Abstract
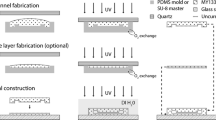
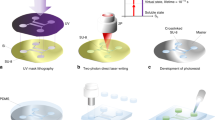
We describe a homebuilt direct laser writing (DLW) system centered on a fluorescence microscope as an alternative means for the creation of microfluidic masters. Such masters are often the starting point of microanalytical platforms and are usually made using transparency masks, which are inexpensive and very convenient. However, these masks can become expensive if features are <25 μm. The linewidth of features made by our DLW system spans from submicron to a millimeter depending on the objective lens, the focal position, the stage speed, and the laser power used. By adjusting these parameters during fabrication, we show that large and small features can be integrated in the same sample. Masters made by DLW were used to create polydimethylsiloxane microfluidic devices and also to perform microcontact printing of alkanethiol monolayers on gold. We also show that registration between sequential patterning steps is readily accomplished and can be used to repair structures or to add features to an existing pattern. The components required to modify a stage-equipped fluorescence microscope into our DLW system are commercially available for under $5000; we contend that this system is a convenient alternative to mask-based lithography for prototyping lab-on-a-chip devices.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldacchini T, LaFratta C, Farrer R, Teich M, Saleh B, Naughton M, Fourkas J (2004) Acrylic-based resin with favorable properties for three-dimensional two-photon polymerization. J Appl Phys 95:6072–6076. doi:10.1063/1.1728296
Chatwin C, Farsari M, Huang S, Heywood M, Birch P, Young R, Richardson J (1998) UV microstereolithography system that uses spatial light modulator technology. Appl Opt 37:7514–7522. doi:10.1364/AO.37.007514
Chung SE, Lee SA, Kim J, Kwon S (2009) Optofluidic encapsulation and manipulation of silicon microchips using image processing based optofluidic maskless lithography and railed microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:2845–2850. doi:10.1039/b903760h
Comina G, Suska A, Filippini D (2014) Low cost lab-on-a-chip prototyping with a consumer grade 3D printer. Lab Chip 14:2978–2982. doi:10.1039/c4lc00394b
Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Irimia D, Tompkins R, Toner M (2008) Equilibrium separation and filtration of particles using differential inertial focusing. Anal Chem 80:2204–2211. doi:10.1021/ac702283m
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984. doi:10.1021/ac980656z
Dweik M, Stringer RC, Dastider SG, Wu Y, Almasri M, Barizuddin S (2012) Specific and targeted detection of viable Escherichia coli O157:H7 using a sensitive and reusable impedance biosensor with dose and time response studies. Talanta 94:84–89. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2012.02.056
Erkal JL, Selimovic A, Gross BC, Lockwood S, Walton E, McNamara S, Martin R, Spence D (2014) 3D printed microfluidic devices with integrated versatile and reusable electrodes. Lab Chip 14:2023–2032. doi:10.1039/c4lc00171k
Fischer J, Wegener M (2012) Three-dimensional optical laser lithography beyond the diffraction limit. Laser Photonics Rev 7:22–44. doi:10.1002/lpor.201100046
Gan Z, Cao Y, Evans RA, Gu M (2013) Three-dimensional deep sub-diffraction optical beam lithography with 9 nm feature size. Nat Commun 4:1–7. doi:10.1038/ncomms3061
Guijt RM, Breadmore MC (2008) Maskless photolithography using UV LEDs. Lab Chip 8:1402–1404. doi:10.1039/b800465j
Itoga K, Kobayashi J, Tsuda Y, Yamato M, Okano T (2008) Second-generation maskless photolithography device for surface micropatterning and microfluidic channel fabrication. Anal Chem 80:1323–1327. doi:10.1021/ac702208d
Jenness NJ, Hill RT, Hucknall A, Chilkoti A, Clark R (2010) A versatile diffractive maskless lithography for single-shot and serial microfabrication. Opt Exp 18:11754–11762. doi:10.1364/OE.18.011754
Kaehr B, Shear JB (2007) Mask-directed multiphoton lithography. J Am Chem Soc 129:1904–1905. doi:10.1021/ja068390y
Kaehr B, Ertaş N, Nielson R, Allen R, Hill R, Plenert M, Shear J (2006) Direct-write fabrication of functional protein matrixes using a low-cost Q-switched laser. Anal Chem 78:3198–3202. doi:10.1021/ac052267s
Kumi G, Yanez CO, Belfield KD, Fourkas JT (2010) High-speed multiphoton absorption polymerization: fabrication of microfluidic channels with arbitrary cross-sections and high aspect ratios. Lab Chip 10:1057–1060. doi:10.1039/b923377f
