Abstract
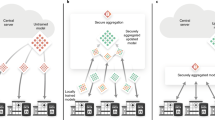
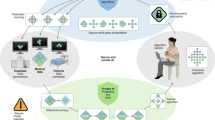
Precision medicine research benefits from machine learning in the creation of robust models adapted to the processing of patient data. This applies both to pathology identification in images, i.e., annotation or segmentation, and to computer-aided diagnostic for classification or prediction. It comes with the strong need to exploit and visualize large volumes of images and associated medical data. The work carried out in this paper follows on from a main case study piloted in a cancer center. It proposes an analysis pipeline for patients with osteosarcoma through segmentation, feature extraction and application of a deep learning model to predict response to treatment. The main aim of the AWESOMME project is to leverage this work and implement the pipeline on an easy-to-access, secure web platform. The proposed WEB application is based on a three-component architecture: a data server, a heavy computation and authentication server and a medical imaging web-framework with a user interface. These existing components have been enhanced to meet the needs of security and traceability for the continuous production of expert data. It innovates by covering all steps of medical imaging processing (visualization and segmentation, feature extraction and aided diagnostic) and enables the test and use of machine learning models. The infrastructure is operational, deployed in internal production and is currently being installed in the hospital environment. The extension of the case study and user feedback enabled us to fine-tune functionalities and proved that AWESOMME is a modular solution capable to analyze medical data and share research algorithms with in-house clinicians.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used during and/or analyzed during the current study are not available; they belong to the producer/host center: CLB. The data used in this study adhere to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Notes
References
König, I.R., Fuchs, O., Hansen, G., al.: What is precision medicine? Eur. [R]espir. [J]. 50 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.00391-2017
Hingorani, A.D., Windt, D.A., Riley, R.D.e.a.: Prognosis research strategy (progress) 4: stratified medicine research. BMJ 346 (2013) https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e5793
Bouhamama, A.: Can Radiomic Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy of Osteosarcomas? European Congress of Radiology, (2019). https://doi.org/10.26044/ECR2019/C-0930
Sun, R., Lerousseau, M., Henry, T., Carré, A.e.a.: Intelligence artificielle en radiothérapie : radiomique, pathomique, et prédiction de la survie et de la réponse aux traitements. Cancer [R]ad. 25(6-7), 630–637 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canrad.2021.06.027
Xie, F., Chan, J.C., Ma, R.C.: Precision medicine in diabetes prevention, classification and management. J. of [D]ia. [I]nv. 9(5), 998–1015 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12830
Bleker, J., Kwee, T.C., Yakar, D.: Quality of multicenter studies using mri radiomics for diagnosing clinically significant prostate cancer: A systematic review. Life 12(7) (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/life12070946
Zhang, Z., Xie, Y., Xing, F., McGough, M., Yang, L.: Mdnet: A semantically and visually interpretable medical image diagnosis network. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 3549–3557 (2017)
Lambin, P., Rios-Velazquez, E., Leijenaar, R.e.a.: Radiomics: extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. [C]ancer 48, 441–6 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036
Haomin, C., Caalina, G., Chien-Ming, H., Mathias, U.: Explainable medical imaging ai needs human-centered design: guidelines and evidence from a systematic review. npj [D]ig. [M]ed. 5 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41746-022-00699-2
Yushkevich, P.A., Piven, J., Hazlett, H.C., Gimpel Smith, R.e.a.: User-guided 3d active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. NeuroImage 31(3), 1116–1128 (2006) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.015
