Abstract
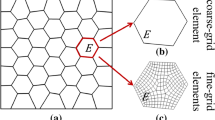
A steady-state thermal hybrid element model is proposed to calculate particle-reinforced composites divided by an improved quadtree mesh. The functional of hybrid flux finite element method (HF-FEM) is constructed using the weighted residual method. This functional independently assumes a heat flux field in the cell domain and a temperature field along cell boundaries. The construction of a universal heat flux function is put forward, which is approximated by a complete polynomial, and the temperature at the cell boundary is obtained by linear interpolation. Also, the hybrid stress finite element method (HS-FEM) is constructed to solve the thermal stress. In this paper, an improved quadtree grid that can accurately describe the shape of elliptical inclusions is built. By comparing several numerical examples with the traditional FEM, it is demonstrated that the hybrid element of the thermal analysis proposed in this paper is practical.



Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
We declare that the published parts of the figures and tables in this manuscript have been cited and explained, and the remaining parts are the original content of this manuscript and are trustworthy and reliable.
References
Trende A, Astrom BT, Nilsson G. Modeling of residual stresses in compression moulded glass-mat reinforced thermoplastics. Compos Part A. 2000;31(11):1241–54.
Talischi C, Paulino GH, Pereira A, Menezes IF. Polymesher: a general-purpose mesh generator for polygonal elements written in matlab. Struct Multidiscip Optim. 2012;45(3):309–28.
Golias N, Dutton R. Delaunay triangulation and 3d adaptive mesh generation. Finite Elem Anal Des. 1997;25(3):331–41.
Zhang Y, Hughes TJ, Bajaj CL. An automatic 3d mesh generation method for domains with multiple materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2010;199(5):405–15.
Mishra SC, Roy HK. Solving transient conduction and radiation heat transfer problems using the lattice Boltzmann method and the finite volume method. J Comput Phys. 2007;223(1):89–107.
Gela G, Dai JJ. Calculation of thermal fields of underground cables using the boundary element method. IEEE Trans Power Deliv. 2002;3(4):1341–7.
Wang H, Qin QH, Xiao Y. Special n-sided Voronoi fiber/matrix elements for clustering thermal effect in natural-hemp-fiber-filled cement composites. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2016;92:228–35.
Wang H, Zhao XJ, Wang JS. Interaction analysis of multiple coated fibers in cement composites by special n-sided interphase/fiber elements. Compos Sci Technol. 2015;118:117–26.
Cannarozzi AA, Momanyi FX, Ubertini F. A hybrid flux axisymmetric model for thermal analysis. Comput Struct. 2001;79(12):1187–201.
Cannarozzi AA, Momanyi FX, Ubertini F. A hybrid flux model for heat conduction problems. Int J Numer Meth Eng. 2000;47(10):1731–49.
Ren W, Yang ZJ, Sharma R, Zhang C, Withers PJ. Two dimensional x-ray ct image based meso-scale fracture modelling of concrete. Eng Fract Mech. 2015;133:24–39.
Partridge PW, Brebbia CA. The dual reciprocity boundary element method for the Helmholtz equation. Mech Electr Eng. 1990;16:311–26.
Wan DT, Hu DA, Yang G, Long T. A fully smoothed finite element method for analysis of axisymmetric problems. Eng Anal Bound Elem. 2016;72:78–88.
Tabarraei A, Sukumar N. Extended finite element method on polygonal and quadtree meshes. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng. 2008;197(5):425–38.
Mishra R, Burela RG, Pathak H. Crack interaction study in piezoelectric materials under thermo-electro-mechanical loading environment. Int J Mech Mater Des. 2019;15:379–412.
Nowak AJ. Application of the multiple reciprocity method for solving nonlinear problems. Adv Comput Methods Heat Transf. 1992;II(21):109–27.
Zheng YG, Zhang HB, Jun LV, Zhang HW. An arbitrary multi-node extended multiscale finite element method for thermoelastic problems with polygonal microstructures. Int J Mech Mater Des. 2020;16(1):35–56.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12062007 and 12072135).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ: methodology, software, theoretical derivation, writing-original manuscript. LW: software, writing-editing. RG: theoretical instruction, writing-a review. JT: writing—editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no commercial or associative interest representing a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhang, R., Guo, R. et al. Hybrid Finite Element Method Based on Polygon-Quadtree Meshes for Heat Transfer and Thermal Elastic Analysis. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 36, 745–753 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-023-00412-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10338-023-00412-0