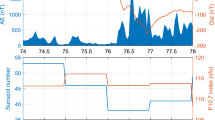
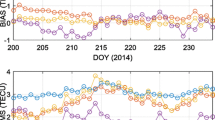
Abstract
We developed a parameterized ionospheric electron density model based on the IRI-2012 model by spherical harmonic expansions in the horizontal and empirical orthogonal functions in the vertical. Then, after assimilating the monthly multisource total electron content (TEC) data from ground-based GPS, LEO radio occultation (RO), and the oceanic altimeter during magnetically quiet time into the model, we reanalyzed the monthly global ionospheric electron density TEC and other key parameters such as foF2 and NmF2. Both the reanalyzed and IRI-2012 model results were compared to the TEC measurements, the monthly median foF2 in a middle-latitude ionosonde station, and the global TEC map from CODE. The comparisons showed that both the reanalyzed and IRI results are consistent with those observations and the reanalyzed results perform better than the IRI model. Furthermore, the reanalyzed results are also consistent with the retrieved maps of HmF2, NmF2, and TEC from COSMIC RO observations. In summary, our method can reanalyze the global TEC and electron density using multisource TEC data assimilated into our model and improve the performance of IRI model.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amerian Y, Hossainali MM, Voosoghi B, Ghaffari MR (2010) Tomographic reconstruction of the ionospheric electron density in term of wavelets. J Aerosp Sci Technol 7(1):19–29
Bilitza D, McKinnell L-A, Reinisch B, Fuller-Rowell T (2011) The international reference ionosphere today and in the future. J Geodesy 85(12):909–920. doi:10.1007/s00190-010-0427-x
Bust GS, Garner TW, Gaussiran TL (2004) Ionospheric data assimilation three-dimensional (IDA3D): a global, multisensor, electron density specification algorithm. J Geophys Res Space Phys 109(A11):A11312. doi:10.1029/2003JA010234
Codrescu M, Palo S, Zhang X, Fuller-Rowell T, Poppe C (1999) TEC climatology derived from TOPEX/POSEIDON measurements. J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys 61(3):281–298. doi:10.1016/S1364-6826(98)00132-1
Ding F, Wan W, Li Q, Zhang R, Song Q, Ning B, Liu L, Zhao B, Xiong B (2014) Comparative climatological study of large-scale traveling ionospheric disturbances over North America and China in 2011–2012. J Geophys Res Space Phys 119(1):519–529. doi:10.1002/2013JA019523
Dumont J, Rosmorduc V, Picot N, Desai S, Bonekamp H, Figa J, Lillibridge J, Scharroo R (2011), Using the (O)(I)GDR data. In: OSTM/Jason-2 products handbook. CNES:SALP-MU-M-OP-15815-CN, EUMETSAT:EUM/OPS-JAS/MAN/08/0041, JPL: OSTM-29-1237, NOAA/NESDIS: Polar Series/OSTM J400, pp 38–44
Foelsche U, Kirchengast G, Steiner A (eds) (2006) Atmosphere and climate: studies by occultation methods. Springer, Berlin
Fu L-L, Christensen EJ, Yamarone CA Jr., Lefebvre M, Ménard Y, Dorrer M, Escudier P (1994) TOPEX/POSEIDON mission overview. J Geophys Res Oceans 99(C12):24369–24381. doi:10.1029/94JC01761
Gao Y, Liu ZZ (2002) Precise ionosphere modeling using regional GPS network data. J Glob Position Syst 1(1):18–24
Gulyaeva T, Titheridge J (2006) Advanced specification of electron density and temperature in the IRI ionosphere–plasmasphere model. Adv Space Res 38(11):2587–2595. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.045
Hannachi A, Jolliffe I, Stephenson D (2007) Empirical orthogonal functions and related techniques in atmospheric science: a review. Int J Climatol 27(9):1119–1152. doi:10.1002/joc.1499
Howe BM, Runciman K, Secan JA (1998) Tomography of the ionosphere: four-dimensional simulations. Radio Sci 33(1):109–128. doi:10.1029/97RS02615
Imel DA (1994) Evaluation of the TOPEX/Poseidon dual-frequency ionosphere correction. J Geophys Res Oceans 99(C12):24895–24906. doi:10.1029/94JC01869
Jakowski N, Leitinger R, Angling M (2004) Radio occultation techniques for probing the ionosphere. Ann Geophys 47(2–3 Supp):1049–1066. doi:10.4401/ag-3285
Jee G, Lee H-B, Kim YH, Chung J-K, Cho J (2010) Assessment of GPS global ionosphere maps (GIM) by comparison between CODE GIM and TOPEX/Jason TEC data: ionospheric perspective. J Geophys Res Space Phys 115(A10):A10319. doi:10.1029/2010JA015432
Lambin J, Morrow R, Fu L-L et al (2010) The OSTM/Jason-2 mission. Mar Geod 33(S1):4–25. doi:10.1080/01490419.2010.491030
Lin C, Liu J, Fang T, Chang P, Tsai H, Chen C, Hsiao C (2007) Motions of the equatorial ionization anomaly crests imaged by FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC. Geophys Res Lett 34:L19101. doi:10.1029/2007GL030741
Liu Z, Gao Y, Skone S (2005) A study of smoothed TEC precision inferred from GPS measurements. Earth Planets Space 57(11):999–1007. doi:10.1186/BF03351880
