Abstract
Purpose
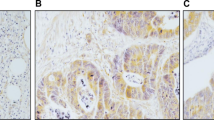
The prognosis varies greatly in colorectal carcinoma patients, even in the same stage. We examined the association between the expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, p27kip1, and clinicopathologic features in patients with colorectal carcinoma to identify a possible panel of tumor markers in predicting prognosis of colorectal carcinoma.
Methods
The expressions of three individual markers in 127 colorectal carcinoma cases were analyzed by immunohistochemistry method. Univariate and multivariate analysis were performed to analyze the expression with the disease-free survival time in colorectal carcinoma.
Results
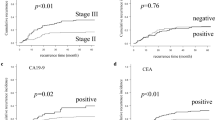
High expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, and low expression of p27kip1 were related to poor prognosis in univariate analysis (P--.0002; P-lt;-.0001; P--.0008). The expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, p27kip1, and tumor differentiation were independent prognostic factors for disease-free survival by Cox regression analysis. The coexpression panel of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, and p27kip had significant prognostic value in all patients (PAB--.0103; PBC--.0068; PCD--.0117). Multivariate analysis with Cox regression reveals that coexpression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, and p27kip1 were independent prognostic factors as tumor differentiation in colorectal carcinoma. In different stages, coexpression tumor markers functioned in Stages II and III but not in the 19 cases of Stage I. The reason might be the number of patients was too small.
Conclusions
The results of this study provided further evidence that the combination of tumor markers of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, and p27kip1 was more informative than any single tumor marker alone for the disease-free survival stratification of colorectal carcinoma. Coexpression of matrix metalloproteinases-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, and p27kip1 might be a useful survival stratification panel for clinical management.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pisani P, Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J. Estimates of the worldwide mortality from 25 cancers in 1990 [erratum]. Int J Cancer 1999;83:870-.
Burt RW, DiSario JA, Cannon-Albright L. Genetics of colon cancer: impact of inheritance on colon cancer risk. Annu Rev Med 1995;46:371-.
Li M, Gu J. Changing patterns of colorectal cancer in China over a period of 20 years. World J Gastroenterol 2005;11:4685-.
Pohl C, Hombach A, Kruis W. Chronic inflammatory bowel disease and cancer. Hepatogastroenterology 2000;47:57–70.
Wolmark N, Rockette H, Fisher B, et al. The benefit of leucovorin modulated 5-fluorouracil as postoperative adjuvant therapy for primary colon cancer: results from the National Surgery and Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project protocol C-03. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1879-7.
Aster VB, Coller FA. The prognosis significance of direct extension of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Ann Surg 1954;192:846-0.
American Joint Committee on Cancer. Cancer staging manual. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven, 1997:83-
Leeman MF, McKay JA, Murray GI. Matrix metalloproteinase 13 activity is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Clin Pathol 2002;55:758-2.
Lyall MS, Dundas SR, Curran S, Murray GI. Profiling markers of prognosis in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2006;12:1184-1.
Kim JC, Roh SA, Kim HC, et al. Coexpression of carcinoembryonic antigen and E-cadherin in colorectal adenocarcinoma with liver metastasis. J Gastrointest Surg 2003;7:931-.
Parsons SL, Watson SA, Brown PD, Collins HM, Steele RJ. Matrix metalloproteinases. Br J Surg 1997;84:160-.
Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Metalloproteinases and cancer invasion. Semin L Cancer Bio 1990;1:99–106.
Mukai M, Sadahiro S, Tokunaga N, et al. The expression of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 in patients with colorectal adenocarcinoma invaded to the submucosal and proper muscle layer. Oncol Rep 1998;5:335-0.
Baker EA, Bergin FG, Leaper DJ. Matrix metalloproteinases, their tissue inhibitors and colorectal cancer staging. Br J Surg 2000;87:1215-1.
Papadopoulou S, Scorilas A, Arnogianaki N, et al. Expression of gelatinase-A (MMP-2) in human colon cancer and normal colon mucosa. Tumour Biol 2001;22:383-.
Sis B, Sagol O, Kupelioglu A, et al. Prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinase-2, cathepsin D, and tenascin-C expression in colorectal carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract 2004;200:379-7.
Duffy MJ. Carcinoembryonic antigen as a marker for colorectal cancer: is it clinically useful? Clin Chem 2001;47:624-0.
Wiggers T, Arends JW, Verstijnen C, Moerkerk PM, Bosman FT. Prognostic significance of CEA immunoreactivity patterns in large bowel carcinoma tissue. Br J Cancer 1986;54:409-4.
Kitadai Y, Radinsky R, Bucana CD, et al. Regulation of carcinoembryonic antigen expression in human colon carcinoma cells by the organ microenvironment. Am J Pathol 1996;149:1157-6.
Nakagoe T, Sawai T, Ayabe H, et al. Prognostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) in tumor tissue of patients with colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 2001;21:3031-.
Thomas GV, Szigeti K, Murphy M, Draetta G, Pagano M, Loda M. Down-regulation of p27 is associated with development of colorectal adenocarcinoma metastases. Am J Pathol 1998;153:681-
Palmqvist R, Stenling R, Oberg A, Landberg G. Prognostic significance of p27(Kip1) expression in colorectal cancer: a clinico-pathologic characterization. J Pathol 1999;188:18–23.
Loda M, Cukor B, Tam SW, et al. Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas. Nat Med 1997;3:231-
Barozzi C, Ravaioli M, D’Errico A, et al. Relevance of biologic markers in colorectal carcinoma: a comparative study of a broad panel. Cancer 2002;94:647-7.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Drs. Yu Wang, Yun-Tao Xie, Yan-Hua Yuan, Yan Han, Zhen-Dong Gu, and Zhen-Yuan Sun for assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the Research fund of the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission (Grant H020920030390); Beijing New Star Project on Science & Technology (Grant 2006B55).
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M., Li, JY., Zhao, AL. et al. Survival Stratification Panel of Colorectal Carcinoma with Combined Expression of Carcinoembryonic Antigen, Matrix Metalloproteinases-2, and p27kip1 . Dis Colon Rectum 50, 1887–1898 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-007-9053-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-007-9053-y