systems, J. Vib. Acoustics 123, 324 (2001).
H. Ding, and L. Q. Chen, Designs, analysis, and applications of nonlinear energy sinks, Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 3061 (2020).
G. G. Tehrani, and M. Dardel, Vibration mitigation of a flexible bladed rotor dynamic system with passive dynamic absorbers, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 69, 1 (2019).
J. Wang, B. Wang, N. E. Wierschem, and B. F. Spencer Jr, Dynamic analysis of track nonlinear energy sinks subjected to simple and stochastice excitations, Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 49, 863 (2020).
C. Snoun, B. Bergeot, and S. Berger, Prediction of the dynamic behavior of an uncertain friction system coupled to nonlinear energy sinks using a multi-element generalized polynomial chaos approach, Eur. J. Mech.-A Solids 80, 103917 (2020).
W. Li, N. E. Wierschem, X. Li, T. Yang, and M. J. Brennan, Numerical study of a single-sided vibro-impact track nonlinear energy sink considering horizontal and vertical dynamics, J. Vib. Acoustics 141, 061013 (2019).
J. Shao, T. Zeng, X. Wu, and J. Yang, Influence of the pre-stress of the nonlinear membrane absorber for targeted energy transfer applied to 3D acoustic cavity, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 42, 557 (2020).
P. Y. Bryk, R. Côte, and S. Bellizzi, Targeted energy transfer from a resonant room to a hybrid electro-acoustic nonlinear membrane absorber: Numerical and experimental study, J. Sound Vib. 460, 114868 (2019).
G. C. Tsiatas, and D. A. Karatzia, Reliability analysis of the hysteretic nonlinear energy sink in shock mitigation considering uncertainties, J. Vib. Control 26, 2261 (2020).
P. Kumar, S. Narayanan, and S. Gupta, Targeted energy transfer in stochastically excited system with nonlinear energy sink, Eur. J. Appl. Math. 30, 869 (2019).
C. E. Silva, A. Maghareh, H. Tao, S. J. Dyke, and J. Gibert, Evaluation of energy and power flow in a nonlinear energy sink attached to a linear primary oscillator, J. Vib. Acoustics 141, 061012 (2019).
K. Dekemele, P. Van Torre, and M. Loccufier, Design, construction and experimental performance of a nonlinear energy sink in mitigating multi-modal vibrations, J. Sound Vib. 473, 115243 (2020).
T. Li, E. Gourc, S. Seguy, and A. Berlioz, Dynamics of two vibroimpact nonlinear energy sinks in parallel under periodic and transient excitations, Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 90, 100 (2017).
D. Bitar, A. Ture Savadkoohi, C. H. Lamarque, E. Gourdon, and M. Collet, Extended complexification method to study nonlinear passive control, Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 1433 (2020).
J. Chen, W. Zhang, J. Liu, and W. Hu, Vibration absorption of parallel-coupled nonlinear energy sink under shock and harmonic excitations, Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 1135 (2021).
M. Oliva, G. Barone, F. Lo Iacono, and G. Navarra, Nonlinear energy sink and Eurocode 8: An optimal design approach based on elastic response spectra, Eng. Struct. 221, 111020 (2020).
J. Xue, Y. Zhang, H. Ding, and L. Chen, Vibration reduction evaluation of a linear system with a nonlinear energy sink under a harmonic and random excitation, Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 41, 1 (2020).
M. A. Al-Shudeifat, and A. S. Saeed, Comparison of a modified vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink with other kinds of NESs, Meccanica 56, 735 (2021).
D. Huang, R. Li, and G. Yang, On the dynamic response regimes of a viscoelastic isolation system integrated with a nonlinear energy sink, Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 79, 104916 (2019).
K. Foroutan, A. Jalali, and H. Ahmadi, Investigations of energy absorption using tuned bistable nonlinear energy sink with local and global potentials, J. Sound Vib. 447, 155 (2019).
