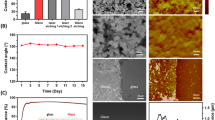
Abstract
Light energy is utilized as an extensive tool for actuation of fluid flow in microfluidic devices. We report a novel method of droplet actuation using LED (light-emitting diode) that can be utilized for microfluidic mixing applications. This low power LED which emits light of peak wavelength 395 nm delivering luminous power of less than 300 millicandela (mcd) was used to create an interfacial tension gradient on solid–liquid interface containing photoresponsive molecule of azobenzene (C12H10N2). LED-induced photoisomerization of azobenzene creates a spatial gradient in interfacial energy on the solid–liquid interface, which enhances the droplet movement. The concept of LED-enhanced fluidic actuation was demonstrated using droplets of water, urine, blood serum over photoresponsive substrate. The substrates were prepared by coating the surface of silicon substrate with azobenzene dissolved in silicone resin solution. Detailed experimental characterization of LED-actuated droplet velocity was performed, where the effect of parameters such as frequency of light actuation, droplet volume, concentration of azobenzene was evaluated. Droplet transport of DI water (de-ionized) of volume 60 µL was achieved at a velocity of 160 µm/s corresponding to LED actuation frequency of 1 Hz. In vitro quantification of blood calcium and urine pH was performed using fabricated chip scale opto-wetting platforms. The proposed work could be useful in the development of droplet microfluidic chips, where combinatorial mixing can be achieved using an array of LEDs.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arscott S (2011) Moving liquids with light: photoelectrowetting on semiconductors. Nat Sci Rep 1:184. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00184
Baigl D (2012) Photoactuation of liquids for light driven microfluidics. Lab Chip 12:3637–3653. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc40596b
Baron DN, Bell JL (1957) A simple specific titration method for serum calcium. Clin Chim Acta 2(4):327–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(57)90010-4
Baroud CN, Robert M, Delville JP (2007) An optical toolbox for total control of droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 7:1029–1033. https://doi.org/10.1039/b702472j
Bonn D, Eggers J, Indekeu J (2009) Wetting and spreading. Rev Mod Phys 81(2):739. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.739
Brochard F (1989) Motion of droplets on solid surface induced by chemical or thermal gradients. Langmuir 5:2. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00086a025
Chiou PY, Park SY, Wu MC (2008a) Continuous optoelectrowetting for picoliter droplet manipulation. Appl Phys Lett 93:221110. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3039070
Chiou PY, Chang Z, Wu MC (2008b) Droplet manipulation with light on optoelectrowetting device. J Microelectromech Syst 17(1):133–138. https://doi.org/10.1109/jmems.2007.904336
Connerty HV, Briggs AR (1966) Determination of serum calcium by means of orthocresolphthalein complexone. Am J Clin Pathol 45(3):290–296. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcp/45.3.290
Cook JD, Caplan YH, Bush DM (2000) The characterization of human urine for specimen validity determination in workplace drug testing. J Anal Toxicol 24(7):579–588
Creeca CR, Roitberg AE (2006) Theoretical study of the isomerization mechanism of azobenzene and distributed azobenzene derivatives. J Phys Chem A 110:8188–8203. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp057413c
Diguet A, Guillermic RM, Baigl D (2009) Photomanipulation of a droplet by the chromocapillary effect. Angew Chem Int 48:9281–9284. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200904868
Diguet A, Li H, Queyriaux N, Chen Y, Baigl D (2011) Photreversible fragmentation of a liquid interface for micro droplet generation by light actuation. Lab Chip 11:2666–2669. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1lc20328b
Edwards SL (2008) Pathophysiology of acid base balance: the theory practice relationship. Intensive Crit Care Nurs 24:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iccn.2007.05.003
Fan SK, Hseih HT, Lin DY (2009) General digital microfluidic platform manipulating dielectric and conductive droplets by dielectrophoresis and electrowetting. Lab Chip 9:1236–1242. https://doi.org/10.1039/b816535a
Inui N (2007) Relationship between contact angle of liquid droplet and light beam position in optoelectrowetting. Sens Actuators A 40:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2007.06.001
Jin J, Ngyuen NT (2018) Manipulation schemes and applications of liquid marbles for micro total analysis systems. Microelectron Eng 197:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2018.06.003
Jin J, Ooi CH, Dao DV, Ngyuen NT (2017) Coalescence processes of droplets and liquid marbles. Micromachines 8:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8110336
