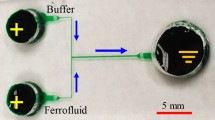
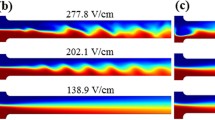
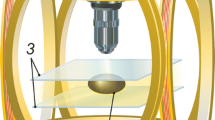
Abstract
Ferrofluids have been increasingly used to manipulate particles and cells in microfluidic devices via negative magnetophoresis. They have also been recently exploited to achieve a fast microfluidic mixing through magnetic field-induced flow instabilities at the ferrofluid/water interface. This work presents the first demonstration of electric field-induced instabilities in electroosmotic ferrofluid/water co-flows through a T-shaped microchannel. With the increase in electric field, instability waves and even chaotic flows can be formed when the two fluids merge at the T-junction due to the significant mismatch of their electrical conductivities. The experimentally observed dynamic behaviors of the ferrofluid/water interface are qualitatively captured by the ferrofluid concentration distribution obtained from a 2D numerical model. The measured threshold electric field for observing sustainable flow instabilities is found to decrease with the increase in ferrofluid concentration. While this trend is correctly predicted by the numerical model, the threshold electric field values are substantially under-predicted. The parametric effects that may be responsible for this discrepancy are discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baygents JC, Baldessari F (1998) Electrohydrodynamic instability in a thin fluid layer with an electrical conductivity gradient. Phys Fluid 10:301–311
Bodenschatz E, Pesch W, Ahlers G (2000) Recent developments in Rayleigh–Bénard convection. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 32:709–778
Castellanos A, Ramos A, Gonzalez A, Green NG, Morgan H (2003) Electrohydrodynamics and dielectrophoresis in microsystems: scaling laws. J Phys D 36:2584–2597
Chang CC, Yang RJ (2007) Electrokinetic mixing in microfluidic systems. Microfluid Nanofluid 3:501–525
Chang HC, Yeo LY (2009) Electrokinetically-driven microfluidics and nanofluidics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Chen CH, Lin H, Lele SK, Santiago JG (2005) Convective and absolute electrokinetic instability with conductivity gradients. J Fluid Mech 524:263–303
Cheng R, Zhu T, Mao L (2014) Three-dimensional and analytical modeling of microfluidic particle transport in magnetic fluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 16:1143–1154
Darrigol O (2002) Stability and instability in nineteenth-century fluid mechanics. Revue d’histoire des mathématiques 8:5–66
El Moctar AO, Aubry N, Batton J (2003) Electro-hydrodynamic micro-fluidic mixer. Lab Chip 3:273–280
Erb RM, Yellen BB (2008) Concentration gradients in mixed magnetic and nonmagnetic colloidal suspensions. J Appl Phys 103:07A312. doi:10.1063/1.2831789
Erb RM, Son HS, Samanta B, Rotello VM, Yellen BB (2009) Magnetic assembly of colloidal superstructures with multipole symmetry. Nature (London) 457:999–1002
Feinstein E, Prentiss M (2006) Three-dimensional self-assembly of structures using the pressure due to a ferrofluid in a magnetic field gradient. J Appl Phys 99:064901
Hoburg JF, Melcher JR (1976) Internal electrohydrodynamic instability and mixing of fluids with orthogonal field and conductivity gradients. J Fluid Mech 73:333–351
Kale A, Patel S, Hu G, Xuan X (2013) Numerical modeling of Joule heating effects in insulator-based dielectrophoresis microdevices. Electrophoresis 34:674–683
Kang KH, Park J, Kang IS, Huh KY (2006) Initial growth of electrohydrodynamic instability of two-layered miscible fluids in T-shaped microchannels. Int J Heat Mass Trans 49:4577–4583
Kirby BJ, Hasselbrink EF Jr (2004) The zeta potential of microfluidic substrates. 2. Data for polymers. Electrophoresis 25:203–213
Knight J (2002) Microfluidics: Honey, I shrunk the lab. Nature 418:474–475
Kose AR, Koser A (2012) Ferrofluid mediated nanocytometry. Lab Chip 12:190–196
Kose AR, Fischer B, Mao L, Koser H (2009) Label-free cellular manipulation and sorting via biocompatible ferrofluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21478–21483
Kull HJ (1991) Theory of the Rayleigh–Taylor instability. Phys Rep 206:197–325
Lee CY, Chang CL, Wang YN, Fu LM (2011) Microfluidic mixing: a review. Int J Mol Sci 12:3263–3287
Li D (2004) Electrokinetics in microfluidics, Academic Press
Li KH, Yellen BB (2010) Magnetically tunable self-assembly of colloidal rings. Appl Phys Lett 97:083105
Liang L, Xuan X (2012a) Diamagnetic particle focusing in ferromicrofluidics using a single magnet. Microfluid Nanofluid 13:637–643
Liang L, Xuan X (2012b) Continuous sheath-free magnetic separation of particles in a U-shaped microchannel. Biomicrofluid 6:044106
Liang L, Zhu J, Xuan X (2011) Three-dimensional diamagnetic particle deflection in ferrofluid microchannel flows. Biomicrofluid 5:034110
Liang L, Zhang C, Xuan X (2013) Enhanced separation of magnetic and diamagnetic particles in a dilute ferrofluid. Appl Phys Lett 102:234101
Lin H (2009) Electrokinetic instability in microchannel flows: a review. Mech Res Comm 36:33–38
Lin H, Storey BD, Oddy MH, Chen CH, Santiago JG (2004) Instability of electrokinetic microchannel flows with conductivity gradients. Phys Fluid 16:1922–1935
Lin H, Storey BD, Santiago JG (2008) A depth-averaged electrokinetic flow model for shallow microchannels. J Fluid Mech 608:43–70
