Abstract
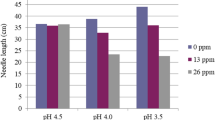
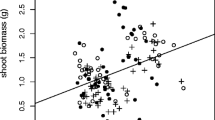
We investigated the short-term and long-term mitigation of Al toxicity by Ca and Mg in pot trials of Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don). We found that in the initial stages of treatment, Al toxicity at high Al concentration (5 mM) was mitigated by Ca and Mg through the stimulation of antioxidant enzyme activities in needles. However, growth reduction occurred after 11 months’ exposure to Al despite the coexistence of Ca and Mg. Growth reduction was related to Al3+ activity in solution rather than the concentration of Ca and Mg. Therefore, when considering the influence of soil acidification on Al toxicity in forest ecosystems, it is important to consider not only the potential for mitigation of Al toxicity by base cations, but also the potential for factors in the soil solution to change the chemical form of Al.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takami, C., Takenaka, C. & Tezuka, T. Mitigation of aluminum toxicity by calcium and magnesium in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica). J For Res 10, 9–14 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-004-0094-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10310-004-0094-y