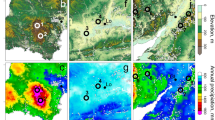
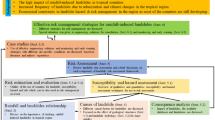
Abstract
As the global climate warms, the frequency of soil slope failures induced by snowmelt is gradually increasing, especially loess landslide disasters in seasonally frozen areas. Landslide disasters in seasonally frozen areas pose a serious threat to human lives and engineering constructions and are gradually drawing greater public attention around the world. However, the mechanism that regulates deformation and failure processes, resulting in snowmelt-driven landslides, remains elusive. The Yili River Valley in Xinjiang, China, is an ideal location for exploring the mechanism of snowmelt-driven landslides. Based on detailed field surveys, remote sensing image identification, meteorological data analysis and loess characteristic tests, this paper takes a representative high-level loess landslide in north-west China as a case in order to explore its evolution history, movement process and resurrection mechanism. It was found that this loess slope had suffered two large-scale sliding failures and different degrees of inherited slope deformation had been found between the two slope failures. The 32 surface cracks identified have a total length of 3,505.10 m, and the total area of the landslide was found to be 135,462m2. The average thickness of the sliding body was about 30 m, and the volume was approximately 504,000 m3. The actual movement time lasted for 32 s with an average moving speed of about 15 m/s. Human grazing activities dominate the formation and development of slope surface cracks in the early stage. The strong water sensitivity of distinctive loess controls soil strength deterioration in the slip zone. Rapid snow removal and infiltration, driven by an abnormal temperature rise in Spring, is the most important triggering factor for slope deformation, evolution and failure. As regional grazing activities increase and global warming intensifies, the potential for resurrection landslides will increase. The results provide essential information for a comprehensive understanding of early warning systems and risk assessment for snowmelt-triggered landslides in cold areas.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allstadt KE, Farin M, Iverson RM, Obryk MK, Kean JW, Tsai VC, Rapstine TD, Logan M (2020) Measuring basal force fluctuations of debris flows using seismic recordings and empirical green's functions. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 125(9):e2020JF005590. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JF005590
Bell R, Petschko H, Röhrs M, Dix A (2012) Assessment of landslide age, landslide persistence and human impact using airborne laser scanning digital terrain models. Geogr Ann Ser A Phys Geogr 94:135–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0459.2012.00454.x
Cardinali M, Ardizzone F, Galli M, Guzzetti F, Paola R, Claps P, Siccardi F (2000) Landslides triggered by rapid snow melting: the December 1996–January 1997 event in Central Italy. In: Mediterranean Storms, Proceedings of the EGS Conference in Maratea, Italy, October 1999. Editoriale Bios, Cosenza, p 439–448
Chamberlain EJ, Gow AJ (1979) Effect of freezing and thawing on the permeability and structure soils. Eng Geol 13:73–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-7952(79)90022-X
Coe JA, Ellis WL, Godt JW, Savage WZ, Savage JE, Michael JA, Kibler JD, Powers PS, Lidke DJ, Debray S (2003) Seasonal movement of the slumgullion landslide determined from global positioning system surveys and field instrumentation, July 1998–March 2002. Eng Geol 68:67–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(02)00199-0
Duan W, Zou S, Chen Y, Nover D, Fang G, Wang Y (2020) Sustainable water management for cross-border resources: the balkhash lake Basin of Central Asia, 1931–2015. J Clean Prod 263:121614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121614
Fan X, Xu Q, Scaringi G, Dai L, Li W, Dong X, Zhu X, Pei X, Dai K, Havenith HB (2017) Failure mechanism and kinematics of the deadly June 24th 2017 Xinmo landslide, Maoxian, Sichuan, China. Landslides 14:1229–2146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-017-0907-7
