Abstract
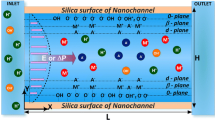
Recent advance in nanotechnology has led to rapid advances in nanofluidics, which has been established as a reliable means for a wide variety of applications, including molecular separation, detection, crystallization and biosynthesis. Although atomic and molecular level consideration is a key ingredient in experimental design and fabrication of nanofluidic systems, atomic and molecular modeling of nanofluidics is rare and most simulations at nanoscale are restricted to one or two dimensions in the literature, to our best knowledge. The present work introduces atomic scale design and three-dimensional (3D) simulation of ionic diffusive nanofluidic systems. We propose a variational multiscale framework to represent the nanochannel in discrete atomic and/or molecular detail while describing the ionic solute by continuum. Apart from the major electrostatic and entropic effects, the non-electrostatic interactions between the channel and solution, and among solvent molecules are accounted in our modeling. We derive generalized Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations for nanofluidic systems. Mathematical algorithms, such as Dirichlet-to-Neumann mapping and the matched interface and boundary methods, are developed to rigorously solve the aforementioned equations to the second-order accuracy in 3D realistic settings. Three ionic diffusive nanofluidic systems, including a negatively charged nanochannel, a bipolar nanochannel and a double-well nanochannel, are designed to investigate the impact of atomic charges to channel current, density distribution and electrostatic potential. Numerical findings, such as gating, ion depletion and inversion, are in good agreements with those from experimental measurements and numerical simulations in the literature.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgrall P, Nguyen NT (2008) Nanofluidic devices and their applications. Anal Chem 80(7):2326–2341
Adalsteinsson H, Debusschere BJ, Long KR, Najm HN (2008) Components for atomistic-to-continuum multiscale modeling of flow in micro- and nanofluidic systems. Sci Prog 16:297–313
Bashford D, Case DA (2000) Generalized Born models of macromolecular solvation effects. Annu Rev Phys Chem 51:129–152
Bazant MZ, Thornton K, Ajdari A (2004) Diffuse-charge dynamics in electrochemical systems. Phys Rev E 70:021506
Bazant MZ, Kilic MS, Storey BD, Ajdari A (2009) Towards an understanding of induced-charge electrokinetics at large applied voltages in concentrated solutions. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 152:48–88
Bazant MZ, Storey BD, Kornyshev AA (2011) Double layer in ionic liquids: overscreening versus crowding. Phys Rev Lett 106:046102
Beglov D, Roux B (1996) Solvation of complex molecules in a polar liquid: an integral equation theory. J Chem Phys 104(21):8678–8689
Belgrader P, Okuzumi M, Pourahmadi F, Borkholder DA, Northrup MA (2000) A microfluidic cartridge to prepare spores for PCR analysis. Biosens Bioelectr 14:849–852
Branton D, Deamer DW, Marziali A, Bayley H, Benner SA, Butler T, Di Ventra M, Garaj S, Hibbs A, Huang X et al (2008) The potential and challenges of nanopore sequencing. Nat Biotechnol 26(10):1146–1153
Burch D, Bazant MZ (2009) Size-dependent spinodal and miscibility gaps for intercalation in nanoparticles. Nano Lett 9(11):3795–3800
Busath DD, Thulin CD, Hendershot RW, Phillips LR, Maughan P, Cole CD, Bingham NC, Morrison S, Baird LC, Hendershot RJ, Cotten M, Cross TA (1998) Noncontact dipole effects on channel permeation. I. Experiments with (5f-indole)trp\(^{13}\) Gramicidin A channels. Biophys J 75:2830–2844
