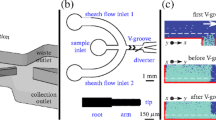
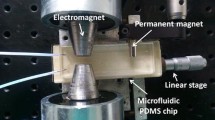
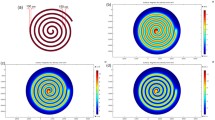
Abstract
Manipulation of cells or bio-targets is required in a variety of biological, diagnostic and therapeutic applications. In this paper, we present a novel magnetic separator for magnetic bead labeled-target sorting in microfluidic systems. This micro magnetic separator includes 3D micro copper coil, soft magnetic tips and FeNi wires. The magnetic tips and FeNi wires are first simulated and optimized by MagNet software to increase the magnetic force exerted on magnetic beads, and fabricated by microfabrication technology. The experiment results show the sorting ratio of the magnetic beads can be up to 92.5% with the current of 200 mA and the flow rate of 5 µL/min. The maximum sorting ratio can reach 78.4% for 100 CFU/mL E. coli O157:H7 sample with the current of 200 mA and the flow rate of 0.5 µL/min. On account of the miniaturization, high sorting efficiency, low excitation current, high level of detection automation and easy integration with micro magnetic sensor, this micro magnetic separation system can be a potential application in bio-target sorting and detecting.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaas E, Kovacs B, Vicsek T, Oltvai ZN, Barabási AL (2004) Global organization of metabolic fluxes in the bacterium Escherichia coli. Nature 427(6977):839
Amini H, Lee W, Di Carlo D (2014) Inertial microfluidic physics. Lab Chip 14(15):2739–2761
Barrett LM, Skulan AJ, Singh AK, Cummings EB, Fiechtner GJ (2005) Dielectrophoretic manipulation of particles and cells using insulating ridges in faceted prism microchannels. Anal Chem 77(21):6798–6804
Bhagat AAS, Bow H, Hou HW, Tan SJ, Han J, Lim CT (2010) Microfluidics for cell separation. Med Biol Eng Comput 48(10):999–1014
Carr C, Espy M, Nath P, Martin SL, Ward MD, Martin J (2009) Design, fabrication and demonstration of a magnetophoresis chamber with 25 output fractions. J Magn Magn Mater 321(10):1440–1445
Chung YC, Wu CM, Lin SH (2016) Particles sorting in micro channel using designed micro electromagnets of magnetic field gradient. J Magn Magn Mater 407:209–217
Deng T, Whitesides GM, Radhakrishnan M, Zabow G, Prentiss M (2001) Manipulation of magnetic microbeads in suspension using micromagnetic systems fabricated with soft lithography. Appl Phys Lett 78(12):1775–1777
Fonnum G, Johansson C, Molteberg A, Mørup S, Aksnes E (2005) Characterisation of Dynabeads® by magnetization measurements and Mössbauer spectroscopy. J Magn Magn Mater 293(1):41–47
Fulcrand R, Jugieu D, Escriba C, Bancaud A, Bourrier D, Boukabache A, Gué AM (2009) Development of a flexible microfluidic system integrating magnetic micro-actuators for trapping biological species. J Micromech Microeng 19(10):105019
Gijs MAM (2004) Magnetic bead handling on-chip: new opportunities for analytical applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 1(1):22–40
Hejazian M, Nguyen NT (2015) Negative magnetophoresis in diluted ferrofluid flow. Lab Chip 15(14):2998–3005
Hejazian M, Nguyen NT (2016) Magnetofluidic concentration and separation of non-magnetic particles using two magnet arrays. Biomicrofluidics 10(4):044103
Hoshino K, Huang YY, Lane N, Huebschman M, Uhr JW, Frenkel EP, Zhang X (2011) Microchip-based immunomagnetic detection of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 11(20):3449–3457
Ibekwe AM, Watt PM, Grieve CM, Sharma VK, Lyons SR (2002) Multiplex fluorogenic real-time PCR for detection and quantification of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in dairy wastewater wetlands. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(10):4853–4862
Inglis DW, Riehn R, Sturm JC, Austin RH (2006) Microfluidic high gradient magnetic cell separation. J Appl Phys 99(8):08K101
Johansson L, Nikolajeff F, Johansson S, Thorslund S (2009) On-chip fluorescence-activated cell sorting by an integrated miniaturized ultrasonic transducer. Anal Chem 81(13):5188–5196
Joung J, Shen J, Grodzinski P (2000) Micropumps based on alternating high-gradient magnetic fields. IEEE Trans Magn 36(4):2012–2014
Kim KS, Park JK (2005) Magnetic force-based multiplexed immunoassay using superparamagnetic nanoparticles in microfluidic channel. Lab Chip 5(6):657–664
Kotzar G, Freas M, Abel P, Fleischman A, Roy S, Zorman C, MMoran J, Melzak J (2002) Evaluation of MEMS materials of construction for implantable medical devices. Biomaterials 23(13):2737–2750
Krüger J, Singh K, O’Neill A, Jackson C, Morrison A, O’Brien P (2002) Development of a microfluidic device for fluorescence activated cell sorting. J Micromech Microeng 12(4):486
Lenshof A, Laurell T (2010) Continuous separation of cells and particles in microfluidic systems. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):1203–1217
