Abstract
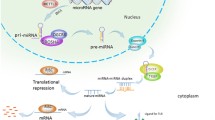
MicroRNAs (miRNAs), which contains approximately 22 nt, belong to a small endogenous, non-coding regulatory single-stranded RNA molecules. They are posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression and highly conserved in evolution. Many researches show that miRNAs involved in many processes, including tumor formation, cell proliferation and apoptosis and proliferation and metastasis of cancer cells. Among that, the relationship between miRNAs and lung cancer is one of the most focal areas for the researchers, because the abnormal expressions of miRNAs were significantly associated with the occurrence and development of lung cancer. The expression level of different miRNAs in lung cancer cells exist differences, compared with normal lung tissue cells, there are two classes of expression: over-expression level and low expression level. In this review, we focused on studying the mechanism of overexpression miRNAs in lung cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu QS, Wang XC. Gene silencing: mechanism and methods. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Publishing Press, 2005. 1–25.
Yates LA, Norbury CJ, Gilbert RI. The long and short of microRNA. Cell. 2013, 153: 516–519.
Xiao LB, Wu ZP, Feng R, et al. MicroRNAs and Cancer. Chinese-German J Clin Oncol, 2010, 9: 547–554.
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, et al. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science, 2001, 294: 853–858.
Xu P, Vernooy SY, Guo M, et al. The Drosophila microRNA Mir-14 suppresses cell death and is required for normal fat metabolism. Curr Biol, 2003, 13: 790–795.
Thompson BJ, Cohen SM. The Hippo pathway regulates the bantam microRNA to control cell proliferation and apoptosis in Drosophila. Cell, 2006, 26: 767–774.
Leaman D, Chen PY, Fak J, et al. Antisense-mediated depletion reveals essential and specific functions of microRNAs in Drosophila development. Cell, 2005, 121: 1097–1108.
Brennecke J, Hipfner DR, Stark A, et al. Bantam encodes a developmentally regulated microRNA that controls cell proliferation and regulates the proapoptotic gene hid in Drosophila. Cell, 2003, 113: 25–36.
Shi Y, Jin YX. MicroRNA and cell differentiation and development. Sci China, 2009, 52: 205–211.
Zhou F, Zhuang SM. MicroRNA and tumor. Chin Bull Life Sci (Chinese), 2008, 20: 207–212.
Kota J, Chivukula RR, O’Donnell KA, et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell, 2009, 137: 1005–1017.
Li YW, Vandenboom TG2nd, Wang ZW, et al. MiR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res, 2010, 70: 1486–1495.
Creighton CJ, Fountain MD, Yu ZF, et al. Molecular profiling uncovers a p53-associated role for micriRNA-31 in inhibiting the proliferation of serous ovarian carcinomas and other cancers. Cancer Res, 2010, 70: 1906–1915.
Luo H, Zhang H, Zhang Z, et al. Down-regulated miR-9 and miR-433 in human gastric carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2009, 28: 82–90.
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global Cancer Statistics. CA Cancer J Clin, 2011, 61: 69–90.
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM. Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med, 2008, 359: 1367–1380.
Xiong S, Zheng Y, Jiang P, et al. MicroRNA-7 inhibits the growth of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells through targeting BCL-2. Int J Biol Sci, 2011, 7: 805–814.
Xia XM, Jin WY, Shi RZ, et al. Clinical significance and the correlation of expression between Let-7 and K-ras in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett, 2010, 1: 1045–1047.
Chen Z, Zeng H, Guo Y, et al. miRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting c-Myc. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 29: 151–160.
Wiggins JF, Ruffino L, Kelnar K, et al. Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res, 2010, 70: 5923–5930.
Sun Y, Bai Y, Zhang F, et al. miR-126 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cells proliferation by targeting EGFL7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2010, 391: 1483–1489.
Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. miR-31: a crucial overseer of tumor metastasis and other emerging roles. Cell Cycle, 2010, 9: 2124–2129.
Liu X, Sempere LF, et al. microRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J Clin Invest, 2010, 120: 1298–1309.
Sun M, Liu XH, Li JH, et al. MiR-196a Is Upregulated in Gastric Cancer and Promotes Cell Proliferation by Downregulating p27 (kip1). Mol Cancer Ther, 2012, 11: 842–852.
Braig S, Mueller DW, Rothhammer T, et al. MicroRNA miR-196a is a central regulator of HOX-B7 and BMP4 expression in malignant melanoma. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2010, 67: 3535–3548.
Mueller DW, Bosserhoff AK. MicroRNA miR-196a controls melanomaassociated genes by regulating HOX-C8 expression. Int J Cancer, 2011, 129: 1064–1074.
Luthra R, Singh RR, Luthra MG, et al. MicroRNA-196a targets annexin A1: a microRNA-mediated mechanism of annexin A1 downregulation in cancers. Oncogene, 2008, 27: 6667–6678.
Liu XH, Lu KH, Wang KM, et al. microRNA-196a promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting HOXA5. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12: 348.
Gao W, Xu J, Liu L, et al. A systematic-analysis of predicted miR-21 targets identifies a signature for lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother, 2012, 66: 21–28.
Lan H, Lin C, Yuan H, et al. Overpression of miR-21 promotes proliferation and reduces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Chin J Oncol (Chinese), 2011, 33: 742–746.
Zhang JG, Wang JJ, Zhao F, et al. miR-21 represses tumor suppressor PTEN and promotes growth and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Chim Acta, 2010, 411: 846–852.
Seike M, Goto A, Okano T, et al. miR-21 is an EGFR-regulated antiapoptotic factor in lung cancer in never-smokers. Proc Natl Sci USA, 2009, 106: 12085–12090.
Zhu WY, Liu XG, He JY, et al. Over expression of members of the microRNA-183 family is a risk factor for lung cancer: A case control study. BMC Cancer, 2011, 11:193.
Babar IA, Czochor J, Steinmetz A, et al. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced miR-155 radio sensitizes hypoxic lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther, 2011, 12: 908–914.
Hutvagner G, Simard MJ, Mello CC, et al. Sequence-specific inhibition of small RNA function. PLoS Biol, 2004, 2: E98.
Luo XP, Zhang YZ, Zhao HF. The progress and application of antisense oligonucleotide technology. Acta Univ Med Second Shanghai (Chinese), 2000, 2: 185–187.
Meister G, Landthaler M, Dorsett Y, et al. Sequence-specific inhibition of microRNA- and siRNA-induced RNA silencing. RNA, 2004, 10: 544–550.
Tan Gana NH, Onuki T, Victoriano AF, et al. microRNAs in HIV-1 infection: an integration of viral and cellular interaction at the genomic level. Front Microbiol, 2012, 3: 306–317.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, L., Wu, Z., Chen, Y. et al. A study on the overexpression of microRNAs and lung cancer. Chin. -Ger. J. Clin. Oncol. 12, 443–447 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-013-1199-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10330-013-1199-6