Abstract
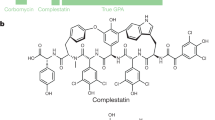
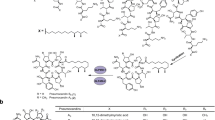
Daptomycin is a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces roseosporus. Cubicin® (daptomycin-for-injection) was approved in 2003 by the FDA to treat skin and skin structure infections caused by Gram-positive pathogens. Daptomycin is particularly significant in that it represents the first new natural product antibacterial structural class approved for clinical use in three decades. The daptomycin gene cluster contains three very large genes (dptA, dptBC, and dptD) that encode the nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS). The related cyclic lipopeptide A54145 has four NRPS genes (lptA, lptB, lptC, and lptD), and calcium dependent antibiotic (CDA) has three (cdaPS1, cdaPS2, and cdaPS3). Mutants of S. roseosporus containing deletions of one or more of the NRPS genes have been trans-complemented with dptA, dptBC, and dptD by inserting these genes under the control of the ermEp* promoter into separate conjugal cloning vectors containing ϕC31 or IS117 attachment (attP int) sites; delivering the plasmids into S. roseosporus by conjugation from Escherichia coli; and inserting the plasmids site-specifically into the chromosome at the corresponding attB sites. This trans-complementation system was used to generate subunit exchanges with lptD and cdaPS3 and the recombinants produced novel hybrid molecules. Module exchanges at positions d-Ala8 and d-Ser11 in the peptide have produced additional novel derivatives of daptomycin. The approaches of subunit exchanges and module exchanges were combined with amino acid modifications of Glu at position 12 and natural variations in lipid side chain starter units to generate a combinatorial library of antibiotics related to daptomycin. Many of the engineered strains produced levels of novel molecules amenable to isolation and antimicrobial testing, and most of the compounds displayed antibacterial activities.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arbeit RD, Maki D, Tally FP, Campanaro E, Eisenstein BI; Daptomycin 98-01 and 99-01 Investigators (2004) The safety and efficacy of daptomycin for the treatment of complicated skin and skin-structure infections. Clin Infect Dis 38:1673–1681
Baltz RH, McHenney MA, Cantwell CA, Queener SW, Solenberg PJ (1997) Application of transposition mutagenesis in antibiotic producing streptomycetes. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 71:179–187
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Boeck LD, Fukuda DS, Abbott BJ, Debono M (1988) Deacylation of A21978C, and acidic lipopeptide antibiotic complex, by Actinoplanes utahensis. J Antibiot 41:1085–1092
Boeck LD, Papiska HR, Wetzel RW, Mynderse JS, Fukuda DS, Mertz FP, Berry DM (1989) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: discovery, taxonomy, fermentation and HPLC. J Antibiot 43:587–593
Counter FT, Allen NE, Fukuda DS, Hobbs JN, Ott J, Ensminger PW, Mynderse JS, Preston DA, Wu CYE (1990) A54145, a new lipopeptide antibiotic complex: microbiological evaluation. J Antibiot 43:616–622
Datsenko KA, Wanner B (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
Debono M, Barnhart M, Carrell CB, Hoffman JA, Occolowitz JL, Abbott BJ, Fukuda DS, Hamill RL, Biemann K, Herlihy WC (1987) A21978C, a complex of new acidic antibiotics: isolation, chemistry, and mass spectral structure elucidation. J Antibiot 40:761–777
Debono M, Abbott BJ, Molloy RM, Fukuda DS, Hunt AH, Daupert VM, Counter FT, Ott JL, Carrell CB, Howard LC, Boeck LD, Hamill RL (1988) Enzymatic and chemical modifications of lipopeptide antibiotic A21978C: the synthesis and evaluation of daptomycin (LY146032). J Antibiot 41:1093–1105
Eisenstein BI (2004) Lipopeptides, focusing on daptomycin, for the treatment of Gram-positive infections. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 13:1159–1169
Grunewald J, Sieber SA, Mahlert C, Linne U, Marahiel MA (2004) Synthesis and derivatization of daptomycin: a chemoenzymatic route to acidic lipopeptide antibiotics. J Am Chem Soc 126:17025–17031
Hahn M, Stachelhaus T (2004) Selective interaction between nonribosomal peptide synthetases is facilitated by short communication-mediating domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15585–15590
Hill J, Siedlecki J, Parr I, Morytko M, Yu X, Zhang Y, Silverman J, Controneo N, Laganas V, Li T, Lai J-J, Keith D, Shimer G, Finn J (2003) Synthesis and biological activity of N-acylated ornithine analogues of daptomycin. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:4187–4191
Hojati Z, Milne C, Harvey B, Gordon L, Borg M, Flett F, Wilkinson B, Sidebottom PJ, Rudd BAM, Hayes MA, Smith CP, Micklefield J (2002) Structure, biosynthetic origin, and engineered biosynthesis of calcium-dependent antibiotics from Streptomyces coelicolor. Chem Biol 9:1175–1187
Hosted TJ, Baltz RH (1996). Mutants of Streptomyces roseosporus that express enhanced recombination within partially homologous genes. Microbiology 142:2803–2813
Hosted TJ, Baltz RH (1997) Use of rpsL for dominance selection and gene replacement in Streptomyces roseosporus. J Bacteriol 179:180–186
Huber FM, Pieper RL, Tietz AJ (1988) The formation of daptomycin by supplying decanoic acid to Streptomyces roseosporus cultures producing the antibiotic complex A21978C. J Biotechnol 7:283–292
Jung D, Rozek A, Okon M, Hancock REW (2004) Structural transitions as determinants of the action of the calcium-dependent antibiotic daptomycin. Chem Biol 11:949–957
