Abstract
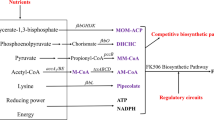
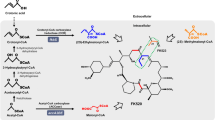
FK506, a secondary metabolite produced by Streptomyces tsukubaensis, is well known for its immunosuppressant properties to prevent rejection of transplanted organs and treat autoimmune diseases. However, the low titer of FK506 in the original producer strain limits the further industrialization efforts and restricts its clinical applications. To address this issue, a highly efficient method combined genome shuffling and dynamic fed-batch strategies was systematically performed in this work. Firstly, after five rounds of genome shuffling based on precursors and product resistances, a higher yielding strain TJ-P325 was successfully acquired, whose production reached 365.6 mg/L, 11-fold increase compared with the original strain. Then, the possible mechanism of different production capabilities between TJ-P325 and the wild type was explored through comparative gene expression analysis of key genes. Results showed that the transcription level of key genes was altered significantly in the mutant. Moreover, precursors addition enhanced the FK506 production by 28 %, as well as reduced the by-products biosynthesis. Finally, the disodium malonate and disodium methylmalonate dynamic fed-batch strategies dramatically led to the production of 514.5 mg/L in a 7.5-L bioreactor. These results demonstrated that genome shuffling and dynamic fed-batch strategies could be successfully applied to generate high-yield strains with value-added natural products during industrial microbial fermentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen D, Zhang Q, Zhang Q, Cen P, Xu Z, Liu W (2012) Improvement of FK506 production in Streptomyces tsukubaensis by genetic enhancement of the supply of unusual polyketide extender units via utilization of two distinct site-specific recombination systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(15):5093–5103. doi:10.1128/aem.00450-12
Chen X, Wei P, Fan L, Yang D, Zhu X, Shen W, Xu Z, Cen P (2009) Generation of high-yield rapamycin-producing strains through protoplasts-related techniques. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(3):507–512. doi:10.1007/s00253-009-1918-7
El-Enshasy HA, Mohamed NA, Farid MA, El-Diwany AI (2008) Improvement of erythromycin production by Saccharopolyspora erythraea in molasses based medium through cultivation medium optimization. Bioresour Technol 99(10):4263–4268. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2007.08.050
Fink D, Weißschuh N, Reuther J, Wohlleben W, Engels A (2002) Two transcriptional regulators GlnR and GlnRII are involved in regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 46(2):331–347. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03150.x
Floriano B, Bibb M (1996) afsR is a pleiotropic but conditionally required regulatory gene for antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 21(2):385–396. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.6491364.x
Gao H, Liu M, Liu J, Dai H, Zhou X, Liu X, Zhuo Y, Zhang W, Zhang L (2009) Medium optimization for the production of avermectin B1a by Streptomyces avermitilis 14-12A using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol 100(17):4012–4016. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.013
Gao Y, Fan Y, Nambou K, Wei L, Liu Z, Imanaka T, Hua Q (2014) Enhancement of ansamitocin P-3 production in Actinosynnema pretiosum by a synergistic effect of glycerol and glucose. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41(1):143–152. doi:10.1007/s10295-013-1374-3
Goranovic D, Blazic M, Magdevska V, Horvat J, Kuscer E, Polak T, Santos-Aberturas J, Martinez-Castro M, Barreiro C, Mrak P, Kopitar G, Kosec G, Fujs S, Martin JF, Petkovic H (2012) FK506 biosynthesis is regulated by two positive regulatory elements in Streptomyces tsukubaensis. BMC Microbiol 12:238. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-12-238
Guan N, Liu L, Shin H-d, Chen RR, Zhang J, Li J, Du G, Shi Z, Chen J (2013) Systems-level understanding of how Propionibacterium acidipropionici respond to propionic acid stress at the microenvironment levels: mechanism and application. J Biotechnol 167(1):56–63. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2013.06.008
