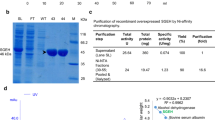
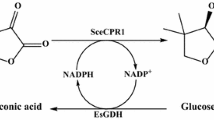
Abstract
A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase (P450SMO) from Rhodococcus sp. can catalyze asymmetric oxygenation of sulfides to S-sulfoxides. However, P450SMO-catalyzed biotransformations require a constant supply of NAD(P)H, the expense of which constitutes a great hindrance for this enzyme application. In this study, we investigated the asymmetric oxygenation of sulfide to S-sulfoxide using E. coli cells, which co-express both the P450SMO gene from Rhodococcus sp. and the glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) gene from Bacillus subtilis, as a catalyst. The results showed that the catalytic performance of co-expression systems was markedly improved compared to the system lacking GDH. When using recombinant E. coli BL21 (pET28a-P450-GDH) whole cell as a biocatalyst, NADPH was efficiently regenerated when glucose was supplemented in the reaction system. A total conversion of 100% was achieved within 12 h with 2 mM p-chlorothioanisole substrate, affording 317.3 mg/L S-sulfoxide obtained. When the initial sulfide concentration was increased to 5 mM, the substrate conversion was also increased nearly fivefold: S-sulfoxide amounted to 2.5 mM (396.6 mg/L) and the ee value of sulfoxide product exceeded 98%. In this system, the effects of glucose concentration and substrate concentration were further investigated for efficient biotransformation. This system is highly advantageous for the synthesis of optically pure S-sulfoxide.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mata EG (1996) Recent advances in the synthesis of sulfoxides from sulfides. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat Elem 117:231–286
Fernández I, Khiar N (2003) Recent developments in the synthesis and utilization of chiral sulfoxides. Chem Rev 103:3651–3705
Holland HL (1988) Chiral sulfoxidation by biotransformation of organic sulfides. Chem Rev 88:473–485
Holland HL (1992) Organic synthesis with oxidative enzymes. VCH, New York, p 255
Holland HL (2001) Biotransformation of organic sulfides. Nat Prod Rep 18:171–181
Holland HL, Brown FM, Kerridge A, Penkos P, Arensdor J (2003) Biotransformation of sulfides by Rhodococcus erythropolis. J Mol Catal B: Enzymatic 22:219–223
Werck-Reichhart D, Feyereisen R (2000) Cytochromes P450: a success story. Genome Biol 1:3003.1–3003.9
Hamman MABD, Haehner-Daniels SA, Wrighton AE, Rettie Hall SD (2000) Stereoselective sulfoxidation of sulindac sulfide by flavin-containing monooxygenases. Comparison of human liver and kidney microsomes and mammalian enzymes. Biochem Pharmacol 60:7–17
Fruetel J, Chang YT, Collins J, Loew G, Ortiz de Montellano PR (1994) Thioanisole sulfoxidation by cytochrome P450cam (CYP101): experimental and calculated absolute stereochemistries. J Am Chem Soc 116:11643–11648
Zhang JD, Li AT, Yang Y, Xu JH (2009) Sequence analysis and heterologous expression of a new cytochrome P450 monooxygenase from Rhodococcus sp. for asymmetric sulfoxidation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:615–624
Roberts GA, Grogan G, Greter A, Flitsch SL, Turner NJ (2002) Identification of a new class of cytochrome P450 from a Rhodococcus sp. J Bacteriol 184:3898–3908
Roberts GA, Celik A, Hunter DJ, Ost TW, White JH, Chapman SK, Turner NJ, Flitsch SL (2003) A self-sufficient cytochrome P450 with a primary structural organization that includes a flavin domain and a [2Fe-2S] redox center. J Biol Chem 278:48914–48920
Liu L, Schmid RD, Urlacher VB (2006) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a self-sufficient cytochrome P450 monooxygenase from Rhodococcus ruber DSM 44319. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:876–882
Itamar W, Daniel M (1989) Enzyme-catalyzed biotransformations through photochemical regeneration of nicotinamide cofactors. Enzyme Microb Technol 11:467–483
Chen G, Kayser MM, Milhovilovic MD, Mrstik ME, Martinez CA, Stewart JD (1999) Asymmetric oxidations at sulfur catalyzed by engineered strains that overexpress cyclohexanone monooxygenase. New J Chem 23:827–832
Xu ZN, Liu Y, Fang LM, Jiang XX, Jing KJ, Cen PL (2006) Construction of a two-strain system for asymmetric reduction of ethyl 4-chloro-3-oxobutanoate to (S)-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate ethyl ester. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:40–46
Xu ZN, Jing KJ, Liu Y, Cen PL (2007) High-level expression of recombinant glucose dehydrogenase and its application in NADPH regeneration. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:83–90
Yang W, Zhang L, Lu Z, Tao W, Zhai Z (2001) A new method for protein coexpression in Escherichia coli using two incompatible plasmids. Protein Expr Purif 22:472–478
Wang FH, Qu HJ, Zhang DW, Tian PF, Tan TW (2007) Production of 1, 3-propanediol from glycerol by recombinant E. coli using incompatible plasmids system. Mol Biotechnol 37:112–119
Omura T, Sato R (1964) The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes. I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature. J Biol Chem 239:2370–2378
Bradford M (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Li AT, Zhang JD, Xu JH, Lu WY, Lin GQ (2009) Isolation of Rhodococcus sp. ECU0066: a new sulfide monooxygenase producing strain for asymmetric sulfoxidation. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:551–556
Mikolajczyk M, Drabowicz J, Kielbasinski P (1997) Chiral sulfur reagents; Applications in asymmetric and stereoselective synthesis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kataoka M, Kita K, Wada M, Yasohara Y, Hasegawa J, Shimizu S (2003) Novel bioreduction system for the production of chiral alcohols. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62:437–445
Ernst M, Kaup B, Müller M, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H (2005) Enantioselective reduction of carbonyl compounds by whole-cell biotransformation, combining a formate dehydrogenase and a (R)-specific alcohol dehydrogenase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:629–634
Weckbecker A, Hummel W (2005) Glucose dehydrogenase for the regeneration of NADPH and NADH. Methods Biotechnol 17:225–237
Zambianchi F, Pasta P, Carrea G, Colonna S, Gaggero N, Woodley JM (2002) Use of isolated cyclohexanone monooxygenase from recombinant Escherichia coli as a biocatalyst for Baeyer-Villiger and sulfide oxidations. Biotechnol Bioeng 78:489–496
Alphand V, Carrea G, Wohlgemuth R, Furstoss R, Woodley JM (2003) Towards large-scale synthetic applications of Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenases. Trends Biotechnol 21:318–323
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant Nos. 20506037 & 20672037&20902023), Ministry of Science and Technology, P.R. China (grant Nos. 2006AA02Z205 & 2007AA02Z225) and China National Special Fund for State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering (grant No. 2060204).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, JD., Li, AT., Yu, HL. et al. Synthesis of optically pure S-sulfoxide by Escherichia coli transformant cells coexpressing the P450 monooxygenase and glucose dehydrogenase genes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 633–641 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0809-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-010-0809-3