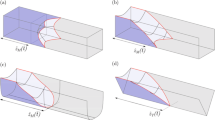
Abstract
We demonstrate a technique to recirculate liquids in a microfluidic channel by alternating predominance of centrifugal and capillary forces to rapidly bring the entire volume of a liquid sample to within one diffusion length, δ, of the surface, even for sample volumes hundreds of times the product of δ and the geometric device area. This is accomplished by repetitive, random sampling of an on-disc sample reservoir to form a thin fluid layer of thickness δ in a microchannel, maintaining contact for the diffusion time, then rapidly exchanging the fluid layer for a fresh aliquot by disc rotation and stoppage. With this technique, liquid volumes of microlitres to millilitres can be handled in many sizes of microfluidic channels, provided the channel wall with greatest surface area is hydrophilic. We present a theoretical model describing the balance of centrifugal and capillary forces in the device and validate the model experimentally.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrantes M, Magone MT, Boyd LF, Schuck P (2001) Adaptation of a surface plasmon resonance biosensor with miorofluidics for use with small sample volumes and long contact times. Anal Chem 73(13):2828–2835
Brenner T, Glatzel T, Zengerle R, Ducree J (2005) Frequency-dependent transversal flow control in centrifugal microfluidics. Lab Chip 5(2):146–150
Bruus H (2008) Theoretical microfluidics. Oxford University Press, USA
Bynum MA, Gordon GB (2004) Hybridization enhancement using microfluidic planetary centrifugal mixing. Anal Chem 76(23):7039–7044
Cao J, Cheng P, Hong FJ (2008) A numerical study of an electrothermal vortex enhanced micromixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 5(1):13–21
Cho YK, Lee JG, Park JM, Lee BS, Lee Y, Ko C (2007) One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7(5):565–573
Chou H-P, Unger MA, Quake SR (2001) A microfabricated rotary pump. Biomed Microdevices 3(4):323–330
Delamarche E, Juncker D, Schmid H (2005) Microfluidics for processing surfaces and miniaturizing biological assays. Adv Mater 17(24):2911–2933
den Toonder J, Bos F, Broer D, Filippini L, Gillies M, de Goede J, Mol T, Reijme M, Talen W, Wilderbeek H, Khatavkar V, Anderson P (2008) Artificial cilia for active micro-fluidic mixing. Lab Chip 8(4):533–541
Dreyer M, Delgado A, Rath HJ (1994) Capillary rise of liquid between parallel plates under microgravity. J Colloid Interface Sci 163(1):158–168
Ducree J, Brenner T, Haeberle S, Glatzel T, Zengerle R (2006) Multilamination of flows in planar networks of rotating microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 2(1):78–84
Ducree J, Haeberle S, Lutz S, Pausch S, von Stetten F, Zengerle R (2007) The centrifugal microfluidic bio-disk platform. J Micromech Microeng 17(7):S103–S115
Duffy DC, Gillis HL, Lin J, Sheppard NF, Kellogg GJ (1999) Microfabricated centrifugal microfluidic systems: characterization and multiple enzymatic assays. Anal Chem 71(20):4669–4678
El Moctar AO, Aubry N, Batton J (2003) Electro-hydrodynamic micro-fluidic mixer. Lab Chip 3(4):273–280
Garcia-Cordero JL, Basabe-Desmonts L, Ducree J, Lee LP, Ricco AJ (2009) Liquid recirculation in microfluidic channels by the interplay of capillary and centrifugal forces. The 15th international conference on solid-state sensors, actuators, and microsystems. IEEE, USA
Golden JP, Floyd-Smith TM, Mott DR, Ligler FS (2007) Target delivery in a microfluidic immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 22(11):2763–2767
Grumann M, Geipel A, Riegger L, Zengerle R, Ducree J (2005) Batch-mode mixing on centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Lab Chip 5(5):560–565
Handique K, Burns MA (2001) Mathematical modeling of drop mixing in a slit-type microchannel. J Micromech Microeng 11(5):548–554
Hofmann O, Voirin G, Niedermann P, Manz A (2002) Three-dimensional microfluidic confinement for efficient sample delivery to biosensor surfaces. Application to immunoassays on planar optical waveguides. Anal Chem 74(20):5243–5250
Hosokawa K, Fujii T, Endo I (1999) Handling of picoliter liquid samples in a poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic device. Anal Chem 71(20):4781–4785
Johnson TJ, Ross D, Locascio LE (2002) Rapid microfluidic mixing. Anal Chem 74(1):45–51