Goch, C.J., Metzger, J., Nolden, M.: Abstract: Medical research data management using MITK and XNAT. In: Informatik Aktuell, pp. 305–305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-54345-0_68
Doran, S., Sa’d, M.A., Petts, J., Darcy, J.e.a.: Integrating the OHIF viewer into XNAT: Achievements, challenges and prospects for quantitative imaging studies. Tomo. 8(1), 497–512 (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography8010040
Zhang, L., Fried, D.V., Fave, X.J., Hunter, L.A., Yang, J., Court, L.E.: An open infrastructure software platform to facilitate collaborative work in radiomics. Med. [P]hy. 42(3), 1341–1353 (2015) https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4908210
Korte, J.C., Cardenas, C., Hardcastle, N.e.a.: Radiomics feature stability of open-source software evaluated on apparent diffusion coefficient maps in head and neck cancer. Scientific Reports 11(17633) (2021) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96600-4
Fedorov, A., Beichel, R., Kalpathy-Cramer, J., Finet, J.e.a.: 3d slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magn. [R]es. [I]mag. 30(9), 1323–1341 (2012) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.05.001
Ziegler, E., Urban, T., Brown, D., Petts, J., Pieper, S.D.e.a. : Open health imaging foundation viewer: An extensible open-source framework for building web-based imaging applications to support cancer research. JCO [C]lin. [C]an. [I]nf. (4), 336–345 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1200/cci.19.00131
Han, S., Shin, J., Jung, H., Ryu, J.e.a.: ADAS-viewer: web-based application for integrative analysis of multi-omics data in alzheimer’s disease. npj [S]yst. [B]iol. [A]ppl. 7(1) (2021) https://doi.org/10.1038/s41540-021-00177-7
Keshavan, A., Datta, E., McDonough, I.M.e.a.: Mindcontrol: A web application for brain segmentation quality control. NeuroImage 170, 365–372 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.03.055
Lajara, N., Espinosa-Aranda, J.L., Deniz, O., Bueno, G.: Optimum web viewer application for DICOM whole slide image visualization in anatomical pathology. Comp. [M]eth. and [P]rog. [B]iomed. 179, 104983 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.104983
Gustafson, C., Bug, W.J., Nissanov, J. BMC Bioinformatics : a client-server system for browsing 3d biomedical image data sets. BMC Bioinformatics 8(1) (2007). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-8-40
Reynolds, S.M., Miller, M., Lee, P.e.a.: The ISB cancer genomics cloud: A flexible cloud-based platform for cancer genomics research. Cancer [R]es. 77(21), 7–10 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-17-0617
Diaz-Pinto, A., Alle, S., Ihsani, A., Asad, M.e.a.: Monai label: A framework for ai-assisted interactive labeling of 3d medical images (2022) arXiv:2203.12362
Nomura, Y., Miki, S., Hayashi, N.e.a.: Novel platform for development, training, and validation of computer-assisted detection/diagnosis software. Int. J. of [C]omp. [A]ss. Rad. [S]ur. 15, 661–672 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-020-02132-z
Rubin, D.L., Akdogan, M.U., Altindag, C., Alkim, E.: ePAD: An image annotation and analysis platform for quantitative imaging. Tomography 5(1), 170–183 (2019) https://doi.org/10.18383/j.tom.2018.00055
Egger, J., Wild, D., Weber, M., Ramirez Bedoya, C.A.e.a.: Studierfenster: an open science cloud-based medical imaging analysis platform. J. [D]ig. [I]ma. 35(2), 340–355 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-021-00574-8
Bouhamama, A., Leporq, B., Khaled, W., Nemeth, A.e.a.: Prediction of histologic neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in osteosarcoma using pretherapeutic mri radiomics. Rad. [I]ma. [C]an. 4(5) (2022) https://doi.org/10.1148/rycan.210107
Bick, U., Lenzen, H.: PACS: the silent revolution. Eur. [R]ad. 9(6), 1152–1160 (1999) https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050811
Richardson, L., S., R.: Restful Web Services, (2007)
Grauer, M., Rose, L., Choudhury, R.: Understanding the resonant platform. Kitware (2016)
Griethuysen, J.J.M., Fedorov, A., Parmar, C.e.a.: Computational radiomics system to decode the radiographic phenotype. Cancer [R]es. 77(21), 104–107 (2017) https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-17-0339
