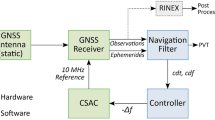
Abstract
Correctly fixing carrier phase integer ambiguities is a prerequisite to achieve high-precision positioning solutions from global navigation satellite system (GNSS). However, for the single-frequency dynamic users, a low ambiguity resolution (AR) success rate is usually associated with the small number of visible satellites. It is expected that the instantaneous single-frequency AR performance will be significantly improved by combining the observations from both global positioning system (GPS) and Chinese BeiDou navigation satellite system (BDS) for enhanced geometric strength. We develop an inertially aided AR technique using single-frequency GPS/BDS observations. With the addition of inertial navigation system (INS) measurements, a highly reliable fixing of ambiguities right after the GNSS signal blockages is possible because of the improved accuracy of the float ambiguities based on the calibrated inertial navigation solutions before the GNSS signal blockages. In addition, a new partial ambiguity resolution (PAR) technique is proposed, which is of great benefit when full ambiguity resolution fails under challenging conditions. The subset of ambiguities is ordered according to the maximum rounding fixing rate ordering method. An a priori decorrelation procedure is applied to the original observations that aim to obtain an optimal subset ordering. A further AR procedure is conducted to resolve the remaining unfixed ambiguities using the ambiguity-fixed phase observations, with the objective of improving the probability of fixing more ambiguities. In order to test the proposed algorithm, a field vehicular test was performed. The results show the availability and reliability of ambiguity resolution for the INS-aided single-frequency GPS/BDS using PAR technique are significantly improved compared to that of GNSS-only, and a success rate greater than 90 % can be obtained for the single-GNSS/INS system as well as combined GPS/BDS/INS system. In terms of positioning accuracy, the best performance is achievable for the single-frequency GPS/BDS/INS system, the RMSs for position difference stay below 1 cm for GPS/INS and GPS/BDS/INS single-epoch solutions; however, the worst positioning performance is from the BDS/INS system. In terms of INS bridging capability, a fast ambiguity recovery within 5 s becomes feasible for a 19-s outage using INS-aided PAR scheme after a long calibration period.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahrami M, Ziebart M (2010) Instantaneous Doppler-aided RTK positioning with single frequency receivers. In: Proceedings of the PLANS, 2010 IEEE/ION (pp 305–313), Indian Wells, California, May 4–6
Baritzhack IY, Berman N (1988) Control theoretic approach to inertial navigation systems. J Guid Control Dyn 11(3):237–245. doi:10.2514/3.20299
Carcanague S, Julien O, Vigneau W, Macabiau C (2013) Low-cost single-frequency GPS/GLONASS RTK for road users. In: Proceedings of the ION 2013 Pacific PNT Meeting(pp 168–184), Honolulu, Hawaii, April 23–25
Deng CL, Tang WM, Liu JN, Shi C (2014) Reliable single-epoch ambiguity resolution for short baselines using combined GPS/BeiDou system. GPS Solut 18(3):375–386. doi:10.1007/s10291-013-0337-5
Dong D, Bock Y (1989) Global positioning system network analysis with phase ambiguity resolution applied to crustal deformation studies in California. J Geophys Res 94(B4):3949–3966
Godha S, Cannon ME (2007) GPS/MEMS INS integrated system for navigation in urban areas. GPS Solut 11(3):193–203. doi:10.1007/s10291-006-0050-8
Grejner-Brzezinska DA, Da R, Toth C (1998) GPS error modeling and OTF ambiguity resolution for high-accuracy GPS/INS integrated system. J Geod 72(11):626–638. doi:10.1007/s001900050202
