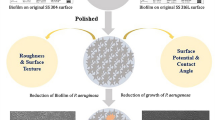
Abstract
Coating of stainless steel with diamond-like carbon or certain fluoropolymers reduced or almost eliminated adhesion and biofilm growth of Staphylococcus epidermidis, Deinococcus geothermalis, Meiothermus silvanus and Pseudoxanthomonas taiwanensis. These species are known to be pertinent biofilm formers on medical implants or in the wet-end of paper machines. Field emission scanning electron microscopic analysis showed that Staph. epidermidis, D. geothermalis and M. silvanus grew on stainless steel using thread-like organelles for adhesion and biofilm formation. The adhesion threads were fewer in number on fluoropolymer-coated steel than on plain steel and absent when the same strains were grown in liquid culture. Psx. taiwanensis adhered to the same surfaces by a mechanism involving cell ghosts on which the biofilm of live cells grew. Hydrophilic (diamond-like carbon) or hydrophobic (fluoropolymer) coatings reduced the adherence of the four test bacteria on different steels. Selected topographic parameters, including root-mean-square roughness (S q), skewness (S sk) and surface kurtosis (S ku), were analysed by atomic force microscopy. The surfaces that best repelled microbial adhesion of the tested bacteria had higher skewness values than those only slightly repelling. Water contact angle, measured (θ m) or roughness corrected (θ y), affected the tendency for biofilm growth in a different manner for the four test bacteria.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2001) In: Anonymous (ed) Image metrology, the scanning probe image processor, SPIP, User’s and reference guide. Copenhagen, Denmark
Arnold JW, Bailey GW (2000) Surface finishes on stainless steel reduce bacterial attachment and early biofilm formation: scanning electron and atomic force microscopy study. Poult Sci 79:1839–1845
Costerton JW, Montanaro L, Arciola CR (2005) Biofilm in implant infections: its production and regulation. Int J Artif Organs 28:1062–1068
Desjardins E, Beaulieu C (2003) Identification of bacteria contaminating pulp and a paper machine in a Canadian paper mill. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:141–145
Donlan RM, Costerton JW (2002) Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 15:167–193
Dunne WM Jr (2002) Bacterial adhesion: seen any good biofilms lately?. Clin Microbiol Rev 15:155–166
Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Rice EW, Greenberg AE (2005) In: Eaton AD, Clesceri LS, Rice EW and Greenberg AE (eds) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Federation, Port City Press, Baltimore, Maryland, USA, pp 9-34–9-36
Ekman J, Kosonen M, Jokela S, Kolari M, Korhonen P, Salkinoja-Salonen M (2007) Detection and quantitation of colored deposit-forming Meiothermus spp. in paper industry processes and end products. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:203–211
Ewald A, Gluckermann SK, Thull R, Gbureck U (2006) Antimicrobial titanium/silver PVD coatings on titanium. Biomed Eng Online 5:22
Geesey GG, Bryers JD (2000) Biofouling of engineered materials and systems. In: Bryers JD (ed) Biofilms II: process analysis and applications. Wiley, New York, pp 237–279
Götz F (2002) Staphylococcus and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 43:1367–1378
Heilmann C, Gerke C, Perdreau-Remington F, Götz F (1996) Characterization of Tn917 insertion mutants of Staphylococcus epidermidis affected in biofilm formation. Infect Immun 64:277–282
Johnson JR, Kuskowski MA, Wilt TJ (2006) Systematic review: antimicrobial urinary catheters to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infection in hospitalized patients. Ann Intern Med 144:116–126
Kalyon BD, Olgun U (2001) Antibacterial efficacy of triclosan-incorporated polymers. See comment. Am J Infect Control 29:124–125
Katsikogianni M, Spiliopoulou I, Dowling DP, Missirlis YF (2006) Adhesion of slime producing Staphylococcus epidermidis strains to PVC and diamond-like carbon/silver/fluorinated coatings. J Mater Sci Mater Med 17:679–689
Klueh U, Wagner V, Kelly S, Johnson A, Bryers JD (2000) Efficacy of silver-coated fabric to prevent bacterial colonization and subsequent device-based biofilm formation. J Biomed Mater Res 53:621–631
Kolari M (2003) Attachment mechanisms and properties of bacterial biofilms on non-living surfaces. Dissertationes Biocentri Viikki Universitatis Helsingiensis 12/2003, PhD Thesis University of Helsinki, Department of Applied Chemistry and Microbiology, Helsinki, Finland
Kolari M, Nuutinen J, Rainey FA, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2003) Colored moderately thermophilic bacteria in paper-machine biofilms. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 30:225–238