Kusumaatmaja H, Pooley CM, Girardo S, Pisignano D, Yeomans JM (2008) Capillary filling in patterned channels. Phys Rev E 77(6):067301
Lai S, Wang SN, Luo J, Lee LJ, Yang ST, Madou MJ (2004) Design of a compact disk-like microfluidic platform for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anal Chem 76(7):1832–1837
Lee HH, Smoot J, McMurray Z, Stahl DA, Yager P (2006) Recirculating flow accelerates DNA microarray hybridization in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 6(9):1163–1170
Lee MG, Choi S, Park JK (2009) Rapid laminating mixer using a contraction–expansion array microchannel. Appl Phys Lett 95(5):1–051902
Li CY, Dong XL, Qin JH, Lin BC (2009) Rapid nanoliter DNA hybridization based on reciprocating flow on a compact disk microfluidic device. Anal Chim Acta 640(1–2):93–99
Liu J, Williams BA, Gwirtz RM, Wold BJ, Quake S (2006) Enhanced signals and fast nucleic acid hybridization by microfluidic chaotic mixing. Angew Chem Int Ed 45(22):3618–3623
Liu CC, Qiu XB, Ongagna S, Chen DF, Chen ZY, Abrams WR, Malamud D, Corstjens PLAM, Bau HH (2009) A timer-actuated immunoassay cassette for detecting molecular markers in oral fluids. Lab Chip 9(6):768–776
Lynn NS, Henry CS, Dandy DS (2008) Microfluidic mixing via transverse electrokinetic effects in a planar microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 5(4):493–505
Madou M, Zoval J, Jia GY, Kido H, Kim J, Kim N (2006) Lab on a CD. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:601–628
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky A, Ryan P, Balis UJ, Tompkins RG, Haber DA, Toner M (2007) Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 450(7173):U10–U1235
Nichols KP, Ferullo JR, Baeumner AJ (2006) Recirculating, passive micromixer with a novel sawtooth structure. Lab Chip 6(2):242–246
Parsa H, Chin CD, Mongkolwisetwara P, Lee BW, Wang JJ, Sia SK (2008) Effect of volume- and time-based constraints on capture of analytes in microfluidic heterogeneous immunoassays. Lab Chip 8(12):2062–2070
Phillips C, Jakusch M, Steiner H, Mizaikoff B, Fedorov AG (2003) Model-based optimal design of polymer-coated chemical sensors. Anal Chem 75(5):1106–1115
Sia SK, Linder V, Parviz BA, Siegel A, Whitesides GM (2004) An integrated approach to a portable and low-cost immunoassay for resource-poor settings. Angew Chem Int Ed 43(4):498–502
Sigurdson M, Wang DZ, Meinhart CD (2005) Electrothermal stirring for heterogeneous immunoassays. Lab Chip 5(12):1366–1373
Squires TM, Messinger RJ, Manalis SR (2008) Making it stick: convection, reaction and diffusion in surface-based biosensors. Nat Biotechnol 26(4):417–426
Stroock AD, Dertinger SKW, Ajdari A, Mezic I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2002) Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295(5555):647–651
Vanderhoeven J, Pappaert K, Dutta B, Van Hummelen P, Desmet G (2005) DNA microarray enhancement using a continuously and discontinuously rotating microchamber. Anal Chem 77(14):4474–4480
Vijayendran RA, Motsegood KM, Beebe DJ, Leckband DE (2003) Evaluation of a three-dimensional micromixer in a surface-based biosensor. Langmuir 19(5):1824–1828
Wang SS, Jiao ZJ, Huang XY, Yang C, Nguyen NT (2009) Acoustically induced bubbles in a microfluidic channel for mixing enhancement. Microfluid Nanofluid 6(6):847–852
Washburn EW (1921) The dynamics of capillary flow. Phys Rev 17(3):273
Yuen PK, Li GS, Bao YJ, Muller UR (2003) Microfluidic devices for fluidic circulation and mixing improve hybridization signal intensity on DNA arrays. Lab Chip 3(1):46–50
Zheng GF, Patolsky F, Cui Y, Wang WU, Lieber CM (2005) Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat Biotechnol 23(10):1294–1301
Zhmud BV, Tiberg F, Hallstensson K (2000) Dynamics of capillary rise. J Colloid Interface Sci 228(2):263–269
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Science Foundation Ireland under Grant No. 05/CE3/B754. We thank Kevin Newman for helping with the camera and motor control, and Profs. Luke P. Lee of U.C. Berkeley and Z. Hugh Fan of University of Florida for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia-Cordero, J.L., Basabe-Desmonts, L., Ducrée, J. et al. Liquid recirculation in microfluidic channels by the interplay of capillary and centrifugal forces. Microfluid Nanofluid 9, 695–703 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0585-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-010-0585-4