LaFratta CN, Fourkas J, Baldacchini T, Farrer R (2007) Multiphoton fabrication. Angew Chem Int Ed 46:6238–6258. doi:10.1002/anie.200603995
Li L, Gattass R, Gershgoren E, Hwang H, Fourkas J (2009) Achieving λ/20 resolution by one-color initiation and deactivation of polymerization. Science 324:910–913. doi:10.1126/science.1168996
Libioulle L, Bietsch A, Schmid H, Michel B, Delamarche E (1999) Contact-inking stamps for microcontact printing of alkanethiols on gold. Langmuir 15:300–304. doi:10.1021/la980978y
Lim D, Kamotani Y, Cho B, Mazumder J (2003) Fabrication of microfluidic mixers and artificial vasculatures using a high-brightness diode-pumped Nd:YAG laser direct write method. Lab Chip 3:318–323. doi:10.1039/b308452c
Madou MJ (2002) Fundamentals of microfabrication: the science of miniaturization. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Maruo S, Ikuta K (2000) Three-dimensional microfabrication by use of single-photon-absorbed polymerization. Appl Phys Lett 76:2656–2658. doi:10.1063/1.126742
Nielson R, Kaehr B, Shear JB (2009) Microreplication and design of biological architectures using dynamic-mask multiphoton lithography. Small 5:120–125. doi:10.1002/smll.200801084
Nuzzo RG, Fusco FA, Allara DL (1987) Spontaneously organized molecular assemblies. 3. Preparation and properties of solution adsorbed monolayers of organic disulfides on gold surfaces. J Am Chem Soc 109:2358–2368. doi:10.1021/ja00242a020
Qin D, Xia Y, Whitesides GM (2010) Soft lithography for micro- and nanoscalepatterning. Nat Protoc 5:491–502. doi:10.1038/nprot.2009.234
Thiel M, Fischer J, von Freymann G, Wegener M (2010) Direct laser writing of three-dimensional submicron structures using a continuous-wave laser at 532 nm. Appl Phys Lett 97:221102. doi:10.1063/1.3521464
Varshney M, Li Y (2009) Interdigitated array microelectrodes based impedance biosensors for detection of bacterial cells. Biosens Bioelectr 24:2951–2960. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2008.10.001
Waldbaur A, Carneiro B, Hettich P, Wilhelm E, Rapp B (2013) Computer-aided microfluidics (CAMF): from digital 3D-CAD models to physical structures within a day. Microfluid Nanofluid 15:625–635. doi:10.1007/s10404-013-1177-x
Wang L, Wang L, Yin H, Xing W, Yu Z, Guo M, Cheng J (2010) Real-time, label-free monitoring of the cell cycle with a cellular impedance sensing chip. Biosens Bioelectr 25:990–995. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.09.012
Xia Y, Whitesides GM (1998) Soft lithography. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 37:550–575. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980316)37:5<550:AID-ANIE550>3.0.CO;2-G
Xia Y, Zhao X-M, Kim E, Whitesides GM (1995) A selective etching solution for use with patterned self-assembled monolayers of alkanethiolates on gold. Chem Mater 7:2332–2337. doi:10.1021/cm00060a023
Zhang J, Yan S, Sluyter R, Li W, Alici G, Nguyen N-T (2014a) Inertial particle separation by differential equilibrium positions in a symmetrical serpentine micro-channel. Sci Rep 4:4527. doi:10.1038/srep04527
Zhang Z, Xu J, Hong B, Chen X (2014b) The effect of 3D channel geometry on CTC passing pressure—towards deformability-based cancer cell separation. Lab Chip 14:2576–2584. doi:10.1039/c4lc00301b
Zhao DS, Roy B, McCormick MT, Kuhr W, Brazill S (2003) Rapid fabrication of a poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic capillary gel electrophoresis system utilizing high precision machining. Lab Chip 3:93–99. doi:10.1039/b300577a
Zhao S, Cong H, Pan T (2009) Direct projection on dry-film photoresist (DP2): do-it-yourself three-dimensional polymer microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:1128–1132. doi:10.1039/b817925e
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge funding from Bard College and the Bard Summer Research Institute that supported this work. We also acknowledge help from Prof. Paul Cadden-Zimansky for his assistance with optical and electron microscopy and Tommaso Baldacchini and Mael Manesse for their help in preparing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LaFratta, C.N., Simoska, O., Pelse, I. et al. A convenient direct laser writing system for the creation of microfluidic masters. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 419–426 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1574-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1574-4