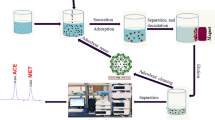
Abstract
A poly(NMA-ST-co-TAIC-EDMA) monolithic column was prepared by redox initiation method using N-methylolacrylamide (NMA) and styrene (ST) as co-monomers. The composite monolith was characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherm and was used as a solid phase extraction (SPE) absorbent for enrichment of β-sitosterol by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Under the optimum conditions for extraction and determination, the calibration equation was y = 1.02247x + 0.1766; the linear range was 0.015–0.75 mg mL−1 and the linear regression coefficient was 0.998. The limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ) were 0.006 mg mL−1 and 0.02 mg mL−1, respectively. The spiked recoveries of β-sitosterol in edible oil samples were 83.60–103.88%; precisions for intra-day and inter-day assays presented as relative standard deviations were less than 6.0% and 6.2%, respectively. The enrichment factor of β-sitosterol was 60 and the results showed that the monolithic column had high selectivity and good permeability as an on-line SPE absorbent for the enrichment and determination of β-sitosterol from edible oils.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asım O, Cesarettin A, Birgül VK, Serap Y, Cihan O, Ayse K, Ebru P, Jerzy Z (2017) Cardio-protective effects of phytosterol-enriched functional black tea in mild hypercholesterolemia subjects. J Funct Foods 31:311–319
Gylling H, Plat J, Turley S, Ginsberg HN, Ellegard L, Jessup W, Jones PJ, Lutjohann D, Maerz W, Masana L (2014) Plant sterols and plant stanols in the management of dyslipidaemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 232:346–360
Moreau RA, Whitaker BD, Hicks KB (2002) Phytosterols, phytostanols, and their conjugates in foods: structural diversity, quantitative analysis, and health-promoting uses. Prog Lipid Res 41:457–500
Bacchetti T, Masciangelo S, Bicchiega V, Bertoli E, Ferretti G (2011) Phytosterols, phytostanols and their esters: from natural to functional foods. Mediter J Nutr Metab 4:165–172
Liu SY, ANaErGuLi M (2012) Determination of β-sitosterol with chemical course and material applications in Jatropha seed oil by high performance liquid chromatography. Adv Mater Res 577:69–72
Micallef MA, Garg ML (2009) Beyond blood lipids: phytosterols, statins and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid therapy for hyperlipidemia. J Nutr Biochem 20:927–939
Franca M, Andrea P (2010) Phytosterols and cardiovascular health. Pharmacol Res 61:193–199
Naiyer S, Wajahatullah K, Shadab MD, Asgar A, Sundeep SS, Sadhana S, Faisal A, Al-Allaf ZA, Ibrahim AAI (2017) Phytosterols as a natural anticancer agent: current status and future perspective. Biomed Pharmacother 88:786–794
Vieno P, David GL, Tatu AM, Jari T, Anna-Maija L (2000) Plant sterols: biosynthesis, biological function and their importance to human nutrition. J Sci Food Agric 80:939–966
Klingberg S, Andersson H, Mulligan A, Bhaniani A, Welch A, Bingham S, Khaw KT, Andersson S, Ellegård L (2008) Food sources of plant sterols in the EPIC Norfolk population. Eur J Clin Nutr 62:695–703
Andrey S, Andrey B, Marcello L, Simone C, Vasil A (2017) Application of deep eutectic solvents in analytical chemistry: a review. Microchem J 135:33–38
Salgueiro-González N, Castiglioni S, Zuccato E, Turnes-Carou I, López-Mahía P, Muniategui-Lorenzo S (2018) Recent advances in analytical methods for the determination of 4-alkylphenols and bisphenol A in solid environmental matrices: a critical review. Anal Chim Acta 1024:39–51
Wajs-Bonikowska A, Stobiecka A, Bonikowski R, Krajewska A, Sikora M, Kula J (2017) A comparative study on composition and antioxidant activities of supercritical carbon dioxide, hexane and ethanol extracts from blackberry (Rubusfruticosus) growing in Poland. Soc Chem Ind 97:3576–3583