Mannucci A, Wilson B, Yuan D, Ho C, Lindqwister U, Runge T (1998) A global mapping technique for GPS-derived ionospheric total electron content measurements. Radio Sci 33(3):565–582. doi:10.1029/97RS02707
Mautz R, Ping J, Heki K, Schaffrin B, Shum C, Potts L (2005) Efficient spatial and temporal representations of global ionosphere maps over Japan using B-spline wavelets. J Geod 78(11–12):660–667. doi:10.1007/s00190-004-0432-z
McNamara LF, Bishop GJ, Welsh JA (2011) Assimilation of ionosonde profiles into a global ionospheric model. Radio Sci 46(2):RS2006. doi:10.1029/2010RS004457
Mitchell CN, Spencer PS (2003) A three-dimensional time-dependent algorithm for ionospheric imaging using GPS. Ann Geophys 46(4):687–696. doi:10.4401/ag-4373
Navarra A, Simoncini V (eds) (2010) Empirical orthogonal functions. In: A guide to empirical orthogonal functions for climate data analysis. Springer, New York, pp 39–67. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-3702-2
Noll CE (2010) The crustal dynamics data information system: a resource to support scientific analysis using space geodesy. Adv Space Res 45(12):1421–1440. doi:10.1016/j.asr.2010.01.018
Orús R, Hernández-Pajares M, Juan J, Sanz J (2005) Improvement of global ionospheric VTEC maps by using kriging interpolation technique. J Atmos Solar-Terr Phys 67(16):1598–1609. doi:10.1016/j.jastp.2005.07.017
Razin MRG (2016) Development and analysis of 3D ionosphere modeling using base functions and GPS data over Iran. Acta Geod Geophys 51(1):95–111. doi:10.1007/s40328-015-0113-9
Schaer S (1999) Mapping and predicting the Earth’s ionosphere using the global positioning system. Dissertation, University of Bern
Wan W, Ding F, Ren Z, Zhang M, Liu L, Ning B (2012) Modeling the global ionospheric total electron content with empirical orthogonal function analysis. Sci China Technol Sci 55(5):1161–1168. doi:10.1007/s11431-012-4823-8
Yuan Y, Ou J (2002) Differential areas for differential stations (DADS): a new method of establishing grid ionospheric model. Chin Sci Bull 47(12):1033–1036. doi:10.1007/BF02907577
Yue X, Wan W, Liu L, Zheng F, Lei J, Zhao B, Xu G, Zhang S-R, Zhu J (2007) Data assimilation of incoherent scatter radar observation into a one-dimensional midlatitude ionospheric model by applying ensemble Kalman filter. Radio Sci 42(6):RS6006. doi:10.1029/2007RS003631
Yue X, Schreiner WS, Hunt DC, Rocken C, Kuo Y-H (2011) Quantitative evaluation of the low Earth orbit satellite based slant total electron content determination. Space Weather 9(9):S09001. doi:10.1029/2011SW000687
Yue X, Schreiner WS, Kuo Y-H et al (2012) Global 3-D ionospheric electron density reanalysis based on multisource data assimilation. J Geophys Res Space Phys 117(A9):A09325. doi:10.1029/2012JA017968
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the use of data from the Chinese Meridian Project (CMP, http://www.meridianproject.ac.cn). We thank the COSMIC Data Analysis and Archive Center of UCAR for providing the reprocessed and post-processed LEO RO TEC and profiles of electron density. CODE GIM data were acquired from the NASA Earth Science Data Systems and archived and distributed by the Crustal Dynamics Data Information System (CDDIS). The ground-based GPS data were obtained mainly from CDDIS, and additionally from the Scripps Orbit and Permanent Array Center's California Spatial Reference Center (SOPAC/CSRC), the Crustal Movement Observation Network of China (CMONOC) and CMP. Jason-1 and Jason-2 altimeter data were downloaded from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Oceanographic Data Center (NOAA/NODC) data centers, respectively. The IRI software code was obtained from the solar–terrestrial models archive of NASA’s Space Physics Data Facility. The solar and geomagnetic activity indices were obtained from NOAA’s National Geophysics Data Center (NGDC). The foF2 data were accessed from the Space Physics Interactive Data Resource (SPIDR) of the NGDC. We acknowledge the support by the Thousand Young Talents Program of China. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (41131066, 41321003, 41404127, and 41404128), project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015T80130), project supported by the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories, National Important Basic Research Project (2011CB811405), and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZZD-EW-01-2). We thank two anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments which have greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
She, C., Wan, W., Yue, X. et al. Global ionospheric electron density estimation based on multisource TEC data assimilation. GPS Solut 21, 1125–1137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0580-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0580-7