Abstract
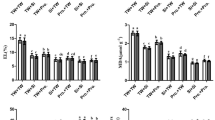
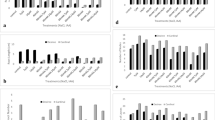
Changes in protein content and amino acid composition of faba bean (Vicia Faba L.) seeds in response to foliar spray of 6‑benzylaminopurine (BAP: 50 μM) and salicylic acid (SA: 1 mM) were investigated under different salinity levels (0, 4, 7, and 10 dS/m NaCl as control, low, moderate and high salinities, respectively). Application of these plant growth regulators (PGR), particularly BAP + SA diminished Na+ content of roots and leaves, while enhanced their K+ content and shoot growth. SA and BAP treatments were caused the highest and the lowest root growth and root/shoot ratio, respectively. Seed number and weight per plant were improved by foliar treatments, especially by BAP + SA. Isoleucine, leucine, lysine, threonine, alanine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine and tyrosine contents of seeds were increased, but valine content was decreased with increasing salinity. SA and BAP + SA enhanced isoleucine, leucine, lysine, valine as essential amino acids, and alanine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, serine and tyrosine as non-essential amino acids. SA also increased phenylalanine under high salinity. However, treatment with plant growth regulators reduced threonine, methionine, glycine and proline contents. These results suggest that exogenous SA can generally improve protein quantity and quality in faba bean seeds.
Zusammenfassung
Die Veränderungen des Proteingehalts und der Aminosäurezusammensetzung von Samen der Ackerbohne (Vicia Faba L.) als Reaktion auf die Blattspritzung mit 6‑Benzylaminopurin (BAP: 50 μM) und Salicylsäure (SA: 1 mM) wurden bei verschiedenen Salzgehalten (0, 4, 7 und 10 dS/m NaCl als Kontrolle, niedrige, moderate bzw. hohe Salzgehalte) untersucht. Die Anwendung dieser Pflanzenwachstumsregulatoren (PGR), insbesondere BAP + SA, verringerte den Na+-Gehalt von Wurzeln und Blättern, während ihr K+-Gehalt und das Triebwachstum gesteigert wurden. Die Behandlungen mit SA und BAP verursachten das höchste bzw. das niedrigste Wurzelwachstum und Wurzel/Spross-Verhältnis. Die Anzahl der Samen und das Gewicht pro Pflanze wurden durch Blattbehandlungen verbessert, insbesondere durch BAP + SA. Der Isoleucin‑, Leucin‑, Lysin‑, Threonin‑, Alanin‑, Asparaginsäure‑, Glutaminsäure‑, Serin- und Tyrosingehalt der Samen stieg an, während der Valingehalt mit zunehmendem Salzgehalt abnahm. SA und BAP + SA erhöhten Isoleucin, Leucin, Lysin und Valin als essenzielle Aminosäuren und Alanin, Asparaginsäure, Glutaminsäure, Serin und Tyrosin als nicht essenzielle Aminosäuren. SA erhöhte auch Phenylalanin bei hohem Salzgehalt. Die Behandlung mit Pflanzenwachstumsregulatoren verringerte jedoch den Gehalt an Threonin, Methionin, Glycin und Prolin. Diese Ergebnisse deuten darauf hin, dass exogene SA die Proteinmenge und -qualität in Ackerbohnensamen generell verbessern kann.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Ahmad R, Ashraf MY, Ashraf M, Waraich EA (2009) Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) response to drought stress at germination and seedling growth stages. Pak J Bot 41:647–654
Alghamdi SS (2009) Chemical composition of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) genotypes under various water regimes. Pak J Nutr 8:477–482
Apse MP, Blumwald E (2007) Na+ transport in plants. FEBS Lett 581:2247–2254
Atkins C, Beevers L (1990) Synthesis, transport and utilization of translocated solutes of nitrogen. In: Abrol YP (ed) Nitrogen in higher plants. John Wiley & Sons, New York, pp 223–295
Bulut F, Akıncı Ş (2010) The effect of salinity on growth and nutrient composition in broad bean (vicia faba L.) Seedlings. Fresen Environ Bull 19:2901–2910
Cao WH, Liu J, He XJ, Mu RL, Zhou HL et al (2007) Modulation of ethylene responses affects plant salt-stress responses. Plant Physiol 143:707–719
Dubay R, Pessarakli M (1995) Physiological mechanisms of nitrogen absorption and assimilation in plants under stressful conditions. In: Pessarakli M (ed) Handbook of plant and crop physiology. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 605–626
El-Nasharty AB, El-Nwehy SS, Rezk AI, Abou El-Nour EAA (2017) Role of kinetin in improving salt tolerance of two wheat cultivars. Biosci Res 14:1–8
Farhangi-Abriz S, Ghassemi-Golezan K (2018) How can salicylic acid and jasmonic acid mitigate salt toxicity in soybean plants? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:1010–1016
Farhangi-Abriz S, Ghassemi-Golezani K (2016) Improving amino acid composition of soybean under salt stress by salicylic acid and jasmonic acid. J Appl Bot Food Qual 89:243–248
Feng B, Zhang C, Chen T, Zhang X, Tao L et al (2018) Salicylic acid reverses pollen abortion of rice caused by heat stress. BMC Plant Biol 18:245
Forde BG, Lea PJ (2007) Glutamate in plants: metabolism, regulation, and signaling. J Exp Bot 58:2339–2358