Cervera J, Schiedt B, Ramirez P (2005) A Poisson/Nernst–Planck model for ionic transport through synthetic conical nanopores. EPL 71(1):35
Chang CC, Yang RJ (2009) A perspective on streaming current in silica nanofluidic channels: Poisson–Boltzmann model versus Poisson–Nernst–Planck model. J Colliod Interface Sci 339:517–520
Chen L, Conlisk AT (2008) Electroosmotic flow and particle transport in micro/nano nozzles and diffusers. Biomed Microdevices 10:289–289
Chen D, Wei GW (2012) Quantum dynamics in continuum for proton transport—generalized correlation. J Chem Phys 136:134109
Chen DP, Eisenberg RS, Jerome JW, Shu CW (1995) Hydrodynamic model of temperature change in open ionic channels. Biophys J 69:2304–2322
Chen Z, Baker NA, Wei GW (2010) Differential geometry based solvation models I: Eulerian formulation. J Comput Phys 229:8231–8258
Chen Z, Baker NA, Wei GW (2011) Differential geometry based solvation models II: Lagrangian formulation. J Math Biol 63:1139–1200
Chen D, Chen Z, Wei GW (2012a) Quantum dynamics in continuum for proton transport II: variational solvent–solute interface. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 28:25–51
Chen Z, Zhao S, Chun J, Thomas DG, Baker NA, Bates PB, Wei GW (2012b) Variational approach for nonpolar solvation analysis. J Chem Phys 137:084101
Cheng L-J, Guo LJ (2010) Nanofluidic diodes. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):923–938
Chou T (2009) Enhancement of charged macromolecule capture by nanopores in a salt gradient. J Chem Phys 131:034703
Chu KT, Bazant MZ (2006) Nonlinear electrochemical relaxation around conductors. Phys Rev E 74:011501
Coalson RD, Kurnikova MG (2005) Poisson–Nernst–Planck theory approach to the calculation of current through biological ion channels. IEEE Trans NanoBiosci 4(1):81–93
Constantin D, Siwy ZS (2007) Poisson–Nernst–Planck model of ion current rectification through a nanofluidic diode. Phys Rev E 76:041202
Daiguji H (2010) Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):901–911
Daiguji H, Yang P, Majumdar A (2004) Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 4(1):137–142
Daiguji H, Oka Y, Shirono K (2005) Nanofluidic diode and bipolar transistor. Nano Lett 5(11):2274–2280
Davis ME, McCammon JA (1990) Electrostatics in biomolecular structure and dynamics. Chem Rev 94:509–521
Dominy BN, Brooks CL III (1999) Development of a generalized Born model parameterization for proteins and nucleic acids. J Phys Chem B 103(18):3765–3773
Duffy DC, Gillis HL, Lin J, Sheppard NF, Kellogg GJ (1999) Microfabricated centrifugal microfluidic systems: characterization and multiple enzymatic assay. Anal Chem 71:5206–5212
Eijkel JC, van den Berg A (2005) Nanofluidics: what is it and what can we expect from it? Microfluid Nanofluid 1(3):249–267
Eisenberg BS, Chen D (1993) Poisson–Nernst–Planck (PNP) theory of an open ionic channel. Biophys J 64:A22
Eisenberg BS, Hyon YK, Liu C (2010) Energy variational analysis of ions in water and channels: field theory for primitive models of complex ionic fluids. J Chem Phys 133:104104
Erickson D, Rockwood T, Emery T, Scherer A, Psaltis D (2006) Nanofluidic tuning of photonic crystal circuits. Opt Lett 31:59–61
Feng X, Xia KL, Tong YY, Wei G-W (2012) Geometric modeling of subcellular structures, organelles and large multiprotein complexes. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 28:1198–1223
Feng X, Xia KL, Tong YY, Wei GW (2013) Multiscale geometric modeling of macromolecules II: Lagrangian representation. J Comput Chem 34:2100–2120
Fogolari F, Briggs JM (1997) On the variational approach to Poisson–Boltzmann free energies. Chem Phys Lett 281:135–139
