Abstract
Background
Although the clinical outcome of esophageal cancer has recently improved, the relapse rate remains high for all disease stages. At present, there is no diagnostic method to predict the long-term outcome for esophageal cancer. In this study, we evaluated serum preoperative proinflammatory cytokine levels and investigated the correlation between preoperative interleukin-6 (IL-6) and IL-8 levels and survival of patients with esophageal cancer.
Methods
Between 2008 and 2015, we evaluated preoperative serum cytokine levels in 122 patients who underwent esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Serum IL-6 and IL-8 levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. We investigated the relationship between serum cytokine levels and the response to chemotherapy and survival.
Results
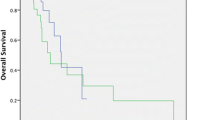
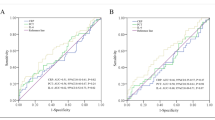
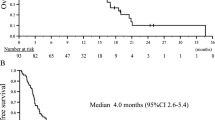
The preoperative IL-6 levels were significantly associated with shorter recurrence-free survival (RFS, p = 0.001) and overall survival (OS, p = 0.001) after esophagectomy. Higher IL-8 levels were significantly associated with RFS (p = 0.018). In the multivariate analysis, age, preoperative chemotherapy, lymph node metastasis, serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and serum IL-6 levels (hazard ratio (HR), 2.888; p = 0.049) were significantly independent prognostic factors of RFS. Additionally, age, pathological stage, and serum IL-6 levels (HR, 3.247; p = 0.027) were shown to be significantly independent prognostic factors of OS. Serum IL-6 levels were significantly higher in the non-responder group (pathological response pGrade0 and pGrade1) after neoadjuvant therapy.
Conclusions
High preoperative serum IL-6 levels are associated with a poor response to chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy and poor prognosis after esophagectomy. Preoperative serum IL-6 levels may be a useful independent prognostic marker for esophageal cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biere SS, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Maas KW, et al. Minimally invasive versus open oesophagectomy for patients with oesophageal cancer: a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2012;379:1887–92.
Chen M-F, Chen P-T, Lu MS, et al. IL-6 expression predicts treatment response and outcome in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:26.
Shiga K, Hara M, Nagasaki T, et al. Preoperative serum interleukin-6 is a potential prognostic factor for colorectal cancer, including stage II patients. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016;2016:9701574 Epub 2015.
Łukaszewicz-Zajac M, Mroczko B, Gryko M, et al. Comparison between clinical signi cance of serum proin ammatory proteins (IL-6 and CRP) and classic tumor markers (CEA and CA 19–9) in gastric cancer. Clin Exp Med. 2011;11:89–96.
Yanagawa H, Sone S, Takahashi Y, et al. Serum levels of interleukin 6 in patients with lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 1995;71:1095–8.
Nakashima J, Tachibana M, Horiguchi Y, et al. Serum interleukin 6 as a prognostic factor in patients with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:2702–6.
Salgado R, Junius S, Benoy I, et al. Circulating interleukin-6 predictors survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2003;103:642–6.
Oka M, Yamamoto K, Takahashi M, et al. Relationship between serum levels of interleukin 6, various disease parameters and malnutrition in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996;56:2776–80.
Wang L-S, Chow K-C, Wu C-W, et al. Expression and up-regulation of interleukin-6 in oesophageal carcinoma cells by n-sodium butyrate. Br J Cancer. 1999;80(10):1617–22.
Okamura S, Fujiwara H, Yoneda M, et al. Overexpression of IL-6 by gene transfer stimulates IL-8-mediated invasiveness of KYSE170 esophageal carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2013;33:1483–90.
Fujiwara H, Suchi K, Okamura S, et al. Elevated serum CRP levels after induction chemoradiotherapy reflect poor treatment response in association with IL-6 in serum and local tumor site in patients with advanced esophageal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:62–8.
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 7th ed. New York: Wiley-Blackwell; 2009.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Kaburagi T, Takeuchi H, Kawakubo H, et al. Clinical utility of a novel hybrid position combining the left lateral decubitus and prone positions during thoracoscopic esophagectomy. World J Surg. 2014;38:410–8.
Okamura A, Takeuchi H, Matsuda S, et al. Factors affecting the systemic inflammatory response after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:3130–5.
Booka E, Takeuchi H, Nishi T, et al. The impact of postoperative complications on survivals after esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Medicine. 2015;94(33):e1369.
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, et al. A randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with cisplatin and 5-fuorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:68–74.
Nakamura K, Kato K. Three-arm phase III trial comparing cisplatin plus 5-FU (CF) versus docetaxel, cisplatin plus 5-FU (DCF) versus radiotherapy with CF (CF-RT) as preoperative therapy for locally advanced esophageal cancer (JCOG1109, NExT Study). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2013;43(7):752–5.
Japanese Esophageal Society. Japanese Classification of Esophageal Cancer, 11th edition: part I. Esophagus. 2017;14:1–36.
Matsuda S, Takeuchi H, Kawakubo H, et al. Cumulative prognostic scores based on plasma fibrinogen and serum albumin levels in esophageal cancer patients treated with transthoracic esophagectomy: comparison with the Glasgow prognostic score. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:302–10.
Groblewska M, Mroczko B, Sosnowska D, et al. Interleukin 6 and C-reactive protein in esophageal cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413:1583–90.
Tsujimoto H, Ono S, Chochi K, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal cancer enhances the postoperative systemic inflammatory response. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2006;36(10):632–7.
Culig Z, Steiner H, Bartsch G, et al. Interleukin-6 regulation of prostate cancer cell growth. J Cell Biochem. 2005;95:497–505.
Heinrich PC, Castell JV, Andus T. Interleukin-6 and the acute phase response. Biochem J. 1990;265:621–36.
Coussens L, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7.
Vakkila J, Lotze M. Inflammation and necrosis promote tumour growth. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:641–8.
Zeh HR, Lotze M. Addicted to death: invasive cancer and the immune response to unscheduled cell death. J Immunother. 2005;28:1–9.
Kotowicz B, Fuksiewicz M, Jonska-Gmyrek J, et al. Clinical significance of pretreatment serum levels of VEGF and its receptors, IL-8, and their prognostic value in type I and II endometrial cancer patients. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0184576. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0184576.
Waugh DJ, Wilson C. The interleukin-8 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:6735–41.
Ogura M, Takeuchi H, Kawakubo H, et al. Clnical significance of CXCL-8/CXCR-2 network in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery. 2013;154:512–20.
Krzystek-Korpacka M, Matusiewicz M, Diakowska D, et al. Elevation of circulating interleukin-8 is related to lymph node and distant metastases in esophageal squamous cell carcinomas–Implication for clinical evaluation of cancer patient. Cytokine. 2008;41:232–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Enago (www.enago.jp) for the English language review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maeda, Y., Takeuchi, H., Matsuda, S. et al. Clinical significance of preoperative serum concentrations of interleukin-6 as a prognostic marker in patients with esophageal cancer. Esophagus 17, 279–288 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-019-00708-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-019-00708-6