Abstract
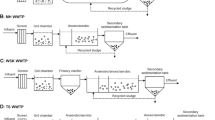
Phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) profiles in four full-scale activated sludge reactors (ASR1 ~ 4) treating municipal wastewater, South Korea, were monitored to evaluate the influence of influent water quality on microbial community structure (MCS) and the effect of the MCS on effluent water quality. In ASR1 ~ 3, PLFA profiles were very similar, regardless of the influent water quality and seasonal differences, and 16:17c/15:0iso2OH and 16:0 were dominant. PLFA profiles in ASR4 during summer and autumn were very similar to those in ASR1 ~ 3, but increases in specific fatty acids, 16:1ω5c, 11methyl18:1ω7c and 15:0iso3OH, were found in ASR4 during winter and spring, with relatively high total suspended solid (TSS) concentrations in the effluent. 16:1ω5c and 15:0iso3OH, possibly related with Flexibacter sp., caused a bulking problem in the activated sludge. The community diversity indices such as Shannon diversity and equability decreased in summer but increased in autumn in all the ASRs. Canonical correspondence analysis results suggested that the influent BOD concentration played the most important role in changing MCS, followed by influent TSS concentration. In addition, the TSS and total phosphorus concentrations in the effluent were significantly affected by the change of the MCS.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Al-Mutairi N (2007) Functional biodiversity of microbial communities in aerobic selector slaughterhouse wastewater. Water Environ Res 79:660–666
Aoi Y, Miyoshi T, Okamoto T, Tsuneda S, Hirata A, Kitayama A, Nagamune T (2000) Microbial ecology of nitrifying bacteria in wastewater treatment process examined by fluorescence in situ hybridization. J Biosci Bioeng 90:234–240
Barbusinski K (1991) Adaptation of activated sludge to laboratory research conditions. Environ Prot Eng 17:57–65
Bathes MH, Torbian A (1981) The effects of the COD: P ratio on laboratory activated sludge systems. Water Res 15:999–1004
Bitton G, Koopman B (1982) Tetrazolium reductionmalachite green method for assessing the viability of filamentous bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:964–966
Blackall LL (1999) Bulking. In: Seviour RJ, Blackall LL (eds) Microbiology of activated sludge. Kluwer, Netherlands
Coenye T, Laevens S, Gillis M, Vandamme P (2001) Genotypic and chemotaxonomic evidence for the reclassification of Pseudomonas woodsii (Smith 1911) Stevens 1925 as Burkholderia andropogonis (Smith 1911) Gillis et al. 1995. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:183–185
de los Reyes FL, Raskin L (2002) The role of filaments in activated sludge foaming relationship of mycolata levels to foaming initiation and stability. Water Res 36:445–459
Drenovsky RE, Elliott GN, Graham KJ, Scow KM (2004) Comparison of phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) and total soil fatty acid methyl esters (TSFAME) for characterizing soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1793–1800
Eichner CA, Erb RW, Timmis KN, Wagner-Dobler I (1999) Thermal gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of bioprotection from pollutant shocks in the activated sludge microbial community. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:102–109
Eschenhagen M, Schuppler M, Roske I (2003) Molecular characterization of the microbial community structure in two activated sludge systems for the advanced treatments of domestic effluents. Water Res 37:3224–3232
Frostegard A, Tunlid A, Baath E (1993) Phospholipid fatty acid composition, biomass, and activity of microbial communities from two soil types experimentally exposed to different heavy metals. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3605–3617
Kämpfer P, Young C, Sridhar KR, Arun AB, Lai WA, Shen FT, Rekha PD (2006) Transfer of [Flexibacter] sancti, [Flexibacter] filiformis, [Flexibacter] japonensis and [Cytophaga] arvensicola to the genus Chitinophaga and description of Chitinophaga skermanii sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:2223–2228
Logemann S, Schantl J, Bijvank S, Loosdrecht MV, Kuenen JG, Jetten M (1998) Molecular microbial diversity in a nitrifying reactor system without sludge retention. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 27:239–249
Molina-Munoz M, Poyatos JM, Sanchez-Peinado M, Hontoria E, Gonzalez-Lopez J, Rodelas B (2009) Microbial community structure and dynamics in a pilot-scale submerged membrane bioreactor aerobically treating domestic wastewater under real operation conditions. Sci Total Environ 407:3994–4003
Pave A (2006) By way of introduction: modelling living systems, their diversity and their complexity: some methodological and theoretical problems. C R Biol 329:3–12
Pholchan MK, Baptista JDC, Davenport RJ, Curtis TP (2010) Systematic study of the effect of operating variables on reactor performance and microbial diversity in laboratory-scale activated sludge reactors. Water Res 44:1341–1352
Pungrasmi W, Lee H, Yokota A, Ohta A (2008) Pseudomonas japonica sp. nov., a novel species that assimilates straight chain alkylphenols. J Gen Appl Microbiol 54:61–69
Shannon CR, Weaver W (1963) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Streichan M, Golecki JR, Schön G (1990) Polyphosphate-accumulating bacteria from sewage plants with different processes for biological phosphorus removal. FEMS Microbiol Lett 73:113–124
Tan TW, Ng HY, Ong SL (2008) Effect of mean cell residence time on the performance and microbial diversity of pre-denitrification submerged membrane bioreactors. Chemosphere 70:387–396
ter Braak CJF, Šmilauer P (2002) CANOCO Reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: Software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Microcomputer Power. Ithaca, NY, USA
Tyagi VK, Subramaniyan S, Kazmi AA, Chopra AK (2008) Microbial community in conventional and extended aeration activated sludge plants in India. Ecol Indic 8:550–554
Victorio L, Gilbride K, Allen D, Liss S (1996) Phenotypic fingerprinting of microbial communities in wastewater treatment systems. Water Res 30:1077–1086
Waldrop MP, Balser TC, Firestone MK (2000) Linking microbial community composition to function in a tropical soil. Soil Biol Biochem 32:1837–1846
Wilèn B, Onuki M, Hermansson M, Lumely D, Mino T (2007) Microbial community structure in activated sludge floc analysed by fluorescence in situ hybridization and its relation to floc stability. Water Res 42:2300–2308
Wu YC, Smith ED, Novak R (1982) Filterability of activated sludge in response to growth conditions. J WPCF 54:444–456
Xia S, Li J, Wang R (2008) Nitrogen removal performance and microbial community structure dynamics response to carbon nitrogen ratio in a compact suspended carrier biofilm reactor. Ecol Eng 32:256–262
Zhang Q, Suidan MT, Zhang K, Oerther DB, Venosa AD (2006) Comparison of biomass selection between a novel membrane bioreactor and activated sludge process. In: WEFTEC. 06, Conference Proceedings, Annual Technology Exhibition & Conference, 79th, Dallas, TX, United States
Zhuang WQ, Tay JH, Yi S, Tay STL (2005) Microbial adaptation to biodegradation of tert-butyl alcohol in a sequencing batch reactor. J Biotechnol 118:45–53
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by an RP-Grant 2009 from Ewha Womans University. The authors appreciate the government of Seoul City, South Korea, for supporting the influent and effluent water quality information of WWPTs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, T., Lee, EH., Kang, S. et al. Structure and dynamics of microbial community in full-scale activated sludge reactors. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39, 19–25 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-0994-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-011-0994-8