Hopwood DA, Bibb MJ, Chater KF, Kieser T, Bruton CJ, Kieser HM, Lydiate DJ, Smith CP, Ward JM, Schrempf H (1985) Genetic manipulation of Streptomyces, a laboratory manual. John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Huang D, Li S, Xia M, Wen J, Jia X (2013) Genome-scale metabolic network guided engineering of Streptomyces tsukubaensis for FK506 production improvement. Microb Cell Fact 12:52. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-12-52
Huang D, Xia M, Li S, Wen J, Jia X (2013) Enhancement of FK506 production by engineering secondary pathways of Streptomyces tsukubaensis and exogenous feeding strategies. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40(9):1023–1037. doi:10.1007/s10295-013-1301-7
Jin Q, Jin Z, Zhang L, Yao S, Li F (2012) Probing the molecular mechanisms for pristinamycin yield enhancement in Streptomyces pristinaespiralis. Curr Microbiol 65(6):792–798. doi:10.1007/s00284-012-0233-1
Jin ZH, Xu B, Lin SZ, Jin QC, Cen PL (2009) Enhanced production of spinosad in Saccharopolyspora spinosa by genome shuffling. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 159(3):655–663. doi:10.1007/s12010-008-8500-0
Kim HS, Park YI (2007) Lipase activity and tacrolimus production in Streptomyces clavuligerus CKD 1119 mutant strains. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17(10):1638–1644
Kino T, Hatanaka H, Hashimoto M, Nishiyama M, Goto T, Okuhara M, Kohsaka M, Aoki H, Imanaka H (1987) FK-506, a novel immunosuppressant isolated from a Streptomyces. I. Fermentation, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological characteristics. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 40(9):1249–1255
Kosec G, Goranovič D, Mrak P, Fujs Š, Kuščer E, Horvat J, Kopitar G, Petković H (2012) Novel chemobiosynthetic approach for exclusive production of FK506. Metab Eng 14(1):39–46. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2011.11.003
Li S, Li F, Chen XS, Wang L, Xu J, Tang L, Mao ZG (2012) Genome shuffling enhanced ε-poly-l-lysine production by improving glucose tolerance of Streptomyces graminearus. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 166(2):414–423. doi:10.1007/s12010-011-9437-2
Lum AM, Huang J, Hutchinson CR, Kao CM (2004) Reverse engineering of industrial pharmaceutical-producing actinomycete strains using DNA microarrays. Metab Eng 6(3):186–196. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2003.12.001
Lv XA, Jin YY, Li YD, Zhang H, Liang XL (2013) Genome shuffling of Streptomyces viridochromogenes for improved production of avilamycin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(2):641–648. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4322-7
Martínez-Castro M, Salehi-Najafabadi Z, Romero F, Pérez-Sanchiz R, Fernández-Chimeno R, Martín J, Barreiro C (2013) Taxonomy and chemically semi-defined media for the analysis of the tacrolimus producer ‘Streptomyces tsukubaensis’. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(5):2139–2152. doi:10.1007/s00253-012-4364-x
Mo S, Ban YH, Park JW, Yoo YJ, Yoon YJ (2009) Enhanced FK506 production in Streptomyces clavuligerus CKD1119 by engineering the supply of methylmalonyl-CoA precursor. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36(12):1473–1482. doi:10.1007/s10295-009-0635-7
Mo S, Yoo YJ, Ban YH, Lee SK, Kim E, Suh JW, Yoon YJ (2012) Roles of fkbN in positive regulation and tcs7 in negative regulation of FK506 biosynthesis in Streptomyces sp. strain KCTC 11604BP. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(7):2249–2255. doi:10.1128/aem.06766-11
Otte B, Grunwaldt E, Mahmoud O, Jennewein S (2009) Genome shuffling in Clostridium diolis DSM 15410 for improved 1,3-propanediol production. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(24):7610–7616. doi:10.1128/aem.01774-09
Park JW, Jung WS, Park SR, Park BC, Yoon YJ (2007) Analysis of intracellular short organic acid-coenzyme A esters from actinomycetes using liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 42(9):1136–1147. doi:10.1002/jms.1240
Park SH, Choi SS, Sherman DH, Kim ES (2009) A global positive regulator afsR2 stimulates tautomycetin production via pathway-specific regulatory gene over-expression in Streptomyces sp. CK4412. Process Biochem 44(11):1298–1301. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2009.08.005