Li Y, Dalton C, Crabtree HJ, Nilsson G, Kaler KV (2007) Continuous dielectrophoretic cell separation microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7(2):239–248
Li C, Wu PM, Han J, Ahn CH (2008) A flexible polymer tube lab-chip integrated with microsensors for smart microcatheter. Biomed Microdevices 10(5):671–679
Link DR, Grasland-Mongrain E, Duri A, Sarrazin F, Cheng Z, Cristobal G, Marquez M, Weitz DA (2006) Electric control of droplets in microfluidic devices. Angew Chem-Int Edit 45(16):2556–2560
Nguyen NT (2012) Micro-magnetofluidics: interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):1–16
Pamme N (2006) Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 6(1):24–38
Pamme N, Manz A (2004) On-chip free-flow magnetophoresis: continuous flow separation of magnetic particles and agglomerates. Anal Chem 76(24):7250–7256
Pamme N, Wilhelm C (2006) Continuous sorting of magnetic cells via on-chip free-flow magnetophoresis. Lab Chip 6(8):974–980
Panaro NJ, Lou XJ, Fortina P, Kricka LJ, Wilding P (2005) Micropillar array chip for integrated white blood cell isolation and PCR. Biomol Eng 21(6):157–162
Petersson F, Åberg L, Swärd-Nilsson AM, Laurell T (2007) Free flow acoustophoresis: microfluidic-based mode of particle and cell separation. Anal Chem 79(14):5117–5123
Prasad KV, Taiyab A, Jyothi D, Srinivas UK, Sreedhar AS (2007) Heat shock transcription factors regulate heat induced cell death in a rat histiocytoma. J Biosci 32(3):585–593
Ramadan Q, Samper V, Poenar D, Yu C (2004) On-chip micro-electromagnets for magnetic-based bio-molecules separation. J Magn Magn Mater 281(2–3):150–172
Ramadan Q, Samper V, Poenar DP, Yu C (2006) An integrated microfluidic platform for magnetic microbeads separation and confinement. Biosens Bioelectron 21(9):1693–1702
Ripka P, Janosek M (2010) Advances in magnetic field sensors. IEEE Sens J 10(6):1108–1116
Rong R, Choi JW, Ahn CH (2006) An on-chip magnetic bead separator for biocell sorting. J Micromech Microeng 16(12):2783
Sajeesh P, Sen AK (2014) Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid Nanofluid 17(1):1–52
Shevkoplyas SS, Siegel AC, Westervelt RM, Prentiss MG, Whitesides GM (2007) The force acting on a superparamagnetic bead due to an applied magnetic field. Lab Chip 7(10):1294–1302
Shikida M, Koyama M, Nagao N, Imai R, Honda H, Okochi M, Tsuchiya H, Sato K (2009) Agitation of magnetic beads by multi-layered flat coils. Sens Actuators B 137(2):774–780
Smistrup K, Hansen O, Bruus H, Hansen MF (2005) Magnetic separation in microfluidic systems using microfabricated electromagnets—experiments and simulations. J Magn Magn Mater 293(1):597–604
Smistrup K, Lund-Olesen T, Hansen MF, Tang PT (2006) Microfluidic magnetic separator using an array of soft magnetic elements. J Appl Phys 99(8):08P102
Sun W, Khosravi F, Albrechtsen H, Brovko LY, Griffiths MW (2002) Comparison of ATP and in vivo bioluminescence for assessing the efficiency of immunomagnetic sorbents for live Escherichia coli O157: H7 cells. J Appl Microbiol 92(6):1021–1027
Varshney M, Li Y, Srinivasan B, Tung S (2007) A label-free, microfluidics and interdigitated array microelectrode-based impedance biosensor in combination with nanoparticles immunoseparation for detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in food samples. Sens Actuators B 128(1):99–107
Yu ZTF, Aw Yong KM, Fu J (2014) Microfluidic blood cell sorting: now and beyond. Small 10(9):1687–1703
Zhi S, Feng Z, Guo L, Lei C, Zhou Y (2017) Investigation of a novel MEMS orthogonal fluxgate sensor fabricated with Co-based amorphous ribbon core. Sens Actuators A 267:121–126
Zhou R, Wang C (2016) Microfluidic separation of magnetic particles with soft magnetic microstructures. Microfluid Nanofluid 20(3):48
Zhu GP, Hejiazan M, Huang X, Nguyen NT (2014) Magnetophoresis of diamagnetic microparticles in a weak magnetic field. Lab Chip 14(24):4609–4615
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61273065), National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAK08B05), Support fund of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (AgriX2015005), Support fund of Joint research center for advanced aerospace technology of Shanghai Academy of Spaceflight Technology-Shanghai Jiao Tong University (USCAST2015-2), Support fund of aerospace technology (15GFZ-JJ02-05), the Analytical and Testing Center in Shanghai Jiao Tong University, the Center for Advanced Electronic Materials and Devices in Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhi, S., Sun, X., Feng, Z. et al. An innovative micro magnetic separator based on 3D micro-copper-coil exciting soft magnetic tips and FeNi wires for bio-target sorting. Microfluid Nanofluid 23, 43 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2215-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2215-0