Abstract
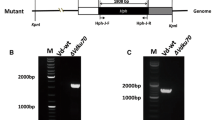
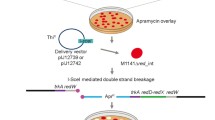
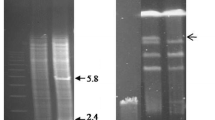
Streptomyces avermitilis is an industrially important soil bacterium known for production of avermectins, which are antiparasitic agents useful in animal health care, agriculture, and treatment of human infections. ku genes play a key role in the non-homologous end-joining pathway for repair of DNA double strand breaks. We identified homologs of eukaryotic ku70 and ku80 genes, termed ku1 and ku2, in S. avermitilis. Mutants with deletion of ku1, ku2, and both genes were constructed and their phenotypic changes were characterized. Deletion of ku genes had no apparent adverse effects on growth, spore formation, or avermectin production. The ku mutants, in comparison to wild-type strain, were slightly more sensitive to the DNA-damaging agent ethyl methanesulfonate, but not to UV exposure or to bleomycin. Gene targeting frequencies by homologous recombination were higher in the ku mutants than in wild-type strain. We conclude that ku-deleted strains will be useful hosts for efficient gene targeting and will facilitate functional analysis of genes in S. avermitilis and other industrially important bacterial strains.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSBs:
-
Double strand breaks
- HR:
-
Homologous recombination
- NHEJ:
-
Non-homologous end-joining
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- EMS:
-
Ethyl methanesulfonate
- MMS:
-
Methyl methanesulfonate
References
Aravind L, Koonin EV (2001) Prokaryotic double-strand break repair system Ku, novel domains in the Ku protein and prediction of a prokaryotic homologs of the eukaryotic DNA-end-binding protein. Genome Res 11:1365–1374
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Burg RW, Miller BM, Baker EE, Birnbaum J, Currie SA, Hartman R, Kong YL, Monaqhan RL, Olson G, Putter I, Tunac JB, Wallick H, Stapley EO, Oiwa R, Omura S (1979) Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 15:361–367
Chen Z, Wen J, Song Y, Wen Y, Li JL (2007) Enhancement and selective production of avermectin B by recombinants of Streptomyces avermitilis via intraspecific protoplast fusion. Chin Sci Bull 52:616–622
da Silva Ferreira ME, Kress MR, Savoldi M, Goldman MH, Härtl A, Heinekamp T, Brakhage AA, Goldman GH (2006) The akuB KU80 mutant deficient for nonhomologous end joining is a powerful tool for analyzing pathogenicity in Aspergillus fumigatus. Eukaryot Cell 5:207–211
Demain AL (1999) Pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites of microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 52:455–463
Gong C, Bongiorno P, Martins A, Stephanou NC, Zhu H, Shuman S, Glickman MS (2005) Mechanism of nonhomologous end-joining in mycobacteria: a low-fidelity repair system driven by Ku, ligase D and ligase C. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12:304–312
Haarmann T, Lorenz N, Tudzynski P (2008) Use of a nonhomologous end joining deficient strain (Deltaku70) of the ergot fungus Claviceps purpurea for identification of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene involved in ergotamine biosynthesis. Fungal Genet Biol 45:35–44
Ikeda H, Kotaki H, Tanaka H, Omura S (1988) Involvement of glucose catabolism in avermectin production by Streptomyces avermitilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 32:282–284
Inbar O, Kupiec M (1999) Homology search and choice of homologous partner during mitotic recombination. Mol Cell Biol 19:4134–4142
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Kobayashi H, Simmons LA, Yuan DS, Broughton WJ, Walker GC (2008) Multiple Ku orthologues mediate DNA non-homologous end-joining in the free-living form and during chronic infection of Sinorhizobium meliloti. Mol Microbiol 67:350–363
Krappmann S (2007) Gene targeting in filamentous fungi: the benefits of impaired repair. Fungal Biol Rev 21:25–29
