Abstract
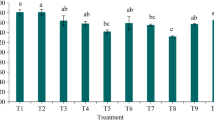
Tree–understory competition is one of the most important aspects that control tree growth after reforestation. The relationship between trees and the understory can be modified by improving acidic soils with lime and by fertilisation. This experiment aims to evaluate the effect of soil improvements on the pasture–tree relationship by liming and fertilisation on different dates in a Pinus radiata-reforested area. Both lime and sewage sludge improved soil fertility by increasing Ca and reducing Al in the soil. Initially, tree development was reduced by lime, which improved the establishment of competitive grasses. Tree growth in limed treatments did not initially respond to sludge inputs, likely because both tree and grass roots shared the same soil depth layer. Three years after establishment, the use of high doses of sewage sludge in limed plots caused a growth rate similar to the best treatments of unlimed plots, which grew with a poorly sown grass establishment. After 2 years of the experiment, the presence of Erica woody shrub diminished tree development. High doses of sewage sludge with lime, as well as high doses of sewage sludge without lime, applied in April and low doses of sewage sludge without lime added in early February improved tree growth. From a practical point of view, lime and sewage sludge dose close to 100 kg total N ha−1 should be recommended if a silvopastoral system is established, as it enhances pasture production and tree growth.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, London
Bailey JS (1995) Liming and nitrogen efficiency: some effects of increased calcium supply and increased soil pH on nitrogen recovery by perennial ryegrass. Commun Soil Sci Plan 26:1233–1246. doi:10.1080/00103629509369366
Benavides R, Douglas GB, Osoro K (2009) Silvopastoralism in New Zealand: review of effects of evergreen and deciduous trees on pasture dynamics. Agroforest Syst 76:327–350. doi:10.1007/s10457-008-9186-6
Benbi DK, Nieder R (2003) Handbook of processes and modelling in the soil-plant system. Haworth Press, New York
BOE (Spanish Official Bolletin) (01/11/1990) Real Decreto 1310/1990 29 de Octubre de 1990, que regula la utilización de los lodos de depuración (Royal Decree 1310/1990 29th October 1990, that regulates the use of sewage sludge. Ministerio Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación, Madrid
CEE Council of the European Union CEE (2005) Proposal for a Council regulation on support for rural development by the European agricultural fund for rural development (EAFRD) http://www.lebensministerium.at/filemanager/download/11314/,%1.92005.Accessed 09 Apr 2009
DOCE no. L (181 04/07/1986) Council directive 86/278/CEE of 12 June 1986 on the protection of the environment and, in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture. http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=CELEX:31986L0278:ES:HTML. Accessed 23 Apr 2010
EEA (European Environment Agency) (2006) European forest types: categories and types for sustainable forest management reporting and policy. EEA Technical Report No. 9, Copenhagen
Egiarte G, Arbestain MC, Alonso A, Ruiz-Romera E, Pinto M (2005) Effect of repeated applications of sewage sludge on the fate of N in soils under Monterey pine stands. Forest Ecol Manag 216:257–269. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2005.05.038
EPA (Environment Protection Agency) (1994) Land application of sewage sludge. A guide for land appliers on the requirements of the federal standards for the use of disposal of sewage sludge, 40 CFR Part 503
Guitián F, Carballás T (1976) Técnicas de análisis de suelos. Pico Sacro, Santiago de Compostela
Jonard M, André F, Giot P, Weissen F, Van der Perre R, Ponette Q (2010) Thirteen-year monitoring of liming and PK fertilization effects on tree vitality in Norway spruce and European beech stands. Eur J Forest R 129:1203–1211. doi:10.1007/s10342-010-0410-3
López-Díaz ML, Mosquera-Losada MR, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (2007) Lime, sewage sludge and mineral fertilization in a silvopastoral system developed in very acid soils. Agroforest Syst 70:91–101. doi:10.1007/s10457-007-9046-9
López-Díaz ML, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, Mosquera-Losada MR (2009) Influence of pasture botanical composition and fertilization treatments on tree growth. Forest Ecol Manag 257:1363–1372. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2008.12.001
Loué A (1988) Los microelementos en agricultura. Ediciones Mundi-Prensa, Madrid
Mehlich A (1985) Mehlich 3 soil test extractant: a modification of Mehlich 2 extractant. Commun Soil Sci Plan 15:1409–1416. doi:10.1080/00103628409367568
MMA (Spanish Environment Ministry) (1998) Tercer Inventario Forestal de España. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Dirección General de Conservación de la Naturaleza, Madrid
Montero MJ, Moreno G, Bertomeu M (2008) Light distribution in scattered-trees open woodlands in Western Spain. Agroforest Syst 73:233–244. doi:10.1007/s10457-008-9143-4
