Abstract
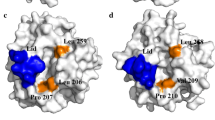
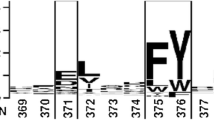
Applications of lipases are mainly based on their catalytic efficiency and substrate specificity. In this study, circular permutation (CP), an unconventional protein engineering technique, was employed to acquire active mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase Lip8p. A total of 21 mutant lipases exhibited significant shifts in substrate specificity. Cp128, the most active enzyme mutant, showed higher catalytic activity (14.5-fold) and higher affinity (4.6-fold) (decreased K m) to p-nitrophenyl-myristate (pNP-C14) than wild type (WT). Based on the three-dimensional (3D) structure model of the Lip8p, we found that most of the functional mutation occurred in the surface-exposed loop region in close proximity to the lid domain (S112–F122), which implies the steric effect of the lid on lipase activity and substrate specificity. The temperature properties of Cp128 were also investigated. In contrast to the optimal temperature of 45 °C for the WT enzyme, Cp128 exhibited the maximal activity at 37 °C. But it is noteworthy that there is no change in thermostability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aloulou A, Rodriguez JA, Puccinelli D et al (2007) Purification and biochemical characterization of the LIP2 lipase from Yarrowia lipolytica. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771:228–237
Bei G, Tao X, Jin PL et al (2011) Improving the catalytic activity of lipase LipK107 from Proteus sp. by site-directed mutagenesis in the lid domain based on computer simulation. J Mol Catal B Enzym 68:286–291
Brocca S, Secundo F, Ossola M, Alberghina L, Carrea G, Lotti M (2003) Sequence of the lid affects activity and specificity of Candida rugosa lipase isoenzymes. Protein Sci 12:2312–2319
Brzozowski AM, Derewenda U, Derewenda ZS (1991) A model for interfacial activation in lipases from the structure of a fungal lipase-inhibitor complex. Nature 351:491–494
Brzozowski DM, Lawson Derewenda S Z (1992) Catalysis at the interface: the anatomy of a conformational change in a triglyceride lipase. Biochem 31:1532–1541
Butler JS, Mitrea DM, Mitrousis G (2009) Structural and thermodynamic analysis of a conformationally strained circular permutant of barnase. Biochem 48(15):3497–3507
Cajal Y, Svendsen A, Girona V et al (2000) Interfacial control of lid opening in Thermomyces lanuginose lipase. Biochem 39:413–423
Charles G, Mohamed A, Mostafa B (2000) Cold-adapted enzymes: from fundamentals to biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 18(3):103–107
Cunningham BA, Hemperly JJ, Hopp TP et al (1979) Favin versus concanavalin A: circularly permuted amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci 76:3218–3222
Derewenda ZS, Derewenda U, Dodson GG (1992) The crystal and molecular structure of the Rhizomucor miehei triglyceride lipase at 1.9 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 227:818–839
Fickers P, Fudalej F, Dall MTL et al (2005) Identification and characterization of LIP7 and LIP8 genes encoding two extracellular triacylglycerol lipases in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Fungal Genet Biol 42(3):264–274
Fickers P, Marty A, Nicaud JM (2011) The lipases from Yarrowia lipolytica: genetics, production, regulation, biochemical characterization and biotechnological applications. Biotechnol Adv 29(6):632–644
Francesco S, Giacomo C, Chiara T et al (2006) The lid is a structural and functional determinant of lipase activity and selectivity. J Mol Catal B Enzym 39:166–170
Graf R, Schachman HK (1996) Random circular permutation of genes and expressed polypeptide chains: application of the method to the catalytic chains of aspartate transcarbamoylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci 93:11591–11596
Hennecke J, Sebbel P, Glockshuber R (1999) Random circular permutation of DsbA reveals segments that are essential for protein folding and stability. J Mol Biol 286:1197–1215
Hisano T, Kasuya K, Tezuka Y et al (2006) The crystal structure of polyhydroxybutyrate depolymerase from Penicillium funiculosum provides insights into the recognition and degradation of biopolyesters. J Mol Biol 356:993–1004