Feng Z, Ran M, Yang Q, Zhai X, Wang W, Zhang X, Huang C (2011) Stratigraphies and chronologies of late Quaternary loess–paleosol sequences in the core area of the central Asian arid zone. Quat Int 240:156–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2010.10.019
Flageollet JC, Maquaire O, Martin B, Weber D (1999) Landslides and climatic conditions in the Barcelonnette and Vars basins (Southern French Alps, France). Geomorphology 30:65–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00045-8
Harris C, Lewkowicz AG (2000) An analysis of the stability of thawing slopes, Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada. Can Geotech J 37:449–462. https://doi.org/10.1139/t99-118
Hibert C, Ekström G, Stark CP (2014) Dynamics of the Bingham canyon mine landslides from seismic signal analysis. Geophys Res Lett 41(13):4535–4541. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014GL060592
Hinds E, Lu N, Mirus B, Wayllace A (2019) Effects of infiltration characteristics on spatial-temporal evolution of stability of an interstate highway embankment. J Geotech Geoenvironmental Eng 145(9):05019008. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)GT.1943-5606.0002127
Huggel C, Clague JJ, Korup O (2012) Is climate change responsible for changing landslide activity in high mountains? Earth Surf Process Landforms 37:77–91. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.2223
Kawamura S, Miura S (2013) Rainfall-induced failures of volcanic slopes subjected to freezing and thawing. Soils Found 53:443–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2013.04.006
Lin CH, Jan JC, Pu HC, Tu Y, Chen CC, Wu YM (2015) Landslide seismic magnitude. Earth Planet Sci Lett 429:122–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.07.068
Ma Y (2017) Yili Hasake autonomous prefecture statistical yearbook. Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture (in Chinese)
Nadim F, Kjekstad O, Peduzzi P, Herold C, Jaedicke C (2006) Global landslide and avalanche hotspots. Landslides 3:159–173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-006-0036-1
Othman MA, Benson CH (1993) Effect of freeze-thaw on the hydraulic conductivity and morphology of compacted clay. Can Geotech J 30(2):236–246. https://doi.org/10.1139/t93-020
Peng J, Wang S, Wang Q, Zhuang J, Huang W, Zhu X, Leng Y, Ma P (2018) Distribution and genetic types of loess landlisdes in China. J Asian Earth Sci 170:329–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.11.015
Saez LJ, Corona C, Stoffel M, Schoeneich P, Berger F (2012) Probability maps of landslide reactivation derived from tree-ring records: pra bellon landslide, southern French Alps. Geomorphology 138:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-31325-7-54
Schulz WH, Kean JW, Wang G (2009a) Landslide movement in southwest Colorado triggered by atmospheric tides. Nat Geosci 2:863–866. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo659
Schulz WH, Mckenna JP, Kibler JD, Biavati G (2009b) Relations between hydrology and velocity of a continuously moving landslide—evidence of pore-pressure feedback regulating landslide motion? Landslides 6:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-009-0157-4
Shan W, Guo Y, Wang F, Marui H, Strom A (2014) Landslides in Cold Regions in the Context of Climate Change. Environmental Science and Engineering, Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-00867-7
Shi J, Wu L, Wu S, Li B, Wang T, Xin P (2016) Analysis of the causes of large-scale loess landslides in Baoji, China. Geomorphology 264:109–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.04.013
Shoop S, Affleck R, Haehnel R, Janoo V (2008) Mechanical behavior modeling of thaw-weakened soil. Cold Reg Sci Technol 52(2):191–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2007.04.023
Simonsen E, Isacsson U (2001) Soil behavior during freezing and thawing using variable and constant confining pressure triaxial tests. Can Geotech J 38:863–875. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-38-4-863
Song Y, Lai Z, Li Y, Chen T, Wang Y (2015) Comparison between luminescence and radiocarbon dating of late Quaternary loess from the Ili Basin in Central Asia. Quat Geochronol 30:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quageo.2015.01.012
Subramanian SS, Ishikawa T, Tokoro T (2017) Stability assessment approach for soil slopes in seasonal cold regions. Eng Geol 221:154–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.008