Han S, Wang J (2011) Integrated GPS/INS navigation system with dual-rate Kalman filter. GPS Solut 16(3):389–404. doi:10.1007/s10291-011-0240-x
Han HZ, Wang J, Wang JL, Tan XL (2015) Performance analysis on carrier phase-based tightly-coupled GPS/BDS/INS integration in GNSS degraded and denied environments. Sensors 15(4):8685–8711. doi:10.3390/S150408685
He HB, Li JL, Yang YX, Xu JY, Guo HR, Wang AB (2014) Performance assessment of single- and dual-frequency BeiDou/GPS single-epoch kinematic positioning. GPS Solut 18(3):393–403. doi:10.1007/s10291-013-0339-3
Henkel P, Gunther C (2010) Partial integer decorrelation: optimum trade-off between variance reduction and bias amplification. J Geod 84(1):51–63. doi:10.1007/s00190-009-0343-0
Lee HK, Wang J, Rizos C (2005) An integer ambiguity resolution procedure for GPS/pseudolite/INS integration. J Geod 79(4–5):242–255. doi:10.1007/s00190-005-0466-x
Li ZK, Wang J, Li BH, Gao JX, Tan XL (2014) GPS/INS/odometer integrated system using fuzzy neural network for land vehicle navigation applications. J Navig 67(6):967–983. doi:10.1017/S0373463314000307
Li JL, Yang YX, Xu JY, He HB, Guo HR (2015) GNSS multi-carrier fast partial ambiguity resolution strategy tested with real BDS/GPS dual- and triple-frequency observations. GPS Solut 19(1):5–13. doi:10.1007/s10291-013-0360-6
Odijk D, Arora BS, Teunissen PJG (2014) Predicting the success rate of long-baseline GPS + Galileo (partial) ambiguity resolution. J Navig 67(3):385–401. doi:10.1017/S037346331400006x
Odolinski R, Teunissen PJG, Odijk D (2015) Combined BDS, Galileo, QZSS and GPS single-frequency RTK. GPS Solut 19(1):151–163. doi:10.1007/s10291-014-0376-6
Parkins A (2011) Increasing GNSS RTK availability with a new single-epoch batch partial ambiguity resolution algorithm. GPS Solut 15(4):391–402. doi:10.1007/s10291-010-0198-0
Shi C, Zhao QL, Hu ZG, Liu JN (2013) Precise relative positioning using real tracking data from COMPASS GEO and IGSO satellites. GPS Solut 17(1):103–119. doi:10.1007/s10291-012-0264-x
Takasu T, Yasuda A. (2010). Kalman-filter-based integer ambiguity resolution strategy for long-baseline RTK with ionosphere and troposphere estimation. In: Proceedings of the ION GNSS 2010 (pp 161–171), Portland, Oregon, September 21–24
Teunissen PJG (1995) The least-squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation. J Geod 70(1–2):65–82. doi:10.1007/Bf00863419
Teunissen PJG (1999) An optimality property of the integer least-squares estimator. J Geod 73(11):587–593. doi:10.1007/s001900050269
Teunissen PJG (2001) Integer estimation in the presence of biases. J Geod 75(7):399–407
Teunissen PJG, Odolinski R, Odijk D (2014) Instantaneous BeiDou plus GPS RTK positioning with high cut-off elevation angles. J Geod 88(4):335–350. doi:10.1007/s00190-013-0686-4
Wang J, Feng Y (2013) Reliability of partial ambiguity fixing with multiple GNSS constellations. J Geod 87(1):1–14. doi:10.1007/s00190-012-0573-4
Yang YX, Li JL, Xu JY, Tang J, Guo HR, He HB (2011) Contribution of the compass satellite navigation system to global PNT users. Chin Sci Bull 56(26):2813–2819. doi:10.1007/s11434-011-4627-4
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2014ZDPY15), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (Grant No. NCET-13-1019), a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the Cooperative Innovation Center of Jiangsu Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, H., Wang, J., Wang, J. et al. Reliable partial ambiguity resolution for single-frequency GPS/BDS and INS integration. GPS Solut 21, 251–264 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0519-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10291-016-0519-z