V. Iurasov, and P. O. Mattei, Bistable nonlinear damper based on a buckled beam configuration, Nonlinear Dyn. 99, 1801 (2020).
M. A. Al-Shudeifat, Nonlinear energy sinks with nontraditional kinds of nonlinear restoring forces, J. Vib. Acoustics 139, 024503 (2017).
X. Lu, Z. Liu, and Z. Lu, Optimization design and experimental verification of track nonlinear energy sink for vibration control under seismic excitation, Struct. Control Health Monit. 24, e2033 (2017).
S. Bellizzi, K. W. Chung, and R. Sampaio, Response regimes of a linear oscillator with a nonlinear energy sink involving an active damper with delay, Nonlinear Dyn. 97, 1667 (2019).
S. Lo Feudo, C. Touzé, J. Boisson, and G. Cumunel, Nonlinear magnetic vibration absorber for passive control of a multi-storey structure, J. Sound Vib. 438, 33 (2019).
Z. Zhang, H. Ding, Y. W. Zhang, and L. Q. Chen, Vibration suppression of an elastic beam with boundary inerter-enhanced nonlinear energy sinks, Acta Mech. Sin. 37, 387 (2021).
J. E. Chen, W. Zhang, M. H. Yao, J. Liu, and M. Sun, Thermal effect on dynamics of beam with variable-stiffness nonlinear energy sink, Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 21, 1 (2020).
H. Yao, Y. Wang, L. Xie, and B. Wen, Bi-stable buckled beam nonlinear energy sink applied to rotor system, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 138, 106546 (2020).
S. Bab, S. E. Khadem, M. Shahgholi, and A. Abbasi, Vibration attenuation of a continuous rotor-blisk-journal bearing system employing smooth nonlinear energy sinks, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 84, 128 (2017).
D. Wang, Z. Hao, F. Chen, and Y. Chen, Nonlinear energy harvesting with dual resonant zones based on rotating system, Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 275 (2021).
X. Y. Mao, H. Ding, and L. Q. Chen, Bending vibration control of pipes conveying fluids by nonlinear torsional absorbers at the boundary, Sci. China Tech. Sci. 64, 1690 (2021).
W. Zhang, and J. Chen, Influence of geometric nonlinearity of rectangular plate on vibration reduction performance of nonlinear energy sink, J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 34, 3127 (2020).
H. Y. Chen, X. Y. Mao, H. Ding, and L. Q. Chen, Elimination of multimode resonances of composite plate by inertial nonlinear energy sinks, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 135, 106383 (2020).
W. Tian, Y. Li, Z. Yang, P. Li, and T. Zhao, Suppression of nonlinear aeroelastic responses for a cantilevered trapezoidal plate in hypersonic airflow using an energy harvester enhanced nonlinear energy sink, Int. J. Mech. Sci. 172, 105417 (2020).
J. Zhou, M. Xu, and W. Xia, Passive suppression of panel flutter using a nonlinear energy sink, Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2020, 1 (2020).
Z. Yan, S. A. Ragab, and M. R. Hajj, Passive control of transonic flutter with a nonlinear energy sink, Nonlinear Dyn. 91, 577 (2018).
W. Tian, Y. Li, P. Li, Z. Yang, and T. Zhao, Passive control of nonlinear aeroelasticity in hypersonic 3-D wing with a nonlinear energy sink, J. Sound Vib. 462, 114942 (2019).
Y. W. Zhang, Y. N. Lu, and L. Q. Chen, Energy harvesting via nonlinear energy sink for whole-spacecraft, Sci. China Tech. Sci. 62, 1483 (2019).
X. F. Geng, H. Ding, X. Y. Mao, and L. Q. Chen, Nonlinear energy sink with limited vibration amplitude, Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 156, 107625 (2021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11772181) and the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (Grant No. 12025204).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, XF., Ding, H., Mao, XY. et al. A ground-limited nonlinear energy sink. Acta Mech. Sin. 38, 521558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-022-09027-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-022-09027-x