Zwanenburg, A., Vallières, M., Abdalah, M., Aerts, H.e.a.: The image biomarker standardization initiative: Standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping. Radiology 295(2), 328–338 (2020) https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020191145
Guérin, J., Laizet, Y., Le Texier, V., Chanas, L.e.a.: OSIRIS: A minimum data set for data sharing and interoperability in oncology. JCO [C]lin. Cancer [I]nf. (5), 256–265 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1200/cci.20.00094
Gorgolewski, K., Auer, T., Calhoun, V.e.a.: The brain imaging data structure, a format for organizing and describing outputs of neuroimaging experiments. Sci/ Data 3(160044) (2016) https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2016.44
Samuel G., Armato Geoffrey, McLennan Luc, Bidaut Michael F., McNitt‐Gray Charles R., Meyer Anthony P., Reeves Binsheng, Zhao Denise R., Aberle Claudia I., Henschke Eric A., Hoffman Ella A., Kazerooni Heber, MacMahon Edwin J. R., van Beek David, Yankelevitz Alberto M., Biancardi Peyton H., Bland Matthew S., Brown Roger M., Engelmann Gary E., Laderach Daniel, Max Richard C., Pais David P.‐Y., Qing Rachael Y., Roberts Amanda R., Smith Adam, Starkey Poonam, Batra Philip, Caligiuri Ali, Farooqi Gregory W., Gladish C. Matilda, Jude Reginald F., Munden Iva, Petkovska Leslie E., Quint Lawrence H., Schwartz Baskaran, Sundaram Lori E., Dodd Charles, Fenimore David, Gur Nicholas, Petrick John, Freymann Justin, Kirby Brian, Hughes Alessi, Vande Casteele Sangeeta, Gupte Maha, Sallam Michael D., Heath Michael H., Kuhn Ekta, Dharaiya Richard, Burns David S., Fryd Marcos, Salganicoff Vikram, Anand Uri, Shreter Stephen, Vastagh Barbara Y., Croft Laurence P., Clarke (2011) The Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) and Image Database Resource Initiative (IDRI): A Completed Reference Database of Lung Nodules on CT Scans Medical Physics 38(2) 915-931. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3528204
Etmann C., K.R., -B., S.: iUNets: Learnable Invertible Up- and Downsam- pling for Large-Scale Inverse Problems, vol. 11 (2020)
Jean-Christophe, Richard Florian, Sigaud Maxime, Gaillet Maciej, Orkisz Sam, Bayat Emmanuel, Roux Touria, Ahaouari Eduardo, Davila Loic, Boussel Gilbert, Ferretti Hodane, Yonis Mehdi, Mezidi William, Danjou Alwin, Bazzani Francois, Dhelft Laure, Folliet Mehdi, Girard Matteo, Pozzi Nicolas, Terzi Laurent, Bitker (2022) Response to PEEP in COVID-19 ARDS patients with and without extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. A multicenter case–control computed tomography study Abstract Critical Care 26(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-022-04076-z
Ludmilla, Penarrubia Aude, Verstraete Maciej, Orkisz Eduardo, Davila Loic, Boussel Hodane, Yonis Mehdi, Mezidi Francois, Dhelft William, Danjou Alwin, Bazzani Florian, Sigaud Sam, Bayat Nicolas, Terzi Mehdi, Girard Laurent, Bitker Emmanuel, Roux Jean-Christophe, Richard (2023) Precision of CT-derived alveolar recruitment assessed by human observers and a machine learning algorithm in moderate and severe ARDS Abstract Intensive Care Medicine Experimental 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40635-023-00495-6
Funding
This work was supported by the CNRS via the INS2I single call. This work was performed within the framework of the LABEX PRIMES (ANR-11-LABX-0063) of Université de Lyon, within the program "Investissements d'Avenir" operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception. Tiphaine Diot and Frederic Cervenansky contribute to the design of AWESOMME. Data collection and analysis were performed by Amine Bouhamama and Benjamin Leporq. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Tiphaine Diot and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
This is a technical study. The CLB Research Ethics Committee has confirmed that no ethical approval is required.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to Publication
The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Fig. 6.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Diot-Dejonghe, T., Leporq, B., Bouhamama, A. et al. Development of a Secure Web-Based Medical Imaging Analysis Platform: The AWESOMME Project. J Digit Imaging. Inform. med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01110-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-024-01110-0