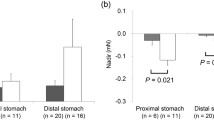
Abstract
PURPOSE: The cause of dysmotility in patients with slow-transit constipation is unknown. Nitric oxide has recently been shown to be a neurotransmitter in the nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory nerves of the human gut. To clarify the physiologic significance of nitric oxide in the colon of patients with slow-transit constipation, we investigated the enteric nerve responses in lesional and normal bowel segments derived from patients with slow-transit constipation and patients who underwent colon resection for colonic cancers. METHODS: Twenty-six preparations were taken from colonic lesions in eight patients with slow-transit constipation (2 men; age, 23 to 69 (mean, 44.8) years). Forty-two preparations were taken from the normal colons of 14 patients with colonic cancer (8 men; age, 40 to 66 (mean, 52.4) years). A mechanographic technique was used to evaluate in vitro muscle responses to electric field stimulation before and after treatment with various autonomic nerve blockers, NG-nitro-L-arginine, and L-arginine. RESULTS: The colons of patients with slow-transit constipation were more strongly innervated by nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory nerves than were normal colons (P <0.05). Nitric oxide was found to act on both normal and slow-transit constipation colons. The colons of patients with slow-transit constipation were more strongly innervated by nitric oxide nerves than were normal colons (P < 0.01). Responses to electric field stimulation were the same in each case among the normal colons and were also the same in each case among the slow-transit constipation colons. CONCLUSION: These findings suggest that an increase of nitric oxide mediates nonadrenergic, noncholinergic inhibitory nerves and plays an important role in the dysmotility observed in the colons of patients with slow-transit constipation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M Candelli EC Nista MA Zocco A Gasbarrini (2001) ArticleTitleIdiopathic chronic constipation Hepatogastroenterology 48 1050–1057
WR Schouten FJ ten Kate EJ de Graaf EC Gilberts JL Simons P Kluck (1993) ArticleTitleVisceral neuropathy in slow-transit constipation Dis Colon Rectum 36 1112–1117
HJ Park MA Kamm AM Abbasi IC Talbot (1995) ArticleTitleImmunohistochemical study of the colonic muscle and innervation in idiopathic chronic constipation Dis Colon Rectum 38 509–513
JB Furness M Costa (1973) ArticleTitleThe nervous release and the action of substances which affect intestinal muscle through neither adrenoreceptors nor cholinoreceptors Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 265 123–133
D Mitolo-Chieppa G Mansi R Rinaldi et al. (1998) ArticleTitleCholinergic stimulation and nonadrenergic, noncholinergic relaxation of human colonic circular muscle in idiopathic chronic constipation Dig Dis Sci 43 2719–2726
MS Faussone-Pellegrini A Infantino P Matini A Masin B Mayer M Lise (1999) ArticleTitleNeuronal anomalies and normal muscle morphology at the hypomotile ileocecocolonic region of patients affected by idiopathic chronic constipation Histol Histopathol 14 1119–1134
H Bult GE Boeckxstaens PA Pelckmans (1990) ArticleTitleNitric oxide as an inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurotransmitter Nature 345 346–347
ME Stark AJ Bauer MG Sarr (1993) ArticleTitleNitric oxide mediates inhibitory nerve input in human and canine jejunum Gastroenterology 104 398–409
T O’Kelly A Brading N Mortensen (1993) ArticleTitleNerve mediated relaxation of the human internal anal sphincter Gut 34 689–693
R Tomita K Munakata Y Kurosu K Tanjoh (1995) ArticleTitleA role of nitric oxide in Hirschsprung’s disease J Pediatr Surg 30 437–440
M Thumshirn M Camilleri MG Choi A Zinsmeister (1999) ArticleTitleModulation of gastric sensory and motor functions by nitrergic and α2-adrenergic agents in humans Gastroenterol 116 573–585
R Tomita K Tanjoh S Fujisaki M Fukuzawa (2000) ArticleTitlePeptidergic nerves in the colon of patients with ulcerative colitis Hepatogastroenterology 32 400–404
D Saur H Paehge V Schusdziarra HD Allescher (2000) ArticleTitleDistinct expression of splice of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in the human gastrointestinal tract Gastroenterol 118 849–858
AJ Porter DA Wattchow A Hunter M Costa (1998) ArticleTitleAbnormalities of nerve fibers in the circular muscle of patients with slow transit constipation Int J Colorectal Dis 13 208–216
DE Burleigh (1988) ArticleTitleEvidence for functional cholinergic deficit in human colonic tissue resected for constipation J Pharm Pharmacol 40 55–57
CH Hoyle MA Kamn JE Lennard-Jones G Burnstock (1992) ArticleTitleAn in vitro electrophysiological study of the colon from patients with idiopathic chronic constipation Clin Auton Res 2 325–333
G Bassotti M Gaburri BP Imbimbo et al. (1993) ArticleTitleImpaired colonic motor response to cholinergic stimulation in patients with severe chronic (slow transit type) constipation Dig Dis Sci 38 1040–1045
JM Gattuso CH Hoyle P Milner MA Kamm G Burnstock (1996) ArticleTitleEnteric innervation in idiopathic megarectum and megacolon Int J Colorectal Dis 11 264–271
AJ Williams KR Palmer (1991) ArticleTitleSevere constipation as the presenting complaint of phaeochromocytoma Aust N Z J Med 21 888–890
JR Grider (1989) ArticleTitleIdentification of neurotransmitters regulating intestinal peristaltic reflex in human Gastroenterol 97 1414–1419
R Tomita K Tanjoh (1998) ArticleTitleRole of nitric oxide in the colon of patients with ulcerative colitis World J Surg 22 88–92
R Tomita K Tanjoh S Fujisaki M Fukuzawa (1999) ArticleTitleA role of nitric oxide (NO) in the human pyloric sphincter Hepatogastroenterology 46 2999–3002
P Alm B Larsson KE Anderson (1992) ArticleTitleNADPH diaphorase activity and non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation of the human gastrointestinal tract Acta Physiol Scand 146 285–287
C Cortesini F Cianchi A Infantio M Lise (1995) ArticleTitleNitric oxide synthase and VIP distribution in enteric nervous system in idiopathic chronic constipation Dig Dis Sci 40 2450–2455
C Pennig JB Delemarre WA Bemelman I Biemond CB Lamers AA Masclee (2000) ArticleTitleProximal and distal gut hormone secretion in slow transit constipation Eur J Clin Invest 30 709–714
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Tomita, R., Fujisaki, S., Ikeda, T. et al. Role of Nitric Oxide in the Colon of Patients With Slow-Transit Constipation. Dis Colon Rectum 45, 593–600 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6251-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-004-6251-8