Hrabovski N, Sinadinović-Fišer S, Nikolovski B, Sovilj M, Borota O (2012) Phytosterols in pumpkin seed oil extracted by organic solvents and supercritical CO2. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 114:1204–1211
Azadmard-Damirchi S, Dutta PC (2006) Novel solid-phase extraction extraction method to separate 4-desmethyl-4-monomethyl and 4,4ʹ-dimethylsterols in vegetable oils. J Chromatogr A 1108:183–187
Płotka-Wasylka J, Szczepańska N, Guardia MDL, Namieśnik J (2016) Modern trends in solid phase extraction: new sorbent media. Trends Anal Chem 77:23–43
Płotka-Wasylka J, Szczepańska N, Guardia M, Namieśnik J (2015) Miniaturized solid-phase extraction techniques. Trends Anal Chem 73:19–38
Yolanda P, Mónica F, MariaJose R, Guillermina F (2007) Current trends in solid-phase-based extraction techniques for the determination of pesticides in food and environment. J Biochem Biophys Methods 70:117–131
Zhu T, Row KH (2010) Extraction and determination of β-sitosterol from Salicornia herbacea L. using monolithic cartridge. Chromatographia 71:981–985
Alghamdi E, Piletsky S, Piletska E (2018) Application of the bespoke solid-phase extraction protocol for extraction of physiologically-active compounds from vegetable oils. Talanta 189(1):157–165
Natália FT, Milena GM, Caio RS, Susanne R (2016) On-line solid phase extraction-ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry as a powerful technique for the determination of sulfonamide residues in soils. J Chromatogr A 1452:89–97
Georges G (2007) Monolithic columns in high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1168:101–168
Catalá-Icardo M, Torres-Cartas S, Meseguer-Lloret S, Gómez-Benito C, Carrasco-Correa E, Simó-Alfonso EF, Ramis-Ramos G, Herrero-Martínez JM (2017) Preparation of organic monolithic columns in polytetrafluoroethylene tubes for reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 960:160–167
Li XJ, Jia M, Zhao YX, Liu ZS, Akber Aisa H (2016) Preparation of phenylboronate affinity rigid monolith with macromolecular porogen. J Chromatogr A 1438:171–178
Seçmeler Ö, Üstündağ ÖG (2017) A rapid in-house validated GC-FID method for simultaneous determination of lipophilic bioactives in olive oil: squalene, α-tocopherol, and β-sitosterol. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 119(1):1–14
Martínez-Vidal JL, Garrido-Frenich A, Escobar-García MA, Romero-González R (2007) LC-MS determination of sterols in olive oil. Chromatographia 65(11–12):695–699
Ma SB, Zhang YR, Qu XL, Jin FY (2015) Determination of β-sitosterol content in ethnodrug guoshangye. Agric Sci Technol 16(11):2546–2548
Qiu FY, Ding L, Cao HY (2014) Determination of β-sitosterol in oils and fats by high performance liquid chromatography. Chin Oil Fat 39(7):91–94
Zhu T, Yoon C, Row K (2011) Solid-phase extraction of β-sitosterol from Salicornia herbacea L. using molecular imprinting polymer. Chin J Chem 29:1246–1250
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21575033, 21505030), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (Nos. H2016201221, B2018201270), and the Hebei Province Science and Technology Research Project (grant number QN 2016128).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Recent Trends in Solid-Phase Extraction for Environmental, Food and Biological Sample Preparation with guest editors Anna Laura Capriotti, Giorgia La Barbera, and Susy Piovesana.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Guo, B., Pang, X. et al. Simultaneous Determination and Enrichment of β-Sitosterol From Edible Oil Samples Using Poly(NMA-ST-co-TAIC-co-EDMA) Monolith as Sorbent with On-line SPE-HPLC. Chromatographia 82, 1285–1293 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3646-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10337-018-3646-6