Kuosmanen T, Peltola M, Raulio M, Pulliainen M, Laurila T, Selin J-, Huopalainen H, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (2006) Effect of polarization on manganese biofouling of heat exchanger surfaces. In: Müller-Steinhagen H, Malayeri MR, Watkinson AP (eds) Proceedings of the 6th international conference on heat exchangers fouling and cleaning—challenges and opportunities. Engineering Conferences International, ECI Symposium Series, http://services.bepress.com/eci/heatexchanger2005/41/. RP2. 41, pp 283–288
Kwok CS, Wan C, Hendricks S, Bryers JD, Horbett TA, Ratner BD (1999) Design of infection-resistant antibiotic-releasing polymers: I. Fabrication and formulation. J Control Release 62:289–299
Labbate M, Zhu H, Thung L, Bandara R, Larsen MR, Willcox MD, Givskov M, Rice SA, Kjelleberg S (2007) Quorum-sensing regulation of adhesion in Serratia marcescens MG1 is surface dependent. J Bacteriol 189:2702–2711
Li C, Zhang X, Whitbourne R (1999) In vitro antimicrobial activity of a new antiseptic central venous catheter. J Biomater Appl 13:206–223
Mack D, Rohde H, Harris LG, Davies AP, Horstkotte MA, Knobloch JK (2006) Biofilm formation in medical device-related infection. Int J Artif Organs 29:343–359
Maki JS, Little BJ, Wagner P, Mitchell R (1990) Biofilm formation on metal surface in Antarctic waters. Biofouling 2:27–38
Palmer J, Flint S, Brooks J (2007) Bacterial cell attachment, the beginning of a biofilm. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:577–588
Peltonen J, Jarn M, Areva S, Linden M, Rosenholm JB (2004) Topographical parameters for specifying a three-dimensional surface. Langmuir 20:9428–9431
Raulio M, Pore V, Areva S, Ritala M, Leskela M, Linden M, Rosenholm JB, Lounatmaa K, Salkinoja-Salonen M (2006) Destruction of Deinococcus geothermalis biofilm by photocatalytic ALD and sol-gel TiO(2) surfaces. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:261–268
Rees EN, Tebbs SE, Elliott TS (1998) Role of antimicrobial-impregnated polymer and Teflon in the prevention of biliary stent blockage. J Hosp Infect 39:323–329
Rupp ME, Fey PD, Heilmann C, Götz F (2001) Characterization of the importance of Staphylococcus epidermidis autolysin and polysaccharide intercellular adhesin in the pathogenesis of intravascular catheter-associated infection in a rat model. J Infect Dis 183:1038–1042
Saarimaa C, Peltola M, Raulio M, Neu TR, Salkinoja-Salonen MS, Neubauer P (2006) Characterization of adhesion threads of Deinococcus geothermalis as Type IV Pili. J Bacteriol 188:7016–7021
Schierholz JM, Lucas LJ, Rump A, Pulverer G (1998) Efficacy of silver-coated medical devices. J Hosp Infect 40:257–262
Schierholz JM, Steinhauser H, Rump AF, Berkels R, Pulverer G (1997) Controlled release of antibiotics from biomedical polyurethanes: morphological and structural features. Biomaterials 18:839–844
Schooling SR, Beveridge TJ (2006) Membrane vesicles: an overlooked component of the matrices of biofilms. J Bacteriol 188:5945–5957
Söderquist B (2007) Surgical site infections in cardiac surgery: microbiology. APMIS 115:1008–1011
Stout KJ, Sullivan PJ, Dong WP, Mainsah E, Luo N, Mathia T, Zahouani H (1994) The development of methods for the characterization of roughness on three dimensions
Suihko ML, Sinkko H, Partanen L, Mattila-Sandholm T, Salkinoja-Salonen M, Raaska L (2004) Description of heterotrophic bacteria occurring in paper mills and paper products. J Appl Microbiol 97:1228–1235
Väisänen OM, Weber A, Bennasar A, Rainey FA, Busse HJ, Salkinoja-Salonen MS (1998) Microbial communities of printing paper machines. J Appl Microbiol 84:1069–1084
van de Belt H, Neut D, Schenk W, van Horn JR, van Der Mei HC, Busscher HJ (2001) Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation on different gentamicin-loaded polymethylmethacrylate bone cements. Biomaterials 22:1607–1611
Wenzel RN (1936) Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind Eng Chem 28:988–994
Acknowledgments
This work was funded as a part of the Technology Programme Clean Surfaces 2002–2006 (PINTA) by the Finnish Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation (Tekes). We also thank the Academy of Finland for the Centre of Excellence grant (53305, MSS), Helsinki University Viikki Science Library for excellent information services, the Faculty of Agriculture and Forestry Instrument Centre for technical support and Leena Steininger, Hannele Tukiainen and Tuula Suortti for many kinds of help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raulio, M., Järn, M., Ahola, J. et al. Microbe repelling coated stainless steel analysed by field emission scanning electron microscopy and physicochemical methods. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35, 751–760 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0343-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-008-0343-8