Kratz A, Ferraro M, Sluss PM, Lewandrowski KB (2004) Normal reference laboratory values. N Engl J Med 351:1548. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmcpc049016
Krogmann F, Qu H, Zappe H (2008) Push/pull actuation using opto-electrowetting. Sens Actuators A 141:499–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2007.08.017
Mahimwalla Z, Yager KG, Barett CJ (2012) Azobenzene photomechanics: prospects and potential applications. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-012-0792-0
Marques AV, Barbaud F, Baigl D (2013) Microfluidic mixing triggered by an external LED illumination. J Am Chem Soc 135:3218–3223. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja311837r
Merino E, Ribagorda M (2012) Control over molecular motion using the cis-trans photoisomerization of the azo group. Beilstein J Org Chem 8:1071–1090. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjoc.8.119
Naghii MR, Ebrahimpour Y, Darvishi P (2012) Effect of consumption of fatty acids, calcium, vitamin D and boron with regular physical activity on bone mechanical properties and corresponding metabolic hormones in rat. Indian J Exp Biol 50(3):223–231
Oh SK, Nakagawa M, Ichimura K (2002) Photocontrol of liquid motion on an azobenzene monolayer. J Mater Chem 12:2262–2269. https://doi.org/10.1039/B110825P
Ooi CH, Jin J, Sreejith KR, Nguyen AH, Evans GM, Nguyen NT (2018a) Manipulation of a floating liquid marble using dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 18:3770–3779. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc01057a
Ooi CH, Jin J, Nguyen AH, Evans GM, Nguyen NT (2018b) Picking up and placing a liquid marble using dielectrophoresis. Microfluid Nanofluid 22:142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2163-0
Park SY, Chiou PY (2011) Light driven droplet manipulation technologies for lab on a chip applications. Adv OptoElectron 1:1. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/909174
Park SY, Kalim S, Callahan C, Chiou PY (2009) A light induced dielectrophoretic droplet manipulation platform. Lab Chip 9:3228–3235. https://doi.org/10.1039/b909158k
Persichetti G, Grimaldi IA, Testa G, Bernini R (2017) Mutlifunctional optofluidic lab-on-chip platform for Raman and fluorescence spectroscopic microfluidic analysis. Lab Chip 17:2631–2639. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7LC00460E
Rola H, Halabieh EI, Mermut O, Barrett CJ (2004) Using light to control physical properties of polymers and surfaces with azobenzene chromophores. IUPAC Pure Appl Chem 76(7–8):1445–1465. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac200476071445
Tandogan B, Ulusu N (2005) Importance of calcium. Perspect Med Sci 35(1):197–201
Teh SY, Lin R, Lee AP (2008) Droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 8:198–220. https://doi.org/10.1039/b715524g
Thomas T, Unni HN (2018) LED based opto-wetting platforms for micromixing. In: Proceedings of SPIE 10491, microfluidics, bioMEMS, and medical microsystems XVI, 104910R. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2290107
Wagner N, Theato P (2014) Light induced wettability changes on polymer surfaces. Polymer 55:3436–3453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2014.05.033
Walker SW, Shapiro B (2006) Modeling the fluid dynamics of electrowetting on dielectric (EWOD). J Microelectromech Syst 15(4):986–1000. https://doi.org/10.1109/JMEMS.2006.878876
Yager KG, Barrett CJ (2006) Novel photoswitching using azobenzene functional material. J Photochem Photobiol A Chem 182:250–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochem.2006.04.021
Yang D, Piech M, Picraux ST (2007) Photon control of liquid motion on reversibly photoresponsive surfaces. Langmuir Am Chem Soc 23:10864–10872. https://doi.org/10.1021/la701507
Zak B, Epstein E, Baginski ES (1975) Review of calcium methodologies. Ann Clin Lab Sci 5(3):195–215
Zhang H, Sun Y (2018) Optofluidic droplet dye laser generated by microfluidic nozzles. Opt Express 26:11284–11291. https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.011284
Zhao W, Wu C-X (1999) Rate equation theory of azobenzene monolayer photoisomerization. Chem Phy Lett 312:572–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2614(99)00988-4
Zhou YN, Jin Li J, Zhang Q, Luo ZH (2014) Light responsive smart surface with controllable wettability and excellent stability. Langmuir 30:12236–12242. https://doi.org/10.1021/la501907w
Acknowledgements
The authors express there sincere thanks to Ministry of Human Resources and Development, Government of India and IIT Hyderabad for their financial support to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors disclose that there is no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomas, T., Unni, H.N. LED-based opto-wetting and fluidic transport for droplet mixing. Microfluid Nanofluid 23, 105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2273-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2273-3