Fountoulakis M, Lahm HW (1998) Hydrolysis and amino acid composition analysis of proteins. J Chromatogr A 826:109–134
Galili G, Amir R, Fernie AR (2016) The regulation of essential amino acid synthesis and accumulation in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:153–178
Ghanem ME, van Elteren J, Albacete A, Quinet M, Martínez-Andújar C et al (2009) Impact of salinity on early reproductive physiology of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) in relation to a heterogeneous distribution of toxic ions in flower organs. Funct Plant Biol 36:125–136
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Farhangi-Abriz S (2018) Foliar sprays of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid stimulate H+-ATPase activity of tonoplast, nutrient uptake and salt tolerance of soybean. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 166:18–25
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Lotfi R (2013) Influence of water stress and pod position on oil and protein accumulation in soybean seeds. Intl J Agron Plant Prod 4:2341–2345
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Lotfi R (2015) The impact of salicylic acid and silicon on chlorophyll a fluorescence in mung bean under salt stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 62:611–616
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Farhangi-Abriz S, Bandehagh A (2018) Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid alter physiological performance, assimilate mobilization and seed filling of soybean under salt stress. Acta Agric Slov 3:597–607
Ghassemi-Golezani K, Taifeh-Noori M, Oustan S, Moghaddam M, Seyyed-Rahmani S (2010) Oil and protein accumulation in soybean grains under salinity stress. Not Sci Biol 2:64–69
Gilbert GA, Gadush MV, Wilson C, Madore MA (1998) Amino acid accumulation in sink and source tissues of Coleus blumei Benth. during salinity stress. J Exp Bot 49:107–114
Grattan SR, Grieve CM (1989) Salinity-mineral nutrient relations in horticultural crops. Sci Hortic 78:127–157
Gunes A, Inal A, Alpaslan M, Eraslan F, Bagci EG et al (2007) Salicylic acid induced changes on some physiological parameters symptomatic for oxidative stress and mineral nutrition in maize (Zea mays L.) grown under salinity. J Plant Physiol 164:728–736
Hayat Q, Hayat S, Irfan M, Ahmad A (2010) Effect of exogenous salicylic acid under changing environment: a review. Environ Exp Bot 68:14–25
Jayakannan M, Bose J, Babourina O, Rengel Z, Shabala S (2015) Salicylic acid in plant salinity stress signalling and tolerance. Plant Growth Regul 76:25–40
Khan NA, Khan MIR, Asgher M, Fatma M, Masood A et al (2014) Salinity tolerance in plants: revisiting the role of sulfur metabolites. J Plant Biochem Physiol 2:1–8
Kiba T, Kudo T, Kojima M, Sakakibara H (2011) Hormonal control of nitrogen acquisition: roles of auxin, abscisic acid, and cytokinin. J Exp Bot 62:1399–1409
Laplaze L, Benkova E, Casimiro I (2007) Cytokinins act directly on lateral root founder cells to inhibit root initiation. Plant Cell 19:3889–3900
Liu Y, Liu H, Pan Q, Yang H, Zhan J et al (2009) The plasma membrane H+ATPase is related to the development of salicylic acid-induced thermotolerance in pea leaves. Planta 229:1087–1098
Liu Y, Wu X, Hou W, Li P, Sha W et al (2017) Structure and function of seed storage proteins in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) vol 7. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 1–14
Mabudi Bilasvar H, Ghassemi-Golezani K, Dabbagh Mohammadi Nassab A (2022) Seed development, oil accumulation and fatty acid composition of drought stressed rapeseed plants affected by salicylic acid and putrescine. Gesunde Pflanz. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-021-00612-z
Maruyama-Nakashita A, Nakamura Y, Yamaya T, Takahashi H (2004) A novel regulatory pathway of sulfate uptake in Arabidopsis roots: implication of CRE1/WOL/AHK4-mediated cytokinin-dependent regulation. Plant J 38:779–789
Mok MC (1994) Cytokinin and plant development. In: Mok DWS, Mok MC (eds) Cytokinin: chemistry, activity and function. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 155–166
Netondo GW, Onyango JC, Beck E (2004) Sorghum and salinity: I. Response of growth, water relations and ion accumulation to NACl salinity. Crop Sci 44:797–805
Neumann P (1997) Salinity resistance and plant growth revisited. Plant Cell Environ 20:1193–1198
Ngullie CR, Tank RV, Bhanderi DR (2014) Effect of salicylic acid and humic acid on flowering, fruiting, yield and quality of mango (Mangifera indica L.) cv. KESAR. Adv Res J Crop Improv 5:136–139
Olmos E, Hellin E (1996) Mechanisms of salt tolerance in a cell line of Pisum sativum: biochemical and physiological aspects. Plant Sci 120:37–45
Peoples MB, Atkins CA, Pate JS, Murray DR (1985) Nitrogen nutrition and metabolic interconversions of nitrogenous solutes in developing cowpea fruits. Plant Physiol 77:382–388
