Abstract
Objective
Very low density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) has been considered as a multiple function receptor due to binding numerous ligands, causing endocytosis and regulating cellular signaling. Our group previously reported that type II VLDLR overexpression in breast cancer tissues. The purpose of this study is to characterize type II VLDLR activities during cell migration using breast cancer cell lines.
Methods
Western blotting was used to test protein expression. Cell migration was analyzed by Scratch wound assay. The mRNA expression was tested by realtime-PCR. Reporter assay was to test the transcription activity.
Results
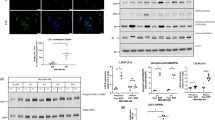
Scratch wound and Report assay indicated up-regulated VLDLR II expression promotes cell migration via activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. The target genes such as VEGF, MMP2 and MMP7 were upregulated in VLDLR II overexpressed cells. On the contrary, cells treated with TFPI had an inhibition effect of cell migration response to down-regulation of VLDLR II.
Conclusion
Type II VLDLR conferred a migration and invasion advantage by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway, then up-regulating VEGF, MMP2 and MMP7 in breast cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, McCarron P, Parkin DM. The changing global patterns of female breast cancer incidence and mortality. Breast Cancer Res, 2004, 6: 229–239.
Friedl P, Wolf K. Tumour-cell invasion and migration: diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer, 2003, 3: 362–374.
He L, Lu Y, Wang P, et al. Up-regulated expression of type II very low density lipoprotein receptor correlates with cancer metastasis and has a potential link to β-catenin in different cancers. BMC Cancer, 2010, 3, 10: 601.
Iijima H, Miyazawa M, Sakai J, et al. Expression and characterization of a very low density lipoprotein receptor variant lacking the O-linked sugar region generated by alternative splicing. J Biochem, 1998, 124: 747–755.
Webb JC, Patel DD, Jones MD, et al. Characterization and tissuespecific expression of the human ‘very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) receptor’ mRNA. Hum Mol Genet, 1994, 3: 531–537.
Elkin RG, Zhong Y. Assessment of reproductive function in mutant restricted ovulator carrier roosters. Poult Sci, 2002, 81: 1280–1282.
Chen T, Wu F, Chen FM, et al. Variations of very low-density lipoprotein receptor subtype expression in gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma cells with various differentiations. World J Gastroenterol, 2005, 11: 2817–2821.
Cai Z, Li F, Peng C, et al. Effect of insulin on the differential expression of VLDL receptor isoforms of SGC7901 cell and its biological implication. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2010, 30: 551–555.
Clevers H. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell, 2006, 127: 469–480.
Lai SL, Chien AJ, Moon RT. Wnt/Fz signaling and the cytoskeleton: potential roles in tumorigenesis. Cell Res, 2009, 19: 532–545.
Yang P, Liu Z, Wang H, et al. Enhanced activity of very low density lipoprotein receptor II promotes SGC7901 cell proliferation and migration. Life Sci, 2009, 27: 402–408.
Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer, 2002, 2: 563–572.
Di Y, Liu Z, Tian J, et al. TFPI or uPA-PAI-1 complex affect cell function through expression variation of type II very low density lipoprotein receptor. FEBS Lett, 2010, 584: 3469–3473.
Brown AM. Wnt signaling in breast cancer: have we come full circle? Breast Cancer Res, 2001, 3: 351–355.
Huang SM, Mishina YM, Liu S, et al. Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling. Nature, 2009, 461: 614–620.
Qian L, Mahaffey JP, Alcorn HL, et al. Tissue-specific roles of Axin2 in the inhibition and activation of Wnt signaling in the mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011, 108: 8692–8697.
Owen JR, Ashton A, Bliss JM, et al. Effect of radiotherapy fraction size on tumour control in patients with early-stage breast cancer after local tumour excision: long-term results of a randomised trial. Lancet Oncol, 2006, 7: 467–471.
Mego M, Mani SA, Cristofanilli M. Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in breast cancer-clinical applications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2010, 7: 693–701.
Nakamura Y, Yamamoto M, Kumamaru E. Very low-density lipoprotein receptor in fetal intestine and gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2000, 124: 119–122.
Liu Z, Li H, Li Y, et al. Up-regulation of VLDL receptor expression and its signaling pathway induced by VLDL and beta-VLDL. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci, 2009, 29: 1–7.
Wada Y, Homma Y, Nakazato K, et al. Effect of overexpression of very low density lipoprotein receptor on cell growth. Heart Vessels, 2000, 15: 74–80.
Tamai K, Semenov M, Kato Y, et al. LDL-receptor-related proteins in Wnt signal transduction. Nature, 2000, 407: 530–535.
Turashvili G, Bouchal J, Burkadze G, et al. Wnt signaling pathway in mammary gland development and carcinogenesis. Pathobiology, 2006, 73: 213–223.
Cowling VH, Cole MD. Turning the tables: Myc activates Wnt in breast cancer. Cell Cycle, 2007, 6: 2625–2627.
Paul S, Dey A. Wnt signaling and cancer development: therapeutic implication. Neoplasma, 2008, 55: 165–176.
Karow M, Popp T, Egea V, et al. Wnt signalling in mouse mesenchymal stem cells: impact on proliferation, invasion and MMP expression. J Cell Mol Med, 2009, 13: 2506–2520.
Thibeault S, Rautureau Y, Oubaha M, et al. S-nitrosylation of betacatenin by eNOS-derived NO promotes VEGF-induced endothelial cell permeability. Mol Cell, 2010, 39: 468–476.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Lu, Y. & Guo, J. Type II VLDLR promotes cell migration by up-regulation of VEGF, MMP2 and MMP7 in breast cancer cells. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 12, 374–378 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-013-1218-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-013-1218-7