Kreuzman AJ, Hodges RL, Swartling JR, Pohl TE, Ghag SK, Baker PJ, McGilvray D, Yeh WK (2000) Membrane-associated echinocandin B deacylase of Actinoplanes utahensis: purification, characterization, heterologous cloning and enzymatic deacylation reaction. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 24:173–180
Kuhstoss S, Huber M, Turner JR, Paschal JW, Rao RN (1996) Production of a novel polyketide through the construction of a hybrid polyketide synthase. Gene 183:231–236
Laganas V, Alder J, Silverman JA (2003) In vitro bactericidal activities of daptomycin against Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis are not mediated by inhibition of lipoteichoic acid biosynthesis. Antimicrob Agent Chemother 47:2682–2684
LaPlante KL, Rybak MJ (2004) Daptomycin—a novel antibiotic against Gram-positive pathogens. Expert Opin Pharmacother 5:2321–2331
Lautru S, Challis GL (2004) Substrate recognition by nonribosomal peptide synthase multi-enzymes. Microbiology 150:1629–1636
Liu F, Garneau S, Walsh CT (2004) Hybrid nonribosomal peptide-polyketide interfaces in epothilone biosynthesis: minimal requirements a N and C termini of EpoB for elongation. Chem Biol 11:1533–1542
McHenney MA, Baltz RH (1996) Gene transfer and transposition mutagenesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: mapping of insertions that influence daptomycin or pigment production. Microbiology 142:2363–2373
McHenney MA, Hosted TJ, DeHoff BS, Rosteck PR Jr, Baltz RH (1998) Molecular cloning and physical mapping of the daptomycin gene cluster from Streptomyces roseosporus. J Bacteriol 180:143–151
Miao V, Coeffet-LeGal M-F, Brian P, Brost R, Penn J, Whiting A, Martin S, Ford R, Parr I, Bouchard M, Silva CJ, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH (2005) Daptomycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: cloning and analysis of the gene cluster and revision of peptide stereochemistry. Microbiology 151:1507–1523
Miao V, Brost R, Chapple J, She K, Coeffet-LeGal M-F, Baltz RH (2005) The lipopeptide antibiotic A54145 biosynthetic gene cluster from Streptomyces fradiae. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol (this issue)
Naganawa H, Hamada M, Maeda K, Okami Y, Takeushi T (1968) Laspartomycin, a new anti-staphylococcal peptide. J Antibiot 21:55–62
O’Connor SE, Walsh CT, Liu F (2003) Biosynthesis of epothilone intermediates with alternative starter units: engineering polyketide-nonribosomal interfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed 42:3917–3921
Penn J, Li X, Whiting A, Brian P, Latif M, Gibson T, Silva CJ, Davies J, Miao V, Wrigley SK, Baltz RH (2005) Heterologous production of daptomycin in Streptomyces lividans. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol (this issue)
Raja A, LaBonte J, Kirkpatrick P (2003) Daptomycin. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:943–944
Rotondi KS, Gierasch LM (2005) A well-defined amphipathic conformation for the calcium-free cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic, daptomycin, in aqueous solution. Biopolymers 80:374–385
Schwarzer D, Finking R, Marahiel MA (2003) Nonribosomal peptides: from genes to products. Nat Prod Rep 20:275–287
Siedlecki J, Hill J, Parr I, Yu X, Morytko M, Zhang Y, Silverman J, Controneo N, Laganas V, Li T, Li J, Keith D, Shimer G, Finn J (2003) Array synthesis of novel lipodepsipeptide. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:4245–4249
Silverman JA, Perlmutter NG, Shapiro HM (2003) Correlation of daptomycin bactericidal activity and membrane depolarization in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agent Chemother 47:2538–2544
Tang L, Fu H, McDaniel R (1999) Formation of functional heterologous complexes using subunits from picromycin, erythromycin and oleandomycin polyketide synthases. Chem Biol 4:77–84
Tsuji SY, Cane DE, Khosla C (2001) Selective protein-protein interactions direct channeling of intermediates between polyketide synthase modules. Biochemistry 40:2326–2331
Vértesy L, Ehlers E, Kogler H, Kurz M, Meiwes J, Seibert G, Vogel M, Hammann P (2000) Friulimicins: novel lipopeptide antibiotics with peptidoglycan synthesis inhibiting activity from Actinoplanes friuliensis sp. nov. II. Isolation and structural characterization. J Antibiot 53:816–827
Wessels P, von Dohren H, Kleinkauf H (1996) Biosynthesis of acylpeptidolactones of the daptomycin type. A comparative analysis of peptide synthetases forming A21978C and A54145. Eur J Biochem 242:665–673
Wu N, Tsuji SY, Cane DE, Khosla C (2001) Assessing the balance between protein–protein interactions and enzyme–substrate interactions in the channeling of intermediates between polyketide synthase modules. J Am Chem Soc 123:6465–6474
Wu N, Cane DE, Khosla C (2002) Quantitative analysis of the relative contributions of donor acyl carrier proteins, acceptor ketosynthases, and linker regions to intermolecular transfer of intermediates in hybrid polyketide synthases. Biochemistry 41:5056–5066
Acknowledgements
We thank Cubist pharmaceuticals for supporting this work. We are indebted to Frank Tally, Barry Eisenstein, Skip Shimer, Dennis Keith, and Jeff Alder for providing support for this project at various stages of development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baltz, R.H., Brian, P., Miao, V. et al. Combinatorial biosynthesis of lipopeptide antibiotics in Streptomyces roseosporus . J IND MICROBIOL BIOTECHNOL 33, 66–74 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0030-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-005-0030-y