Mosquera-Losada MR, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, López-Díaz ML (2001) Sewage sludge fertilization of a silvopastoral system with pines in northwestern Spain. Agroforest Syst 53:1–10. doi:10.1023/A:1012239419829
Mosquera-Losada MR, Fernández-Núñez E, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (2006) Pasture, tree and soil Evolution in silvopastoral systems of Atlantic Europe. Forest Ecol Manag 232:135–145. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2006.05.057
Mosquera-Losada MR, Morán-Zuloaga D, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (2011) Effects of lime and sewage sludge on soil, pasture production and tree growth in a six year old Populus euroamericana (Dode) Guinier silvopastoral system. J Plant Nutr Soil Sc 174:145–153. doi:10.1002/jpln.200900231
Nair PKR, Gordon AM, Mosquera-Losada MR (2008) Agroforestry. In: Jorgensen SE, Fath BD (eds) Ecological Engineering, Encyclopedia of Ecology, 1st edn. Elsevier, Oxford, pp 101–110
Peri PL, Lucas RJ, Moot DJ (2007) Dry matter production, morphology and nutritive value of Dactylis glomerata growing under different light regimes. Agroforest Syst 70:63–79. doi:10.1007/s10457-007-9029-x
Peyraud JL, Mosquera-Losada MR, Delaby L (2004) Challenges and tools and develop efficient dairy systems based on grazing: how to meet animal performance and grazing management. Grassland Sci Europe 9:373–384
Prietzel J, Rehfuess KE, Stetter U, Pretzsch H (2008) Changes of soil chemistry, stand nutrition, and stand growth at two Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) sites in Central Europe during 40 years after fertilization, liming, and lupine introduction. Eur J Forest Res 127:43–61. doi:10.1007/s10342-007-0181-7
Richardson B (1993) Vegetation management practices in plantation forests of Australia and New Zealand. Can J Forest Res 23:1989–2005. doi:10.1139/x93-250
Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, Mosquera-Losada MR, Romero-Franco R et al (2005) Silvopastoral Systems as a forest fire prevention technique. In: Mosquera-Losada MR, McAdam J, Rigueiro-Rodríguez A (eds) Silvopastoralism and sustainable land management, 1 st edn. CAB International Publishing, Wallingford, pp 380–387
Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, Fernández-Núñez E, González-Hernández P et al (2009) Agroforestry systems in Europe: productive, ecological and social perspectives. In: Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, McAdam J, Mosquera-Losada MR (eds) Agroforestry in Europe. Advances in agroforestry, 1 st edn. Springer, Netherland, pp 43–66
Rigueiro-Rodríguez A, Castro S, Mosquera-Losada MR (2010) Effects of dose and period of sewage sludge application on soil, tree and pasture components in a Pinus radiata D. Don silvopastoral system. Agroforest Syst 79(2):237–247. doi:10.1007/s10457-010-9281-3
Rodríguez-Barreira S (2007) Crecimiento del arbolado, producción de pasto y efectos edáficos en sistemas silvopastorales fertilizados con lodos de depuradora. Efecto residual.Tesis Doctoral, Universidad de Santiago de Compostela
SAS (2001) User’s Guide. Statistics. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, USA
Sánchez-Rodríguez F, Rodríguez-Soalleiro R, Español E (2002) Influence of edaphic factor and tree nutritive status on the productivity of Pinus radiata D. plantations in northwestern Spain. Forest Ecol Manag 171:181–189. doi:10.1016/S0378-1127(02)00471-1
Smith SR (1996) Agricultural recycling of sewage sludge and the environment. CAB International, Wallingford
Smith DM, Larson BC, Kelty MJ, Ashton PMS (1997) The practice of silviculture: applied forest ecology. Wiley, New York
USDA (2001) Soil quality test kit, section II: background and interpretive guide for individual test. Soil Quality Institute, Washington
Wagner RG, Mohammed GH, Noland TL (1999) Critical period of interspecific competition for northern conifers associated with herbaceous vegetation. Can J Forest Res 29:890–897. doi:10.1139/cjfr-29-7-890
Wagner RG, Little KM, Richardson B, McNabb K (2006) The role of vegetation management for enhancing productivity of the world’s forests. Forestry 79:57–79. doi:10.1093/forestry/cpi057
Wheeler DM (1998) Investigation into the mechanisms causing lime responses in a grass/clover pasture on a clay loam soil. New Zeal J Agr Res 41:497–515. doi:10.1080/00288233.1998.9513333
Zutter BR, Miller JH (1998) Eleventh-year response of loblolly pine and competing vegetation to woody and herbaceous plant control on a Georgia flatwoods site. South J Appl For 22:85–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Merino.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosquera-Losada, M.R., Cuiña-Cotarelo, R. & Rigueiro-Rodríguez, A. Effect of understory vegetation management through liming and sewage sludge fertilisation on soil fertility and Pinus radiata D. Don growth after reforestation. Eur J Forest Res 130, 997–1008 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-011-0489-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-011-0489-1