Abstract
Discontinuities, such as joints and beddings, usually play a significant role in the seismic response and corresponding failure process of slopes, especially for anti-dip rock slide according to field observations. Shaking table tests associated with numerical analyses are carried out in this paper to explore the effect of seismic wave on response of jointed anti-dip rock slopes. Shaking table tests involve anti-dip rock slope models with different rock types and different excitation intensities. Ten accelerometers are installed inside each slope model to monitor the dynamic response and spectrum shifting characteristics. It is found that the area of failure zone in the soft rock anti-dip slope is approximate 1.5 times the size of that in the hard rock anti-dip slope. Meanwhile, the width and ridge number of the fast Fourier-transformation spectrum along the slope surface can reveal the internal damage features within the anti-dip rock slopes, and the multiple failure planes can also be recognized according to the variation of distance between the innermost and outermost ridges in the fast Fourier-transformation spectrum. Moreover, the distinct element method incorporating a damage model is used to interpret the test results and to identify the main influencing factors for seismic instability. It is found that the failure pattern of a jointed anti-dip rock slope is more sensitive to bedding inclination than to joint inclination.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikary DP, Dyskin AV, Jewell RJ, Stewart DP (1997) A study of the mechanism of flexural toppling failure of rock slopes. Rock Mech Rock Eng 30:75–93
Almaz T, Havenith HB (2016) 2D dynamic studies combined with the surface curvature analysis to predict Arias Intensity amplification. J Seismol 20(3):711–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-016-9553-0
Alzo’ubi AK, Martin CD, Cruden DM (2010) Influence of tensile strength on toppling failure in centrifuge tests. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47:974–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.05.011
Asr AA, Toufigh MM, Salajegheh A (2012) Determination of the most probable slip surface in 3D slopes considering the effect of earthquake force direction. Comput Geosci 45:119–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2011.10.024
Aurelian CT, Toshitaka K, Roy CS (2009) Earthquake-induced displacements of gravity retaining walls and anchor-reinforced slopes. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 29(3):428–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2008.04.005
Bhasin R, Kaynia AM (2004) Static and dynamic simulation of a 700-m high rock slope failure in Western Norway. Eng Geol 71(3–4):213–226
Che AL, Yang HK, Wang B et al (2016) Wave propagations through jointed rock masses and their effects on the stability of slopes. Engineering Geology 201:45–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.12.018
Cruden DM (1989) Limits to common toppling. Can Geotech J 26:737–742
Cruden DM, Varnes DJ (1996) Landslide types and processes. In: Turner AK, Schuster RL (eds) Landslides investigation and mitigation. Transportation research board, US National Research Council. Special Report 247, Chapter 3, Washington, DC, pp 36–75
Dong JY, Yang GX, Wu F et al (2011) The large-scale shaking table test study of dynamic response and failure mode of bedding rock slope under earthquake. Rock Soil Mech 32(10):2977–2982 (In Chinese)
Eberhardt E, Stead D, Coggan J (2004) Numerical analysis of initiation and progressive failure in natural rock slopes—the 1991 Randa rockslide. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(1):69–87
Fan G, Zhang J, Wu J, Yan K (2016) Dynamic response and dynamic failure mode of a weak intercalated rock slope using a shaking table. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(8):3243–3256. (In Chinese). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-0971-7
Gischig VS, Eberhardt E, Moore JR, Hungr O (2015a) On the seismic response of deep-seated rock slope instabilities—insights from numerical modeling. Eng Geol 193(2):1–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.04.003
Gischig V, Preisig G, Eberhardt E (2015b) Numerical investigation of seismically induced rock mass fatigue as a mechanism contributing to the progressive failure of deep-seated landslides. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(6):2457–2478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0821-z
Goodman RE (1989) Introduction to rock mechanics, Second edn. Wiley, New York
Goodman RE, Bray JW (1976) Toppling of rock slopes, Vol. 2. Procs., ASCE specialty conference on rock engineering for foundation and Slopes, Boulder, Colo
Gordan B, Armaghani DJ, Hajihassani M, Monjezi M (2016) Prediction of seismic slope stability through combination of particle swarm optimization and neural network. Eng Comput 32(1):85–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-015-0400-7
Griffith AA (1921) Phenomena of rupture and flow in solids. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A221:163–198
Hatzor YH, Arzi AA, Zaslavsky Y (2004) Dynamic stability analysis of jointed rock slopes using the DDA method: King Herod’s Palace, Masada, Israel. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(5):813–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.02.002
He JM, Li SD, Yin YP, Qian HT (2010) Study of seismic response of colluvium accumulation slope by particle flow code. Granul Matter 12:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10035-010-0213-8
Hovius N, Meunier P (2012) Earthquake ground motion and patterns of seismically induced landsliding. In: Clague J, Stead D (eds) Landslides: types, mechanisms and modeling. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 24–36. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511740367.004
Huang R, Fan X (2013) The landslide story. Nat Geosci 6(5):321–411. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1806
Hungr O, Leroueil S, Picarelli L (2014) The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update. Landslides 11:167–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y
Itasca Consulting Group Inc (2014) Universal distinct element code user’s manual. Itasca Consulting Group Inc., Minneapolis
Koukouvelas I, Litoseliti A, Nikolakopoulos K (2015) Earthquake triggered rock falls and their role in the development of a rock slope: the case of Skolis Mountain, Greece. Eng Geol 191:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.03.011
Lan HX, Martin CD, Hu B (2010) Effect of heterogeneity of brittle rock on micromechanical extensile behavior during compression loading. J Geophys Res-Atmos 115(B01202):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JB006496