Mao L, Koser H (2007) Overcoming the diffusion barrier: Ultra-fast micro-scale mixing via ferrofluids. In: Transducers & Eurosensors’ 07, Proceedings of 14th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Lyon, France, pp 1829–1832
Melcher JR (1981) Continuum electromechanics. MIT press, Cambridge
Melcher JR, Taylor GI (1969) Electrohydrodynamics: a review of the role of interfacial shear stresses. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 1:111–146
Navaneetham G, Posner JD (2009) Electrokinetic instabilities of non-dilute colloidal suspensions. J Fluid Mech 619:331–365
Nguyen NT, Wu Z (2005) Micromixers: a review. J Micromech Microeng 15:R1–R16
Oddy MH, Santiago JG (2005) Multiple-species model for electrokinetic instability. Phys Fluid 17:064108
Park J, Shin SM, Huh KY, Kang IS (2005) Application of electrokinetic instability for enhanced mixing in various micro-T-channel geometries. Phys Fluid 17:118101
Posner JD (2009) Properties and electrokinetic behavior of non-dilute colloidal suspensions. Mech Res Comm 36:22–32
Posner JD, Santiago JG (2006) Convective instability of electrokinetic flows in a cross-shaped microchannel. J Fluid Mech 555:1–42
Posner JD, Pérez CL, Santiago JG (2012) Electric fields yield chaos in microflows. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:14353–14356
Probstein RF (1994) Physicochemical hydrodynamics: an introduction. Wiley, New York
Rahman M (2005) Instability of Flows. WIT Press, Southampton
Rosensweig RE (1985) Ferrohydrodynamics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sajeesh P, Sen AK (2014) Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:1–52
Saville DA (1997) Electrohydrodynamics: the Taylor–Melcher leaky dielectric model. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 29:27–64
Shin SM, Kang IS, Cho YK (2005) Mixing enhancement by using electrokinetic instability under time-periodic electric field. J Micromech Microeng 15:455–462
Sridharan S, Zhu J, Hu G, Xuan X (2011) Joule heating effects on electroosmotic flow in insulator-based dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 32:2274–2281. doi:10.1002/elps.201100011
Storey BD, Tilley BS, Lin H, Santiago JG (2005) Electrokinetic instabilities in thin microchannels. Phys Fluid 17:018103
Stratton JA (2007) Electromagnetic theory, 33rd edn. Wiley, New York
Theofilis V (2011) Global linear instability. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 43:319–352
Vasudevan SVK (2009). Electrohydrodynamic instabilities in microchannels: a computational study. Graduate Thesis and Dissertations, Iowa State University
Wang GR, Yang F, Zhao W (2014) There can be turbulence in microfluidics at low Reynolds number. Lab Chip 14:1452–1458
Watarai H (2013) Continuous separation principles using external microaction forces. Annu Rev Anal Chem 6:353–378
Wen CY, Yeh CP, Tsai CH, Fu LM (2009) Rapid magnetic microfluidic mixer utilizing AC electromagnetic field. Electrophoresis 30:4179–4186
Wen CY, Liang KP, Chen H, Fu LM (2011) Numerical analysis of a rapid magnetic microfluidic mixer. Electrophoresis 32:3268–3276
Wilbanks JJ, Kiessling G, Zeng J, Zhang C, Xuan X (2014) Exploiting magnetic asymmetry to concentrate diamagnetic particles in ferrofluid microflows. J Appl Phys 115:044907
Zeng J, Chen C, Vedantam P, Brown V, Tzeng T, Xuan X (2012a) Three-dimensional magnetic focusing of particles and cells in ferrofluid flow through a straight microchannel. J Micromech Microeng 22:105018
Zeng J, Chen C, Vedantam P, Tzeng T, Xuan X (2012b) Magnetic concentration of particles and cells in ferrofluid flow through a straight microchannel using attracting magnets. Microfluid Nanofluid 15:49–55
Zeng J, Deng Y, Vedantam P, Tzeng T, Xuan X (2013) Magnetic separation of particles and cells in ferrofluid flow through a straight microchannel using two offset magnets. J Magnet Magnet Mat 346:118–123
Zhu G, Nguyen NT (2012a) Magnetofluidic spreading in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 13:655–663
Zhu G, Nguyen NT (2012b) Rapid magnetofluidic mixing in a uniform magnetic field. Lab Chip 12:4772–4780
Zhu T, Marrero F, Mao L (2010) Continuous separation of non-magnetic particles inside ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:1003–1009
Zhu T, Cheng R, Mao L (2011) Focusing microparticles in a microchannel with ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 11:695–701
Zhu T, Cheng R, Lee SA, Rajaraman E, Eiteman MA, Querec TD, Unger ER, Mao L (2012) Continuous-flow ferrohydrodynamic sorting of particles and cells in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 13:645–654
Zhu T, Cheng R, Liu Y, He J, Mao L (2014) Combining positive and negative magnetophoresis to separate particles of different magnetic properties. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:973–982
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NSF under grant CBET-1150670 and by Clemson University through a departmental SGER (Small Grants for Exploratory Research) grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thanjavur Kumar, D., Zhou, Y., Brown, V. et al. Electric field-induced instabilities in ferrofluid microflows. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 43–52 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1546-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1546-8