Fogolari F, Brigo A, Molinari H (2002) The Poisson–Boltzmann equation for biomolecular electrostatics: a tool for structural biology. J Mol Recognit 15(6):377–392
Fu JP, Schoch RB, Stevens AL, Tannenbaum SR, Han JY (2007) A patterned anisotropic nanofluidic sieving structure for continuous-flow separation of dna and proteins. Nat Nanotechnol 2:121–128
Fu JP, Mao P, Han JY (2009) Continuous-flow bioseparation using microfabricated anisotropic nanofluidic sieving structures. Nat Protoc 4:1681–1698
Geng W, Yu S, Wei GW (2007) Treatment of charge singularities in implicit solvent models. J Chem Phys 127:114106
Gilson MK, Davis ME, Luty BA, McCammon JA (1993) Computation of electrostatic forces on solvated molecules using the Poisson–Boltzmann equation. J Phys Chem 97(14):3591–3600
Grochowski P, Trylska J (2008) Continuum molecular electrostatics, salt effects, and counterion binding—a review of the Poisson–Boltzmann theory and its modifications. Biopolymers 89(2):93–113
Hadd AG, Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM (1999) Microfluidic assays of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Anal Chem 71:5206–5212
He Y, Gillespie D, Boda D, Vlassiouk I, Eisenberg BS, Siwy ZS (2009) Tuning transport properties of nanofluidic devices with local charge inversion. J Am Chem Soc 131:5194–5202
Hollerbach U, Chen DP, Eisenberg RS (2001) Two- and three-dimensional Poisson–Nernst–Planck simulations of current flow through Gramicidin A. J Sci Comput 16(4):373–409
Holm C, Kekicheff P, Podgornik R (2001) Electrostatic effects in soft matter and biophysics. NATO science series. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston
Holst MJ (1994) The Poisson–Boltzmann equation: analysis and multilevel numerical solution. Ph.D. thesis, Numerical Computing Group, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Huber DE, Markel ML, Pennathur S, Patel KD (2009) Oligonucleotide hybridization and free-solution electrokinetic separation in a nanofluidic device. Lab Chip 9:2933–2940
Hyon Y, Eisenberg BS, Liu C (2011) A mathematical model for the hard sphere repulsion in ionic solution. Commun Math Sci 9:459–475
Isebe D, Nerin P (2013) Numerical simulation of particle dynamics in an orifice-electrode system. Application to counting and sizing by impedance measurement. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 29:462–475
Jerome J (1995) Analysis of charge transport. Mathematical theory and approximation of semiconductor models. Springer, New York
Kamholz AE, Weigl BH, Finlayson BA, Yager P (1999) Quantitative analysis of molecular interaction in a microfluidic channel: the t-sensor. Anal Chem 71:5340–5347
Karnik R, Castelino K, Fan R, Yang P, Majumdar A (2005) Effects of biological reactions and modifications on conductance of nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett 5:1638–1642
Karnik R, Duan C, Castelino K, Daiguji H, Majumdar A (2007) Rectification of ionic current in a nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett 7(3):547–551
Kilic MS, Bazant MZ, Ajdari A (2007) Steric effects in the dynamics of electrolytes at large applied voltages. II. Modified Poisson–Nernst–Planck equations. Phys. Rev. E 75:021503
Kim BY, Yang J, Gong MJ, Flachsbart BR, Shannon MA, Bohn PW, Sweedler JV (2009) Multidimensional separation of chiral amino acid mixtures in a multilayered three-dimensional hybrid microfluidic/nanofluidic device. J Anal Chem 81:2715–2722
Kurnikova MG, Coalson RD, Graf P, Nitzan A (1999) A lattice relaxation algorithm for three-dimensional Poisson–Nernst–Planck theory with application to ion transport through the Gramicidin A channel. Biophys J 76:642–656
