Abstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to compare a pure macromolecular contrast agent (Gd-DTPA-albumin) with a new protein-binding blood pool contrast agent (B22956/1) in terms of their capacity to investigate the microvasculature in an experimental model of mammary carcinoma.
Materials and methods
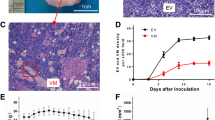
Tumors were induced by subcutaneous injection of 5 × 105 BB1 cells into the backs of 5–7 week-old female FVB/neuNT233 mice. The animals were observed using DCE-MRI when the longest diameter of the tumor was 10.2±2.0 mm. DCE-MRI experiments were carried out using B22956/1 and (24 h later) Gd-DTPA-albumin.
Results
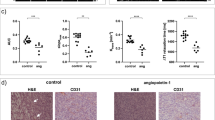
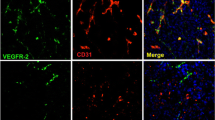
DCE-MRI data showed that vasculature in the tumor rim was characterized by greater fractional plasma volume and transendothelial permeability than vasculature in the tumor core as measured by both contrast agents. Permeability to Gd-DTPA-albumin in the tumor core was hardly measurable while permeability to B22956/1 was substantial. Histologically the tumor core showed areas of well vascularized, viable tissue surrounded by necrotic regions.
Conclusions
DCE-MRI experiments performed with B22956/1 are useful in the investigation of vasculature in those tumor regions that are characterized by low permeability to macromolecules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choyke PL, Dwyer AJ, Knopp MV (2003) Functional tumor imaging with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 17: 509–520
McDonald DM, Choyke PL (2003) Imaging of angiogenesis: from microscope to clinic. Nat Med 9: 713–725
Jeswani T, Padhani AR (2005) Imaging tumour angiogenesis. Cancer Imaging 5: 131–138
Preda A, Wielopolski PA, Ten Hagen TL, van Vliet M, Veenland JF, Ambagtsheer G, van Tiel ST, Vogel MW, Eggermont AM, Krestin GP, van Dijke CF (2004) Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI using macromolecular contrast media for monitoring the response to isolated limb perfusion in experimental soft-tissue sarcomas. Magn Reson Mater Phys 17: 296–302
Bhujwalla ZM, Artemov D, Natarajan K, Solaiyappan M, Kollars P, Kristjansen PE (2003) Reduction of vascular and permeable regions in solid tumors detected by macromolecular contrast magnetic resonance imaging after treatment with antiangiogenic agent TNP-470. Clin Cancer Res 9: 355–362
Preda A, van Vliet M, Krestin GP, Brasch RC, van Dijke CF (2006) Magnetic resonance macromolecular agents for monitoring tumor microvessels and angiogenesis inhibition. Invest Radiol 41: 325–331
Turetschek K, Preda A, Novikov V, Brasch RC, Weinmann HJ, Wunderbaldinger P, Roberts TP (2004) Tumor microvascular changes in antiangiogenic treatment: assessment by magnetic resonance contrast media of different molecular weights. J Magn Reson Imaging 20: 138–144
Turetschek K, Preda A, Floyd E, Shames DM, Novikov V, Roberts TP, Wood JM, Fu Y, Carter WO, Brasch RC (2003) MRI monitoring of tumor response following angiogenesis inhibition in an experimental human breast cancer model. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30: 448–455
Bjornerud A, Johansson LO, Ahlstrom HK (2001) Pre-clinical results with Clariscan (NC100150 Injection); experience from different disease models. Magn Reson Mater Phys 12: 99–103
Marzola P, Ramponi S, Nicolato E, Lovati E, Sandri M, Calderan L, Crescimanno C, Merigo F, Sbarbati A, Grotti A, Vultaggio S, Cavagna F, Lorusso V, Osculati F (2005) Effect of tamoxifen in an experimental model of breast tumor studied by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and different contrast agents. Invest Radiol 40: 421–429