Latha GM, Arunakumari G (2010) Seismic stability analysis of a Himalayan rock slope. Rock Mech Rock Eng 43(6):831–843. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-010-0088-3
Li AJ, Lyamin AV, Merifield RS (2009) Seismic rock slope stability charts based on limit analysis methods. Comput Geotech 36(1–2):135–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2008.01.004
Li X, Tang H, Xiong C, Wartman J, Yin Y (2015) Dynamic centrifuge modelling tests for toppling rock slopes. In: Lollino G et al (eds) Engineering geology for society and territory—volume 2. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09057-3_130
Lin CH, Li HH, Weng MC (2018) Discrete element simulation of the dynamic response of a dip slope under shaking table tests. Eng Geol 243(4):168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.07.005
Liu HX, Xu Q (2011) Shaking table model test on slope dynamic deformation and failure. Rock Soil Mech 32(supplement 2). (in Chinese). DOI:https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2011.s2.028
Liu YQ, Li HB, Xiao KQ (2014) Seismic stability analysis of a layered rock slope. Comput Geotech 55(1):474–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.10.002
Majdi A, Amini M (2011) Analysis of geo-structural defects in flexural toppling failure. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48:175–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.11.007
Mavrouli O, Corominas J, Wartman J (2009) Methodology to evaluate rock slope stability under seismic conditions at Solade Santa Coloma, Andorra. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 9(6):1763–1773. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-9-1763-2009
Meguid MA, Saada O, Nunes MA (2008) Physical modeling of tunnels in soft ground: a review. Tunn Undergr Space Technol 23(2):185–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2007.02.003
Mineo S, Pappalardo G, Rapisarda F, Cubito A, Maria GD (2015) Integrated geostructural, seismic and infrared thermography surveys for the study of an unstable rock slope in the Peloritani Chain (NE Sicily). Eng Geol 195:225–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.06.010
Monnereau M, Yuen DA (2007) Topology of the postperovskite phase transition and mantle dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104(22):9156–9161. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0608480104
Nakajima S, Watanabe K, Shinoda M, et al. (2016) Consideration on evaluation of seismic slope stability based on shaking table model test. The 15th Asian Regional Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Tokyo. 1:957–962. Tokyo: Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3208/jgssp.JPN-100
Nichol S, Hungr O (2002) Brittle and ductile toppling of large rock slopes. Can Geotech J 39:1–16
Nishimura T, Nakamura K, Hiramatsu H, et al (2012) A study on toppling failure of rock slopes using small scale laboratory test. ISRM Regional Symposium-7th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium, Seoul. 1: 1219-1226. Texas: OnePetro
Pal S, Kaynia AM, Bhasin R, Paul DK (2012) Earthquake stability analysis of rock slopes: a case study. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(2):205–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0145-6
Regmi RK, Jung K, Nakagawa H et al (2017) Numerical analysis of multiple slope failure due to rainfall: based on laboratory experiments. Catena 150:173–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2016.11.007
Ruan XB, Sun SL, Liu WL (2013) Seismic stability of anchored rock slope using pseudo-dynamic method. Rock Soil Mech 34(S1):293–293 (In Chinese)
Schumm SA, Chorley RJ (1964) The fall of threatening rock. Am J Sci 262:1041–1064
Shinoda M, Nakajima S, Nakamura H, et al (2013) Shaking table test of large-scaled slope model subjected to horizontal and vertical seismic loading using E-Defense. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Paris. 1: 1-4. Tokyo: Japanese Geotechnical Society Special Publication
Stead D, Eberhardt E, Coggan JS (2006) Developments in the characterization of complex rock slope deformation and failure using numerical modelling techniques. Eng Geol 83(1–3):217–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.06.033
Wartman J, Seed RB, Bray JD (2005) Shaking table modeling of seismically induced deformations in slopes. J Geotech Geoenviron 131(5):610–622. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1090-0241(2005)131:5(610)
Zhang YB, Chen GQ, Wu J et al (2012) Numerical simulation of seismic slope stability analysis based on tension-shear failure mechanism. Geotechnical Engineering 43(2):19–28
Zhang Y, Chen G, Zheng L, Li Y, Wu J (2013) Effects of near-fault seismic loadings on run-out of large-scale landslide: a case study. Eng Geol 166:216–236
Zhang Y, Wang J, Xu Q, Chen G, Zhao JX, Zheng L, Han Z, Yu P (2015a) DDA validation of the mobility of earthquake-induced landslides. Eng Geol 194(8):38–51
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Chen G, Zheng L, Li Y (2015b) Effects of vertical seismic force on initiation of the Daguangbao landslide induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake. Soil Dyn Earthq Eng 73:91–102
Zheng Y, Chen CX, Zhu XX et al (2014) Node quasi-static stability analysis of rock slope under excavation blasting based on UDEC. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 33(Supplement 2):3932–3940. (in Chinese). https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2014.s2.068
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the editors and reviewers for their comments on our manuscript.
Funding
The present study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41502299, 41372306) as well as Research Planning of Sichuan Education Department, China (Grant No. 16ZB0105), State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection Independent Research Project (Grant No. SKLGP2016Z007), Chengdu University of Technology Young and Middle-Aged Backbone Program (Grant No. KYGG201720), Sichuan provincial science and technology department program (Grant No. 19YYJC2087), and China Scholarship Council Project (Grant No. 201708515101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
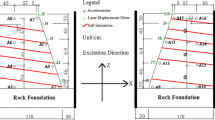
The published version of this article, unfortunately, contained error. A compass went unconverted in the upper-right corner of Figure 1. Given in this article is the correct image.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Lq., Ju, Np., Zhang, S. et al. Seismic wave propagation characteristic and its effects on the failure of steep jointed anti-dip rock slope. Landslides 16, 105–123 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1071-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-018-1071-4