Lamm G (2003) The Poisson–Boltzmann equation. In: Lipkowitz KB, Larter R, Cundari TR (eds) Reviews in computational chemistry. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 147–366
Levin Y (2002) Electrostatic correlations: from plasma to biology. Rep Prog Phys 65:1577–1632
Li L, Ismagilov RF (2010) Protein crystallization using microfluidic technologies based on valves, droplets, and slipchip. Annu Rev Biophys 39:139–158
Li SC, Hoyles M, Kuyucak S, Chung S-H (1998) Brownian dynamics study of ion transport in the vestibule of membrane channels. Biophys J 74(1):37–47
Li J, Gershow M, Stein D, Brandin E, Golovchenko J (2003) Dna molecules and configurations in a solid-state nanopore microscope. Nat Mater 2(9):611–615
Macounova K, Cabrera CR, Holl MR, Yager P (2000) Generation of natural PH gradients in microfluidic channels for use in isoelectric focusing. Anal Chem 72:3745–3751
Manciu M, Ruckenstein E (2003) On the chemical free energy of the electrical double layer. Langmuir 19(4):1114–1120
Mei Y, Ji CG, Zhang JZH (2006) A new quantum method for electrostatic solvation energy of protein. J Chem Phys 125:094906
Modi N, Winterhalter M, Kleinekathöfer U (2012) Computational modeling of ion transport through nanopores. Nanoscale 4(20):6166–6180
Mukhopadhyay R (2006) What does nanofluidics have to offer? Anal Chem 78(21):7379–7382
Netz RR, Orland H (2000) Beyond Poisson–Boltzmann: fluctuation effects and correlation functions. Eur Phys J E 1(2–3):203–214
Perry JM, Zhou K, Harms ZD, Jacobson SC (2010) Ion transport in nanofluidic funnels. ACS Nano 4(7):3897–3902
Pinho D, Lima R, Pereira AI, Gayubo F (2013) Automatic tracking of labeled red blood cells in microchannels. Int J Numer Methods Biomed Eng 29:977–987
Pu Q, Yun J, Temkin H, Liu S (2004) Ion-enrichment and ion-depletion effect of nanochannel structures. Nano Lett 4(6):1099–1103
Roux B, Allen T, Berneche S, Im W (2004) Theoretical and computational models of biological ion channels. Q Rev Biophys 37(01):15–103
Schoch RB, Han J, Renaud P (2008) Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev Mod Phys 80(3):839
Sharp KA, Honig B (1990a) Calculating total electrostatic energies with the nonlinear Poisson–Boltzmann equation. J Phys Chem 94:7684–7692
Sharp KA, Honig B (1990b) Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules—theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem 19:301–332
Siwy ZS, Howorka S (2010) Engineered voltage-responsive nanopores. Chem Soc Rev 39(3):1115–1132
Snider RF, Wei GW, Muga JG (1996a) Moderately dense gas quantum kinetic theory: transport coefficient expressions. J Chem Phys 105:3066–3078
Snider RF, Wei GW, Muga JG (1996b) Moderately dense gas quantum kinetic theory: aspects of pair correlations. J Chem Phys 105:3057–3065
Song JH, Evans R, Lin YY, Hsu BN, Fair RB (2009) A scaling model for electrowetting-on-dielectric microfluidic actuators. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:75–89
Sparreboom W, Van Den Berg A, Eijkel J (2009) Principles and applications of nanofluidic transport. Nat Nanotechnol 4(11):713–720
Stein D, Kruithof M, Dekker C (2004) Surface-charge-governed ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Phys Rev Lett 93(3):035901
Tomasi J, Mennucci B, Cammi R (2005) Quantum mechanical continuum solvation models. Chem Rev 105:2999–3093
Tu B, Chen MX, Xie Y, Zhang LB, Eisenberg B, Lu BZ (2013) A parallel finite element simulator for ion transport through three-dimensional ion channel systems. J Comput Chem 34:2065–2078
