Abstract
Object
To this day, no parameter can really monitor the progression of multiple sclerosis (MS). In this study, an index the skewness (S) derived from parameters calculated in diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been tested on MS patients for its ability to monitor the disease course.
Materials and methods
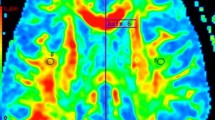
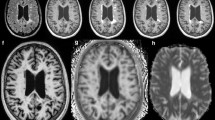
Eighteen patients underwent two examinations within 3 months consisting of a clinical evaluation (EDSS) and DTI acquisitions on a 1.5 T imager. Tensor was calculated thanks to“home-made” software. Mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA) histograms were described for normal-appearing white matter (NAWM) and gray matter (GM) of patients with S and also with usually indices peak position (pp) and peak height (ph) for the whole group of patients and for two separate groups according to their clinical status (EDSS ≤ 3 and EDSS > 3 at month 0).
Results
Although no significant clinical evolution is observed over 3 months, S in GM showed a significant shift for both MD/FA histograms towards abnormal values for the whole group of patients (p = 0.02/p = 0.04) and for the group with EDSS ≤ 3 (p = 0.04/p = 0.007), while ph and pp do not.
Conclusion
S in GM could be an alternative marker to monitor the disease course before the repercussion on the clinical score.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller DH, Grossman RI, Reingold SC, McFarland HF (1998) The role of magnetic resonance techniques in understanding and managing multiple sclerosis. Brain 121: 3–24
Lucchinetti CF, Bruck W, Rodriguez M, Lassman H (1996) Distinct patterns of multiple sclerosis pathology indicate heterogeneity in pathogenesis. Brain Pathol 6: 259–274
Barkhof F (1999) MRI in multiple sclerosis: correlation with expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Mult Scler 5: 283–286
Filippi M, Paty DW, Kappos L, Barkhof F, Compston DAS, Thompson AJ, Zhao GJ, Wiles CM, McDonald WI, Miller DH (1995) Correlations between changes in disability and T 2 weighted brain MRI activity in multiple sclerosis: A follow-up study. Neurology 45: 255–260
Van Walerveen MA, Lycklama A, Nijeholt GJ, Ader HJ, Jongen PJ, Polman CH, Castelijns JA, Barkhof F (2001) Hypointense lesions on T1-weighted spin-echo magnetic resonance imaging: relation to clinical characteristics in subgroups of patients with multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 58: 76–81
Basser PJ, Mattielo J, Le Bihan D (1994) Estimation of the effective self-diffusion tensor from the NMR spin echo. J Magn Reson B 103: 247–254
Tanner JE, Stejskal EO (1968) Restricted self-diffusion of protons in colloidal systems by the pulsed gradients spin-echo method. J Chem Phys 49: 1768–1777
Le Bihan D, Turner R, Pekar J, Moonen CTW (1991) Diffusion and perfusion imaging by gradient sensitization: design, strategy and significance. J Magn Reson Imaging 1: 7–8
Cleveland GG, Chang DC, Hazlewood CF, Rorschach HE (1976) Nuclear magnetic resonance measurement of skeletal muscle. Biophys J 16: 1043–1053
Chenevert TL, Brunberg JA, Pipe JG (1990) Anisotropic diffusion in human white matter: demonstration with MR techniques in vivo. Radiology 177: 401–405
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 111: 209–219
Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ (1996) Toward a quantitative assessment of diffusion anisotropy. Magn Reson Med 36: 893–906
Le Bihan D (1991) Molecular diffusion nuclear magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Q 7: 1–30
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, Chabriat H (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13: 534–546
Bammer R, Augustin M, Strasser-Fuchs S, Seifert T, Kapeller P, Stollberger R, Ebner F, Hartung HP, Fazekas F (2000) Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging for characterizing diffuse and focal white matter abnormalities in multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Med 44: 583–591
Castriota Scanderberg A, Fasano F, Hagberg G, Nocentini U, Filippi M, Caltagirone C (2003) Coefficient is more sensitive than fractional anisotropy in monitoring the progression of the irreversible tissue damage in focal non-active multiple sclerosis lesions. Am J Neuroradiol 24: 663–670
Filippi M, Ianucci G, Cercignani M, Rocca MA, Pratesi A, Comi G (2000) A quantitative study of water diffusion in multiple sclerosis and normal-appearing white matter using echo-planar imaging. Arch Neurol 57: 1017–1021
Filippi M, Cercignani M, Inglese M, Horsfield MA, Comi G (2001) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 56: 304–311
Werring DJ, Clark CA, Barker GJ, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (1999) Diffusion tensor imaging of lesions and normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 52: 1626–1632
Kidd D, Barkhof F, McConnell R, Algra PR, Allen IV, Revesz T (1999) Cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Brain 122: 17–26
Miki Y, Grossman RI, Udupa JK, Wei L, Kolson DL, Mannon LJ, Grossman M (1998) Isolated U-fiber involvement in MS: preliminary observations. Neurology 50: 1301–1306
Rovaris M, Filippi M, Minicucci L, Iannucci G, Santuccio G, Possa F, Comi G (2000) Cortical/subcortical disease burden and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Am J Neuroradiol 21: 402–408
Rovaris M, Bozzali M, Ianucci G, Ghezzi A, Caputo D, Montanari E, Bertolotto A, Bergamaschi R, Capra R, Mancardi GL, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M (2002) Assessment of normal-appearing white and gray matter in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. A diffusion-tensor magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol 59: 1406–1412
Bozzali M, Cercignani M, Sormani MP, Comi G, Filippi M (2002) Quantification of brain gray matter damage in different MS phenotypes by use of diffusion tensor MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol 23: 985–988
