Abstract
Background
The clinical impact of monitoring serum p53 antibodies, carbohydrate antigen19-9, and carcinoembryonic antigen in patients with colorectal cancer has not been fully evaluated.
Methods
A total of 420 surgically treated stage II/III colorectal cancer patients were retrospectively analyzed. Among them, 101 patients developed disease recurrence. The prognostic impact of preoperative and recurrence levels of serum p53 antibodies, carbohydrate antigen19-9, and carcinoembryonic antigen status was evaluated.
Results
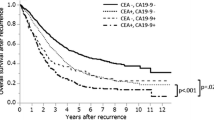
Although preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen- and carbohydrate antigen19-9-positive status was significantly associated with recurrence, preoperative serum p53 antibody levels were not. Among two marker combinations, carcinoembryonic antigen + serum p53 antibodies showed the highest positive rate at recurrence. Although carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen19-9 frequently converted from preoperative-negative status to positive status at recurrence, serum p53 antibodies converted to positive status in only one patient. Carcinoembryonic antigen- and carbohydrate antigen19-9-positive status were significant prognostic factors for overall survival after recurrence, but the presence of serum p53 antibodies at recurrence was not.
Conclusions
Postoperative serum p53 antibody status should only be followed in patients with preoperative-positive status. Carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen19-9 should be followed even in preoperative-negative patients. Unlike carcinoembryonic antigen- and carbohydrate antigen19-9-positive status, serum p53 antibody-positive status as recurrence was not a poor prognostic indicator.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CA19-9:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9
- s-p53-Abs:
-
Serum p53 antibodies
References
McKeown E, Nelson DW, Johnson EK et al (2014) Current approaches and challenges for monitoring treatment response in colon and rectal cancer. J Cancer 5:31–43
Kahi CJ, Anderson JC, Rex DK (2013) Screening and surveillance for colorectal cancer: state of the art. Gastrointest Endosc 77:335–350
Tokunaga R, Sakamoto Y, Nakagawa S et al (2017) The utility of tumor marker combination, including serum p53 antibody, in colorectal cancer treatment. Surg Today 47:636–642
Kunizaki M, Sawai T, Takeshita H et al (2016) Clinical value of serum p53 antibody in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 36:4171–4175
Ochiai H, Ohishi T, Osumi K et al (2012) Reevaluation of serum p53 antibody as a tumor marker in colorectal cancer patients. Surg Today 42:164–168
Yamaguchi T, Takii Y, Maruyama S (2013) Usefulness of serum p53 antibody measurement in colorectal cancer: an examination of 1384 primary colorectal cancer patients. Surg Today 44:1529–1535
Suzuki T, Funahashi K, Ushigome M et al (2017) Diagnostic and prognostic impact of serum p53 anti body titration in colorectal cancer. Toho J Med 11:107–115
Suzuki T, Shimada H, Ushigome M et al (2016) Three-years monitoring of serum p53 antibody during chemotherapy and surgery for stage IV rectal cancer. Clin J Gastroenterol 9(55–58):16
Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H et al (2014) Hirakawa K Significance of CEA and CA19-9 combination as a prognostic indicator and for recurrence monitoring in patients with stage II colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 34:3753–3758
Kawahara H, Watanabe K, Enomoto H et al (2013) Normalization of serum p53 antibody levels in patients after curative resection for colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res 33:2221–2225
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind C (2010) TNM classification of malignant tumors, 7th edn. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken
Suzuki T, Yajima S, Ishioka N et al (2018) Prognostic significance of high serum p53 antibody titers in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Esophagus 15:294–300
Shimada H, Ochiai T, Nomura F (2003) Titration of serum p53 antibodies in 1,085 patients with various types of malignant tumors: a multi-institutional analysis by the Japan p53 Antibody Research Group. Cancer 97:682–689
Ito M, Oshima Y, Yajima S et al (2019) Diagnostic impact of high serum midkine level in patients with gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 3(2):195–201
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl 48:452–458
Shimada H, Shiratori T, Takeda A et al (2009) Perioperative changes of serum p53 antibody titer is a predictor for survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg. 33:272–277
Tang R, Yeh CY, Wang JY et al (2009) Serum p53 antibody as tumor marker for follow-up of colorectal cancer after curative resection. Ann Surg Oncol 16:2516–2523
Ushigome M, Nabeya Y, Soda H et al (2018) Multi-panel assay of serum autoantibodies in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 23:917–923
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI (grant number 26462029). The authors would like to thank MARUZEN-YUSHODO Co., Ltd. (https://kw.maruzen.co.jp/kousei-honyaku/) for the English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ushigome, M., Shimada, H., Miura, Y. et al. Changing pattern of tumor markers in recurrent colorectal cancer patients before surgery to recurrence: serum p53 antibodies, CA19-9 and CEA. Int J Clin Oncol 25, 622–632 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01597-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10147-019-01597-6