Preda A, Novikov V, Moglich M, Turetschek K, Shames DM, Brasch RC, Cavagna FM, Roberts TP (2004) MRI monitoring of Avastin antiangiogenesis therapy using B22956/1, a new blood pool contrast agent, in an experimental model of human cancer. J Magn Reson Imaging 20: 865–873
Turetschek K, Floyd E, Helbich T, Roberts TP, Shames DM, Wendland MF, Carter WO, Brasch RC (2001) MRI assessment of microvascular characteristics in experimental breast tumors using a new blood pool contrast agent (MS-325) with correlations to histopathology. J Magn Reson Imaging 14: 237–242
Cavagna FM, Lorusso V, Anelli PL, Maggioni F, de Haen C (2002) Preclinical profile and clinical potential of gadocoletic acid trisodium salt (B22956/1), a new intravascular contrast medium for MRI. Acad Radiol 9(Suppl 2): S491–S494
Galie M, D’Onofrio M, Montani M, Amici A, Calderan L, Marzola P, Benati D, Merigo F, Marchini C, Sbarbati A (2005) Tumor vessel compression hinders perfusion of ultrasonographic contrast agents. Neoplasia 7: 528–536
Maisano F, Gozzini L, de Haen C (1992) Coupling of DTPA to proteins: a critical analysis of the cyclic dianhydride method in the case of insulin modification. Bioconjug Chem 3: 212–217
Marzola P, Degrassi A, Calderan L, Farace P, Crescimanno C, Nicolato E, Giusti A, Pesenti E, Terron A, Sbarbati A, Abrams T, Murray L, Osculati F (2004) In vivo assessment of antiangiogenic activity of SU6668 in an experimental colon carcinoma model. Clin Cancer Res 10: 739–750
Demsar F, Roberts TP, Schwickert HC, Shame DM, van Dijke CF, Mann JS, Saeed M, Brasch RC (1997) A MRI spatial mapping technique for microvascular permeability and tissue blood volume based on macromolecular contrast agent distribution. Magn Reson Med 37: 236–242
Daldrup H, Shames D, Wendland M, Okuhata Y, Link TM, Rosenau W, Lu Y, Brasch RC (1998) Correlation of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging with histological tumor grade: comparison of macromolecular and small molecular contrast media. Pediatr Radiol 28: 67–78
Marzola P, Degrassi A, Calderan L, Farace P, Nicolato E, Crescimanno C, Sandri M, Giusti A, Pesenti E, Terron A, Sbarbati A, Osculati F (2005) Early antiangiogenic activity of SU11248 evaluated in vivo by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in an experimental model of colon carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 15: 5827–5832
de Haën C, Anelli PL, Lorusso V, Morisetti A, Maggioni F, Zheng J, Uggeri F, Cavagna FM (2006) Gadocoletic acid trisodium salt (b22956/1): a new blood pool magnetic resonance contrast agent with application in coronary angiography. Invest Radiol 41: 279–291
Misselwitz B, Schmitt-Willich H, Ebert W, Frenzel T, Weinmann HJ (2001) Pharmacokinetics of Gadomer-17, a new dendritic magnetic resonance contrast agent. MAGMA 12: 128–134
Cheng HL, Wallis C, Shou Z, Farhat WA (2007) Quantifying angiogenesis in VEGF-enhanced tissue-engineered bladder constructs by dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI using contrast agents of different molecular weights. J Magn Reson Imaging 25: 137–145
Jain RK (2001) Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 46: 149–168
Raman V, Artemov D, Pathak AP, Winnard PT Jr, McNutt S, Yudina A, Bogdanov A Jr, Bhujwalla ZM (2006) Characterizing vascular parameters in hypoxic regions: a combined magnetic resonance and optical imaging study of a human prostate cancer model. Cancer Res 66: 9929–9936
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boschi, F., Marzola, P., Sandri, M. et al. Tumor microvasculature observed using different contrast agents: a comparison between Gd-DTPA-Albumin and B-22956/1 in an experimental model of mammary carcinoma. Magn Reson Mater Phy 21, 169–176 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0106-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10334-008-0106-6