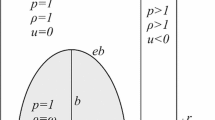
Abstract
High-precision numerical methods are utilized to study the shock waves interacting with an elliptical heavy bubble. The influence of different bubble gases (SF\(_6\) and R22) and shock intensities (\(Ma=1.21\) and \(Ma=2.1\)) is analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively. The results show that the focusing position is farther from the right bubble interface in the SF\(_6\) bubble (case 1) than in the R22 bubble (case 2) when \(Ma=1.21\); thus, case 2 exhibits an outward jet structure, while case 1 does not. When \(Ma=2.1\) (case 3), the shock wave propagates faster, and the shock focusing is nearer to the right bubble interface. Finally, outward jet structures form on the bubble interfaces. The maximum values of density and pressure of shock focusing are different in the three cases, which imply that different gas densities and shock intensities significantly affect the shock–bubble interaction. The effective bubble volume and gases mixing degree are both smaller in case 2 than in case 1, but the trends over time are essentially the same. The increased shock intensity in case 3 leads to a smaller effective bubble volume than in case 1, but a much greater gases mixing degree. In all three cases, the compression term plays a more important role in the vorticity development than the other terms.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan, Z.H., Chen, K.P., Qi, J., et al.: The propagation characteristics of curved detonation wave: Experiments in helical channels. Proc. Combust. Inst. 37, 3585–3592 (2019)
Pan, Z.H., Qi, J., Pan, J.F., et al.: Fabrication of a helical detonation channel: Effect of initial pressure on the detonation propagation modes of ethylene/oxygen mixtures. Combust. Flame 192, 1–9 (2018)
Zhu, Y.J., Pan, Z.H., Zhang, P.G., et al.: Stable detonation characteristics of premixed C\(_2\)H\(_4\)/O\(_2\) gas in narrow gaps. Exp. Fluids 58, 1–6 (2017)
Haas, J.F., Sturtevant, B.: Interaction of weak shock waves with cylindrical and spherical gas inhomogeneities. J. Fluid Mech. 181, 41–76 (1987)
Layes, G., Jourdan, G., Houas, L.: Experimental investigation of the shock wave interaction with a spherical gas inhomogeneity. Phys. Fluids 17, 028103 (2005)
Layes, G., Metayer, O.L.: Quantitative numerical and experimental studies of the shock accelerated heterogeneous bubbles motion. Phys. Fluids 19(4), 042105 (2007)
Layes, G., Jourdan, G., Houas, L.: Experimental study on a plane shock wave accelerating a gas bubble. Phys. Fluids 21(7), 074102 (2009)
Zhai, Z.G., Si, T., Luo, X.S., et al.: On the evolution of spherical gas interfaces accelerated by a planar shock wave. Phys. Fluids 23(8), 084104 (2011)
Si, T., Zhai, Z.G., Yang, J.M., et al.: Experimental investigation of reshocked spherical gas interfaces. Phys. Fluids 24(5), 054101 (2012)
Zhu, Y.J., Yu, L., Pan, J.F., et al.: Jet formation of SF\(_6\) bubble induced by incident and reflected shock waves. Phys. Fluids 29, 126105 (2017)
Zhu, Y.J., Yang, Z.W., Pan, Z.H., et al.: Numerical investigation of shock-SF\(_6\) bubble interaction with different mach numbers. Comput. Fluids 177, 78–86 (2018)
Zhu, Y.J., Yang, Z.W., Luo, K.H., et al.: Numerical investigation of planar shock wave impinging on spherical gas bubble with different densities. Phys. Fluids 31, 056101 (2019)
Zhu, Y.J., Gao, L.K., Yang, Z.W.: Sulfur hexauoride bubble evolution in shock accelerated flow with a transverse density gradient. Phys. Fluids 32, 026101 (2020)
Luo, X.S., Wang, M.H., Si, T., et al.: On the interaction of a planar shock with an SF\(_6\) polygon. J. Fluid Mech. 773, 366–394 (2015)
Igra, D., Igra, O.: Numerical investigation of the interaction between a planar shock wave with square and triangular bubbles containing different gases. Phys. Fluids 30, 056104 (2018)
Zheng, C., Zhang, H.H., Chen, Z.H., et al.: Interaction of cylindrical converging shocks with an equilateral triangular SF\(_6\) cylinder. Phys. Fluids 31, 086104 (2019)
Fan, E., Guan, B., Wen, C.Y., et al.: Numerical study on the jet formation of simple-geometry heavy gas inhomogeneities. Phys. Fluids 31, 026103 (2019)
Ray, J., Samtaney, R., Norman, J.Z.: Shock interactions with heavy gaseous elliptic cylinders: Two leeward-side shock competition modes and a heuristic model for interfacial circulation deposition at early times. Phys. Fluids 12, 707 (2000)
Zou, L.Y., Liu, C.L., Tan, D.W., et al.: On interaction of shock wave with elliptic gas cylinder. J. Visual. 13, 347–353 (2010)
Zou, L.Y., Liao, S.F., Liu, C.L., et al.: Aspect ratio effect on shock-accelerated elliptic gas cylinders. Phys. Fluids 28, 036101 (2016)
Georgievskiy, P.Y., Levin, V.A., Sutyrin, O.G.: Interaction of a shock with elliptical gas bubbles. Shock Waves 25, 357–369 (2015)
Sembian, S., Liverts, M., Apazidis, N.: Plane blast wave interaction with an elongated straight and inclined heat-generated inhomogeneity. J. Fluid Mech. 851, 245–267 (2018)
Li, D.D., Wang, G., Guan, B.: On the circulation prediction of shock-accelerated elliptical heavy gas cylinders. Phys. Fluids 31, 056104 (2019)
Jiang, G.S., Shu, C.W.: Efficient implementation of weighted ENO schemes. J. Comput. Phys. 126, 202–228 (1996)
Chen, X., Dong, G., Li, B.M.: Numerical study of three-dimensional developments of premixed flame induced by multiple shock waves. Acta. Mech. Sin. 34, 1035–1047 (2018)
Winkler, K.A., Chalmers, J.W., Hodson, S.W., et al.: A numerical laboratory. Phys. Today 40(10), 28–37 (1987)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11872193), and the Youth Talent Cultivation Plan of Jiangsu University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Executive Editor: Jianqiang Chen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Zhu, Y. Computational study of planar shock wave interacting with elliptical heavy gas bubble. Acta Mech. Sin. 37, 1264–1277 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-01085-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-021-01085-z