Parsons WH, Sigal NH, Wyvratt MJ (1993) FK-506—a novel immunosuppressant. Ann N Y Acad Sci 685(1):22–36. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb35847.x
Patnaik R, Louie S, Gavrilovic V, Perry K, Stemmer WPC, Ryan CM, del Cardayre S (2002) Genome shuffling of Lactobacillus for improved acid tolerance. Nat Biotechnol 20(7):707–712
Shin HY, Lee JY, Jung YR, Kim SW (2010) Stimulation of cephalosporin C production in Acremonium chrysogenum M35 by glycerol. Bioresour Technol 101(12):4549–4553. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.095
Sierra-Paredes G, Sierra-Marcuño G (2008) Ascomycin and FK506: pharmacology and therapeutic potential as anticonvulsants and neuroprotectants. CNS Neurosci Ther 14(1):36–46. doi:10.1111/j.1527-3458.2008.00036.x
Tiffert Y, Supra P, Wurm R, Wohlleben W, Wagner R, Reuther J (2008) The Streptomyces coelicolor GlnR regulon: identification of new GlnR targets and evidence for a central role of GlnR in nitrogen metabolism in actinomycetes. Mol Microbiol 67(4):861–880. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2007.06092.x
Turło J, Gajzlerska W, Klimaszewska M, Król M, Dawidowski M, Gutkowska B (2012) Enhancement of tacrolimus productivity in Streptomyces tsukubaensis by the use of novel precursors for biosynthesis. Enzyme Microb Technol 51(6–7):388–395. doi:10.1016/j.enzmictec.2012.08.008
Wang PM, Zheng DQ, Liu TZ, Tao XL, Feng MG, Min H, Jiang XH, Wu XC (2012) The combination of glycerol metabolic engineering and drug resistance marker-aided genome shuffling to improve very-high-gravity fermentation performances of industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Bioresour Technol 108:203–210. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2011.12.147
Xu B, Jin Z, Wang H, Jin Q, Jin X, Cen P (2008) Evolution of Streptomyces pristinaespiralis for resistance and production of pristinamycin by genome shuffling. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80(2):261–267. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1540-0
Yoon YJ, Choi CY (1997) Nutrient effects on FK-506, a new immunosuppressant, production by Streptomyces sp. in a defined medium. J Ferment Bioeng 83(6):599–603. doi:10.1016/s0922-338x(97)81145-2
Yu L, Pei X, Lei T, Wang Y, Feng Y (2008) Genome shuffling enhanced l-lactic acid production by improving glucose tolerance of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. J Biotechnol 134(1–2):154–159. doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2008.01.008
Yu S, Huang D, Wen J, Li S, Chen Y, Jia X (2012) Metabolic profiling of a Rhizopus oryzae fumaric acid production mutant generated by femtosecond laser irradiation. Bioresour Technol 114:610–615. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2012.03.087
Zhang J, Wang X, Diao J, He H, Zhang Y, Xiang W (2013) Streptomycin resistance-aided genome shuffling to improve doramectin productivity of Streptomyces avermitilis NEAU1069. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40(8):877–889. doi:10.1007/s10295-013-1280-8
Zhang YX, Perry K, Vinci VA, Powell K, Stemmer WPC, del Cardayre SB (2002) Genome shuffling leads to rapid phenotypic improvement in bacteria. Nature 415(6872):644–646
Zhao J, Li Y, Zhang C, Yao Z, Zhang L, Bie X, Lu F, Lu Z (2012) Genome shuffling of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for improving antimicrobial lipopeptide production and an analysis of relative gene expression using FQ RT-PCR. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39(6):889–896. doi:10.1007/s10295-012-1098-9
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National 973 Project of China (No. 2013CB733600), the Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21236005), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20936002), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 65141028) and the Programme of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (No. B06006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, W., Huang, D., Xia, M. et al. Improved FK506 production by the precursors and product-tolerant mutant of Streptomyces tsukubaensis based on genome shuffling and dynamic fed-batch strategies. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 1131–1143 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1450-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1450-3