Rovaris M, Judica E, Gallo A, Benedetti B, Sormani MP, Caputo D, Ghezzi A, Montanari E, Bertolotto A, Mancardi G, Bergamaschi R, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M (2006) Grey matter damage predicts the evolution of primary progressive multiple sclerosis at 5 years. Brain 29: 2628–2634
Nusbaum AO, Tang CY, Buchsbaum MS, Wei TC, Atlas SW (2001) Regional and global changes in cerebral diffusion with normal aging. Am J Neuroradiol 22: 136–142
Grenier D, Pelletier D, Normandeau M, Newitt D, Nelson S, Goodkin DE, Majumdar S (2002) T2 relaxation time histograms in multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Imaging 20: 733–741
Tessa C, Gianelli M, Della Nave R, Lucetti C, Berti C, Ginestroni A, Bonuccelli U, Mascalchi M (2008) A whole-brain analysis in de novo Parkinson disease. Am J Neuroradiol 29: 674–680
Della Nave R, Foresti S, Pratesi A, Ginestroni A, Inzitari M, Salvadori E, Giannelli M, Diciotti S, Inzitari D, Mascalchi M (2007) Whole-brain histogram and voxel-based analyses of diffusion tensor imaging in patients with leukoaraiosis: correlation with motor and cognitive impairment. Am J Neuroradiol 28: 1313–1319
Lublin FD, Reingold SC (1996) Advisory committee on clinical trials of new agents in multiple sclerosis. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. Neurology 46: 907–911
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurological impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33: 1444–1452
Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark C, Le Bihan D, Bloch I (2002) Distortion correction and robust tensor estimation for MR diffusion imaging. Med Image Anal 6: 191–198
Jenkinson M, Smith S (2001) A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5: 143–156
Oreja-Guevara C, Rovaris M, Iannucci G, Valsasina P, Caputo D, Cavarretta R, Sormani MP, Ferrante P, Comi G, Filippi M (2005) Progressive gray matter damage in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. A longitudinal diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol 62: 578–584
Vrenken H, Pouwels PJW, Geurts JJG, Knol DL, Polman CH, Barkhof F, Castelijns JA (2006) Altered diffusion tensor in multiple sclerosis normal-appearing brain tissue: cortical diffusion changes seem related to clinical deterioration. J Magn Reson Imag 23: 628–636
Cassol E, Ranjeva JP, Ibarrola D, Mékies C, Manelfe C, Clanet M, Berry I (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging in multiple sclerosis: a tool for monitoring changes in normal-appearing white matter. Mult Scler 16: 37–50
Rovaris M, Gallo A, Valsasina P, Benedetti B, Caputo D, Ghezzi A, Montanari E, Sormani MP, Bertolotto A, Mancardi G, Bergamaschi R, Martinelli V, Comi G, Filippi M (2005) Short-term accrual of grey matter pathology in patients with progressive mutiple sclerosis: an in vivo study using diffusion tensor MRI. Neuroimage 24: 1139–1146
Li DKB (2003) Meta-analysis of conventional MRI data (abstract). Mult Scler 1: 218–222
Miller DH, Barkhof F, Frank JA, Parker GJM, Thompson AJ (2002) Measurement of atrophy in multiple sclerosis: pathological basis, methodological aspects and clinical relevance. Brain 125: 1676–1695
Rao SM, Leo GJ, Haughton VM, St. Aubin-Faubert P, Bernardin L (1989) Correlation of magnetic resonance imaging with neuropsychological testing in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 39: 161–166
Peterson JW, Bo L, Mork S, Chang A, Trapp BD (2001) Transected neuritis, apoptotic neurons and reduced inflammation in cortical multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50: 389–400
Cifelli A, Arridge M, Jezzard P, Esiri M, Palace J, Matthews PM (2002) Thalamic neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 52: 650–653
Chard DT, Griffin CM, McLean MA, Kapeller P, Kapoor R, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2002) Brain metabolites changes in cortical grey and normal-appearing white matter in clinically early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Brain 125: 2342–2352
Sarchielli P, Presciutti O, Tarducci R, Gobbi G, Alberti A, Pelliccioli GP, Chiarini P, Gallai V (2002) Localized (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy in mainly cortical gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 249: 902–910
Cercignani M, Bozzali M, Iannucci G, Comi G, Filippi M (2001) Magnetisation transfer ratio and mean diffusivity of normal appearing white and grey matter from patients with multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70: 311–317
Davies GR, Ramio-Torrenta L, Hadjiprocopis A, Chard DT, Griffin CM, Rashid W, Barker GJ, Kappor R, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2004) Evidence for grey matter MTR abnormality in minimally disabled patients with early relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75: 998–1002
Calabrese M, Atzori M, Bernardi V, Morra A, Romualdi C, Rinaldi L, McAuliffe MJM, Barachino L, Perini P, Fischl B, Battistin L, Gallo P (2007) Cortical atrophy is relevant in multiple sclerosis at clinical onset. J Neurol 254: 1212–1220
Tiberio M, Chard DT, Altmann DR, Davies G, Griffin CM, Rashid W, Sastre-Garriga J, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2005) Gray and white matter volume changes in early RRMS. A 2-year longitudinal study. Neurology 64: 1001–1007
Wheeler-Kingshott CAM, Boulby P, Symms MR, Barker GJ (2002) Optimised cardiac gating for high-resolution whole brain DTI on a standard scanner. Proc Intl Soc Magn Reson Med 10: 1118
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graulières, E., Lotterie, JA., Cassol, E. et al. Relevance of the skewness index in DTI exploration of multiple sclerosis. Magn Reson Mater Phy 22, 89–100 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0149-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0149-8