Krappmann S, Sasse C, Braus GH (2006) Gene targeting in Aspergillus fumigatus by homologous recombination is facilitated in a nonhomologous end-joining-deficient genetic background. Eukaryot Cell 5:212–215
Li M, Chen Z, Zhang X, Song Y, Wen Y, Li JL (2010) Enhancement of avermectin and ivermectin production by overexpression of the maltose ATP-binding cassette transporter in Streptomyces avermitilis. Bioresour Technol 101:9228–9235
MacNeil DJ, Klapko LM (1987) Transformation of Streptomyces avermitilis by plasmid DNA. J Ind Microbiol 2:209–218
Meyer V, Arentshorst M, El-Ghezal A, Drews AC, Kooistra R, van den Hondel CA, Ram AF (2007) Highly efficient gene targeting in the Aspergillus niger kusA mutant. J Biotechnol 128:770–775
Moeller R, Stackebrandt E, Reitz G, Berger T, Rettberg P, Doherty AJ, Horneck G, Nicholson WL (2007) Role of DNA repair by nonhomologous-end joining in Bacillus subtilis spore resistance to extreme dryness, mono- and polychromatic UV, and ionizing radiation. J Bacteriol 189:3306–3311
Nayak T, Szewczyk E, Oakley CE, Osmani A, Ukil L, Murray SL, Hynes MJ, Osmani SA, Oakley BR (2006) A versatile and efficient gene-targeting system for Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 172:1557–1566
Ninomiya Y, Suzuki K, Ishii C, Inoue H (2004) Highly efficient gene replacements in Neurospora strains deficient for nonhomologous end-joining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:12248–12253
Omura S, Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Takahashi C, Shinose M, Takahashi Y, Horikawa H, Nakazawa H, Osonoe T, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M (2001) Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:12215–12220
Osipovich O, Durum SK, Muegge K (1997) Defining the minimal domain of Ku80 for interaction with Ku70. J Biol Chem 272:27259–27265
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Takahashi T, Masuda T, Koyama Y (2006) Enhanced gene targeting frequency in ku70 and ku80 disruption mutants of Aspergillus sojae and Aspergillus oryzae. Mol Gen Genomics 275:460–470
Takanhashi T, Masuda T, Koyama Y (2006) Identification and analysis of Ku70 and Ku80 homologs in the koji molds Aspergillus sojae and Aspergillus oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:135–143
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Van Dyck E, Stasiak AZ, Stasiak A, West SC (1999) Binding of double-strand breaks in DNA by human Rad52 protein. Nature 398:728–731
Villalba F, Collemare J, Landraud P (2008) Improved gene targeting in Magnaporthe grisea by inactivation of MgKU80 required for non-homologous end joining. Fungal Genet Biol 45:68–75
Weller GR, Kysela B, Roy R, Tonkin LM, Scanlan E, Della M, Devine SK, Day JP, Wilkinson A, d’Adda di Fagagna F, Devine KM, Bowater RP, Jeggo PA, Jackson SP, Doherty AJ (2002) Identification of a DNA nonhomologous end-Joining complex in bacteria. Science 297:1686–1689
William SD, Sunghan Y (1998) Interaction of Ku protein and DNA-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit with nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res 26:71551–71559
Zhang GT, Lukas H, Andre S (2009) Gene targeting in a nonhomologous end joining deficient Hypocrea jecorina. J Biotechnol 139:146–151
Zhao JL, Wen Y, Chen Z, Song Y, Li JL (2007) An adpA homologue in Streptomyces avermitilis is involved in regulation of morphogenesis and melanogenesis. Chin Sci Bull 52:623–630
Zhao XJ, Wang YX, Wang SW, Chen Z, Wen Y, Song Y (2009) Construction of a doramectin producing mutant from an avermectin-overproducing industrial strain of Streptomyces avermitilis. Can J Microbiol 55:1355–1363
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2009CB118905).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Chen, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Deletion of ku homologs increases gene targeting frequency in Streptomyces avermitilis . J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 917–925 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1097-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1097-x