Turner SWP, Cabodi M, Craighead HG (2002) Confinement-induced entropic recoil of single DNA molecules in a nanofluidic structure. Phys Rev Lett 88:128103
Vlachy V (1999) Ionic effects beyond Poisson–Boltzmann theory. Annu Rev Phys Chem 50:145–165
Vlassiouk I, Smirnov S, Siwy Z (2008a) Ionic selectivity of single nanochannels. Nano Lett 8:1978–1985
Vlassiouk I, Smirnov S, Siwy Z (2008b) Nanofluidic ionic diodes. Comparison of analytical and numerical solutions. ACS Nano 2:1589–1602
Wang J, Lin M, Crenshaw A, Hutchinson A, Hicks B, Yeager M, Berndt S, Huang WY, Hayes RB, Chanock SJ, Jones RC, Ramakrishnan R (2009a) High-throughput single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using nanofluidic dynamic arrays. BMC Genomics 10:561
Wang Y, Pant K, Chen ZJ, Wang GR, Diffey WF, Ashley P, Sundaram S (2009b) Numerical analysis of electrokinetic transport in micro-nanofluidic interconnect preconcentrator in hydrodynamic flow. Microfluid Nanofluid 7:683–696
Ward N, Mu X, Serrano G, Covington E, Kurdak C, Zellers ET, Mason AJ, Li W (2012) Microfluidic-packaged CMOS chemiresistor detector for micro-scale gas chromatograph. Micro Nano Lett 7:721–724
Weeks JD, Chandler D, Andersen HC (1971) Role of repulsive forces in determining the equilibrium structure of simple liquids. J Chem Phys 54(12):5237–5247
Wei GW (2010) Differential geometry based multiscale models. Bull Math Biol 72:1562–1622
Wei G-W (2013) Multiscale, multiphysics and multidomain models I: basic theory. J Theor Comput Chem 12(8):1341006
Wei G-W, Zheng Q, Chen Z, Xia K (2012) Variational multiscale models for charge transport. SIAM Rev 54(4):699–754
Weigl BH, Yager P (1997) Silicon-microfabricated diffusion-based optical chemical sensor. Sens Actuators B-Chem 39:452–457
Wu DP, Steckl AJ (2009) High speed nanofluidic protein accumulator. Lab Chip 9:1890–1896
Xia KL, Opron K, Wei GW (2013) Multiscale multiphysics and multidomain models—flexibility and rigidity. J Chem Phys 139:194109
Xia KL, Feng X, Tong YY, Wei GW (2014) Multiscale geometric modeling of macromolecules. J Comput Phys 275:912–936
Yan RX, Liang WJ, Fan R, Yang PD (2009) Nanofluidic diodes based on nanotube heterojunctions. Nano Lett 9:3820–3825
Yu S, Wei GW (2007) Three-dimensional matched interface and boundary (mib) method for treating geometric singularities. J Comput Phys 227(1):602–632
Yuan Z, Garcia AL, Lopez GP, Petsev DN (2007) Electrokinetic transport and separations in fluidic nanochannels. Electrophoresis 28(4):595–610
Zheng Q, Wei GW (2011) Poisson–Boltzmann–Nernst–Planck model. J Chem Phys 134:194101
Zheng Z, Hansford DJ, Conlisk AT (2003) Effect of multivalent ions on electroosmotic flow in micro- and nanochannels. Electrophoresis 24:3006–3017
Zheng Q, Chen D, Wei GW (2011) Second-order Poisson–Nernst–Planck solver for ion transport. J Comput Phys 230:5239–5262
Zhou YC, Lu BZ, Huber GA, Holst MJ, McCammon JA (2008) Continuum simulations of acetylcholine consumption by acetylcholinesterase: a Poisson–Nernst–Planck approach. J Phys Chem B 112:270–275
Zhou K, Perry JM, Jacobson SC (2011) Transport and sensing in nanofluidic devices. Annu Rev Anal Chem 4:321–341
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NSF Grants IIS-1302285 and DMS-1160352, and NIH Grant R01GM-090208. The authors thank an anonymous reviewer for useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.K., Xia, K. & Wei, GW. Atomic scale design and three-dimensional simulation of ionic diffusive nanofluidic channels. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 665–692 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1593-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1593-1