Iwakura M, Nakamura T (1998) Effects of the length of a glycine linker connecting the N- and C-termini of a circularly permuted dihydrofolate reductase. Protein Eng 11:707–713
Liu Z, Li XY, Chi Z et al (2008) Cloning, characterization and expression of the extracellular lipase gene from Aureobasidium pullulans HN2-3 isolated from sea saltern. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 94:245–255
Lo WC, Lyu PC (2008) CPSARST: an efficient circular permutation search tool applied to the detection of novel protein structural relationships. Genome Biol 9:R11
Joseph B, Ramteke PW, Thomas J (2008) Cold active microbial lipases: some hot issues and recent developments. Biotech Adv 26:457–470
Qian Z, Fields CJ, Lutz S (2007) Investigating the structural and functional consequences of circular permutation on lipase B from Candida antarctica. Chem Bio Chem 8:1989–1996
Qian Z, Horton JR, Cheng XD et al (2009) Structural redesign of lipase B from Candida Antarctica by circular permutation and incremental truncation. Mol Biol 393(1):191–201
Rotticci D, Rotticci-Mulder JC, Denman S et al (2001) Improved enantioselectivity of a lipase by rational protein engineering. Chem Bio Chem 2:766–770
Reitinger S, Yu Y, Wicki J, Ludwiczek M (2010) Circular Permutation of Bacillus circulans Xylanase: a Kinetic and Structural Study. Biochem 49(11):2467–2474
Ronald T, Piervincenzi Ashutosh Chilkoti (2004) Effect of genetic circular permutation near the active site on the activity and stability of an enzyme inhibitor. Biomol Eng 21:33–42
Seizaburo S, Masaji I, Harukazu F et al (2005) Creation of Rhizopus oryzae lipase having a unique oxyanion hole by combinatorial mutagenesis in the lid domain. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 68:779–785
Simon T, Jens H, Rudi G (1999) Circularly permuted variants of the green fluorescent protein. FEBS Lett 457:283–289
Skjot M, De Maria L, Chatterjee R et al (2004) Understanding the plasticity of the alpha/beta hydrolase fold: lid swapping on the Candida antarctica lipase B results in chimeras with interesting biocatalytic properties. Chem Bio Chem 10:520–527
Song HT, Jiang ZB, Ma LX (2006) Expression and purification of two lipases from Yarrowia lipolytica AS 2.1216. Protein Expr Purif 47:393–397
Suen WC, Zhang N, Xiao L et al (2004) Improved activity and thermostability of Candida antarctica lipase B by DNA family shuffling. Protein Eng Des Sel 17:133–140
Tougard P, Bizebard T, Ritco-Vonsovici M et al (2002) Structure of a circularly permuted phosphorglycerate kinase. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58:2018–2023
Weiner J, Bornberg-Bauer E (2006) Evolution of circular permutations in multidomain proteins. Mol Biol Evol 23:734–743
Wyder M, Bachmann HP, Puhan Z (1999) Role of selected yeasts in cheese ripening: an evaluation in foil wrapped raclette cheese. Lebensm Wiss Technol 32:333–343
Yu XW, Tan NJ, Xiao R et al (2012) Engineering a disulfide bond in the lid hinge region of Rhizopus chinensis lipase: increased thermostability and altered acyl chain length specificity. PLoS ONE 7(10):e46388. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046388
Zhang T, Bertelsen E, Benvegnu D et al (1993) Circular permutation of T4 lysozyme. Biochem 32:12311–12318
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants 2011AA090703 from the Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863), the Central Government and Public Research Institutes for Basic Research funds (20603022013016) and the China International Science and Technology Cooperation special items (2011DFA32200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheng, J., Ji, X.F., Wang, F. et al. Engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica lipase Lip8p by circular permutation to alter substrate and temperature characteristics. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 757–762 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1428-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-014-1428-1