Subramanian SS, Ishikawa T, Tokoro T (2018) An early warning criterion for the prediction of snowmelt-induced soil slope failures in seasonally cold regions. Soils Found 58(3):582–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2018.02.021
Subramanian SS, Fan X, Yunus AP, van Asch T, Scaringi G, Xu Q, Dai L, Ishikawa T, Huang R (2020) A Sequentially Coupled Catchment-Scale Numerical Model for Snowmelt-Induced Soil Slope Instabilities. J Geophys Res Earth Surf 125:e2019JF005468. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JF005468
Trandafir AC, Ertugrul OL, Giraud RE, McDonald GN (2015) Geomechanics of a snowmelt-induced slope failure in glacial till. Environ Earth Sci 73:3709–3716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3658-y
Wang G, Zhang D, Furuya G, Yang J (2014) Pore-pressure generation and fluidization in a loess landslide triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake, China: A case study. Eng Geol 174:36–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.006
Wen B, Yan Y (2014) Influence of structure on shear characteristics of the unsaturated loess in Lanzhou. China Eng Geol 168:46–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.10.023
Wu K, Chen N, Hu G, Han Z, Ni H, Rahman M (2021) Failure mechanism of the Yaoba loess landslide on March 5, 2020: the early-spring dry spell in Southwest China. Landslides 18:3183–3195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-021-01703-8
Xu L, Dai FC, Gong QM, Tham LG, Min HBT (2012) Irrigation-induced loess flow failure in Heifangtai Platform. North-West China Environ Earth Sci 66:1707–1713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-011-0950-y
Yan Y, Cui YF, Guo J, Hu S, Wang Z, Yin S (2020) Landslide reconstruction using seismic signal characteristics and numerical simulations: Case study of the 2017 "6.24" Xinmo landslide. Eng Geol 270:105582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105582
Zeng L, Yi S, Zhang W, Feng H, Lv A, Zhao W, Luo Y, Wang Q, Lu H (2020) Provenance of loess deposits and stepwise expansion of the desert environment in NE China since ~1.2 Ma: Evidence from Nd-Sr isotopic composition and grain-size record. Glob Planet Change 185:103087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2019.103087
Zhang D, Wang G (2007) Study of the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake-induced landslides in loess (China). Eng Geol 94:76–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2007.07.007
Zhang F, Wang G, Kamai T, Chen W, Zhang D, Yang J (2013) Undrained shear behavior of loess saturated with different concentrations of sodium chloride solution. Eng Geol 155:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.12.018
Zhang Z, He S (2019) Analysis of broadband seismic recordings of landslide using empirical Green’s function. Geophys Res Lett 46(9):4628–4635. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018gl081448
Zhuang J, Peng J, Wang G, Javed I, Wang Y, Li W (2018) Distribution and characteristics of landslide in Loess Plateau: A case study in Shaanxi province. Eng Geol 236:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.001
Zou S, Abuduwaili J, Ding J, Duan W, De Voorde TV (2020) Description and attribution analysis of the 2017 spring anomalous high temperature causing floods in kazakhstan. J Meteorol Soc JPN 98(6):1353–1368. https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2020-070
Zou S, Abuduwaili J, Duan W, Ding J, De Maeyer P, De Voorde TV, Ma L (2021) Attribution of changes in the trend and temporal non-uniformity of extreme precipitation events in Central Asia. Sci Rep 11:15032. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94486-w
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors Yu Xian and Xueli Wei are employed by Chengdu University of Information Technology, Chengdu, China. Authors Haibo Zhou, Feng Liu and Hao Sun is employed by Sichuan Highway Planning, Survey, Design and Research Institute Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xian, Y., Wei, X., Zhou, H. et al. Snowmelt-triggered reactivation of a loess landslide in Yili, Xinjiang, China: mode and mechanism. Landslides 19, 1843–1860 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01879-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-022-01879-7