Abstract
Objective and methods
This study deals with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) in type 1 diabetic patients and its association with other complications. We searched for CAN in 684 patients (age, 47 ± 12 years; diabetes duration, 22 ± 11 years) by cardiovascular responses to deep breathing and standing. Patients considered as positive had laboratory evaluation: “Ewing” tests (deep breathing, Valsalva, stand test, hand grip); heart rate variability (HRV) [low frequency (LF) and high frequency (HF) power] and spontaneous baroreflex slope (SBS). Logistic regression was used to identify the combination of patient characteristics, including other complications, most associated with CAN severity according to Ewing Score (ES 0–5).
Results
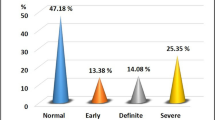
66.2% presented no significant abnormality (ES 0–0.5), 21.5 % had mild abnormalities (ES 1–2), and 12.3% had confirmed autonomic failure (ES > 2). Decrease in LF, HF and SBS was highly correlated to CAN severity. In the stepwise regression, age, retinopathy, nephropathy, bladder dysfunction, erectile dysfunction, peripheral neuropathy and hypertension remained correlated with CAN, whereas digestive neuropathy, BMI and HbA1c were excluded. Despite a small number of events, we found a significant association between coronary disorders and CAN severity.
Conclusions
Simple bedside tests can detect CAN. HRV and SBS provide additional elements on CAN severity. Diabetes duration did not discriminate sufficiently patients with CAN. The association with retinopathy is in favor of the role of poor glycemic control in CAN development. This study shows the interest of CAN detection and the need to look for extracardiac autonomic neuropathy and silent myocardial ischemia in patients with confirmed CAN.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Vinik AI, Freeman R (2003) The association between cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and mortality in individuals with diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 26:1895–1901
Vinik AI, Ziegler D (2007) Diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Circulation 115:387–397
Boulton AJ, Vinik AI, Arezzo JC, Bril V, Feldman EL, Freeman R, Malik RA, Maser RE, Sosenko JM, Ziegler D, American Diabetes Association (2005) Diabetic neuropathies: a statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 28:956–962
Rydén L, Standl E, Bartnik M, Van den Berghe G, Betteridge J, de Boer MJ, Cosentino F, Jönsson B, Laakso M, Malmberg K, Priori S, Ostergren J, Tuomilehto J, Thrainsdottir I, Vanhorebeek I, Stramba-Badiale M, Lindgren P, Qiao Q, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Camm J, Dean V, Deckers J, Dickstein K, Lekakis J, McGregor K, Metra M, Morais J, Osterspey A, Tamargo J, Zamorano JL, Deckers JW, Bertrand M, Charbonnel B, Erdmann E, Ferrannini E, Flyvbjerg A, Gohlke H, Juanatey JR, Graham I, Monteiro PF, Parhofer K, Pyörälä K, Raz I, Schernthaner G, Volpe M, Wood D, Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) (2007) Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases: executive summary. The Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Eur Heart J 28:88–136
Valensi P, Attali JR (1997) Why and how should cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in the diabetic be researched? Recommendations of ALFEDIAM (French Language Association for the Study of Diabetes and Metabolic Diseases). Diabetes Metab 23:351–356
Bannister R, Mathias CJ (1992) Autonomic failure—a textbook of clinical disorders of the autonomic nervous system, 3rd edn, Oxford Medical Publications, 953 p
Low P (1997) Clinical autonomic disorders—evaluation and management, 2nd, Lippincott–Raven, 845 p
(1996) Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure, and multiple system atrophy. The Consensus Committee of the American Autonomic Society and the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 46:1470
(1996) Heart rate variability. Standards of measurement, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Eur Heart J 17:354–381
Bertinieri G, di Rienzo M, Cavallazzi A, Ferrari AU, Pedotti A, Mancia G (1985) A new approach to analysis of the arterial baroreflex. J Hypertens Suppl 3:79–81
Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group (1991) Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs. An extension of the modified Airlie House Classification ETDRS report no. 10. Ophthalmology 98:786–806
Mogensen CE, Christensen CK (1984) Predicting diabetic nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetics. N Engl J Med 311:89–93
Wieling W, van Brederode JF, de Rijk LG, Borst C, Dunning AJ (1982) Reflex control of heart rate in normal subjects in relation to age: a data base for cardiac vagal neuropathy. Diabetologia 22:163–166
Vinik AI, Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Freeman R (2003) Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 26:1553–1579
Ziegler D, Dannehl K, Mühlen H, Spüler M, Gries FA (1992) Prevalence of cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction assessed by spectral analysis, vector analysis, and standard tests of heart rate variation and blood pressure responses at various stages of diabetic neuropathy. Diabet Med 9:806–814
O’Brien IA, McFadden JP, Corrall RJ (1991) The influence of autonomic neuropathy on mortality in insulin-dependent diabetes. Q J Med 79:495–502
Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, Ward JD, Manes C, Ionescu-Tirgoviste C, Witte DR, Fuller JH, EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Group (2005) Vascular risk factors and diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med 352:341–350
Valensi P, Pariès J, Attali JR, French Group for Research and Study of Diabetic Neuropathy (2003) Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetic patients: influence of diabetes duration, obesity, and microangiopathic complications—the French multicenter study. Metabolism 52:815–820
Bilal N, Erdogan M, Ozbek M, Cetinkalp S, Karadeniz M, Ozgen AG, Saygili F, Yilmaz C, Tüzün M, Kabalak T (2008) Increasing severity of cardiac autonomic neuropathy is associated with increasing prevalence of nephropathy, retinopathy, and peripheral neuropathy in Turkish type 2 diabetics. J Diabetes Complicat 22:181–185
Witte DR, Tesfaye S, Chaturvedi N, Eaton SE, Kempler P, Fuller JH, EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study Group (2005) Risk factors for cardiac autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 48:164–171
Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, Raskin P, Zinman B, Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group (2005) Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 353:2643–2653
Valensi P, Sachs RN, Harfouche B, Lormeau B, Paries J, Cosson E, Paycha F, Leutenegger M, Attali JR (2001) Predictive value of cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetic patients with or without silent myocardial ischemia. Diabetes Care 24:339–343
Ziegler D, Laude D, Akila F, Elghozi JL (2001) Time- and frequency-domain estimation of early diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy. Clin Auton Res 11:369–376
De Ferrari GM, Sanzo A, Bertoletti A, Specchia G, Vanoli E, Schwartz PJ (2007) Baroreflex sensitivity predicts long-term cardiovascular mortality after myocardial infarction even in patients with preserved left ventricular function. J Am Coll Cardiol 50:2285–2290
Ormezzano O, Cracowski JL, Quesada JL, Pierre H, Mallion JM, Baguet JP (2008) EVAluation of the prognostic value of BARoreflex sensitivity in hypertensive patients: the EVABAR study. J Hypertens 26:1373–1378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavy-Le Traon, A., Fontaine, S., Tap, G. et al. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy and other complications in type 1 diabetes. Clin Auton Res 20, 153–160 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-010-0062-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-010-0062-x