Poonia SR, Virmani SM, Bhumbla DR (1972) Effect of ESP (exchangeable sodium percentage) of soil on the yield, chemical composition and uptake of applied calcium by wheat. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 20:183–185
Pratelli R, Pilot G (2014) Regulation of amino acid metabolic enzymes and transporters in plants. J Exp Bot 65:5535–5556
Puvanitha S, Mahendran S (2017) Effect of salinity on plant height, shoot and root dry weight of selected rice cultivars. Sch J Agric Vet Sci 4:126–131
Ranade-Malvi U (2011) Interaction of micronutrients with major nutrients with special reference to potassium. Karnataka J Agric Sc 24:106–109
Rao R, Gnanam A (1990) Inhibition of nitrate and nitrite reductase activities by salinity stress in Sorghum vulgare. Phytochemistry 29:1047–1049
Rathke G, Christen WO, Diepenbrock W (2005) Effect of nitrogen source and rate on productivity and quality of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) grown in different crop rotation. Field Crop Res 94:103–113
Ruan YL, Patrick JW, Bouzayen M, Osorio S, Fernie AR (2012) Molecular regulation of seed and fruit set. Trends Plant Sci 17:656–665
Sakakibara H (2010) Cytokinin biosynthesis and metabolism. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones: biosynthesis, signal transduction, action. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 95–114
Sakakibara H, Takei K, Hirose N (2006) Interactions between nitrogen and cytokinin in the regulation of metabolism and development. Trends Plant Sci 11:440–448
Samea-Andabjadid S, Ghassemi-Golezani K, Nasrollahzadeh S, Najafi N (2018) Exogenous salicylic acid and cytokinin alter sugar accumulation, antioxidants and membrane stability of faba bean. Acta Biol Hung 69:86–96
Sedera AFA, Amany AL, El-Latif AAA, Bader A, Rezk SM (2010) Effect of NPK mineral fertilizer levels and foliar application with humic and amino acids on yield and quality of strawberry. Egypt J Applied Sci 25:154–169
Shabala S (2009) Salinity and programmed cell death: unraveling mechanisms for ion specific signalling. J Exp Bot 60:709–712
Shabala S, Pottosin I (2014) Regulation of potassium transport in plants under hostile conditions: implications for abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. Physiol Plant 151:257–279
Shewry PR, Napier JA, Tatham AS (1995) Seed storage proteins: structures and biosynthesis. Plant Cell 7:945–956
Shi J, Hou W, Liu Y (2013) Comparative study on seed storage protein of Faba bean. J Plant Genet Resour 13:304–307
Singh AP, Dixit G, Kumar A, Mishra S, Kumar N, Dixit S, Singh PK, Dwivedi S, Trivedi PK, Pandey V, Dhankher OP (2017) A protective role for nitric oxide and salicylic acid for arsenite phytotoxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 115:163–173
Szepesi A, Csiszar J, Bajkan S, Gemes K, Horvath F et al (2005) Role of salicylic acid pre-treatment on the acclimation of tomato plants to salt and osmotic stress. Acta Biol Szeged 49:123–125
Tammam AA (2003) Response of vicia faba plants to the interactive effect of sodium chloride salinity and salicylic acid treatment. Acta Agron Hung 51:239–248
Tunçtürk M, Tunçtürk R, Yildirim B, Çiftçi V (2011) Effect of salinity stress on plant fresh weight and nutrient composition of some Canola (Brassica napus L.) cultivars. Afr J Biotechnol 10:1827–1832
Ullah MA, Anwar M, Rana AS (2010) Effect of nitrogen fertilization and harvesting intervals on the yield and forage quality of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum L.) under mesic climate of Pothowar plateau. Pak J Agri Sci 47:231–234
Webb A, Cottage A, Wood T, Khamassi K, Hobbs D et al (2016) A SNP-based consensus genetic map for synteny based trait targeting in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Plant Biotechnol J 14:177–185
Weiss M, Manneberg M, Juranville JF, Lahm HW, Fountoulakis M (1998) Effect of the hydrolysis method on the determination of the amino acid composition of proteins. J Chromatogr A 795:263–275
Werner T, Motyka V, Strnad M, Schmulling T (2001) Regulation of plant growth by cytokinin. Plant Biol 98:10487–10492
Funding
We appreciate the financial support of this work by the University of Tabriz.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kazem Ghassemi-Golezani: Experimental design, supervision and manuscript writing. Samira Samea-Andabjadid: Experimental work, statistical analysis and writing
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K. Ghassemi-Golezani and S. Samea-Andabjadid declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghassemi-Golezani, K., Samea-Andabjadid, S. Exogenous Cytokinin and Salicylic Acid Improve Amino Acid Content and Composition of Faba Bean Seeds Under Salt Stress. Gesunde Pflanzen 74, 935–945 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00673-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00673-8