Abstract
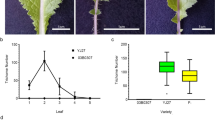
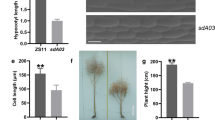
Brassica rapa show a wide range of morphological variations. In particular, the leaf morphologies of the Japanese traditional leafy vegetables Mizuna and Mibuna (Brassica rapa L. subsp. nipposinica L. H. Bailey) are distinctly different, even though they are closely related cultivars that are easy to cross. In addition to the differences in the gross morphology of leaves, some cultivars of Mibuna (Kyo-nishiki) have many trichomes on its leaves, whereas Mizuna (Kyo-mizore) does not. To identify the genes responsible for the different number of trichomes, we performed a quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis of Mizuna and Mibuna. To construct linkage maps for these cultivars, we used RNA-seq data to develop cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) markers. We also performed a restriction site-associated DNA sequencing (RAD-seq) analysis to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Two QTL analyses were performed in different years, and both analyses indicated that the largest effect was found on LG A9. Expression analyses showed that a gene homologous to GLABRA1 (GL1), a transcription factor implicated in trichome development in Arabidopsis thaliana, and the sequences 3′-flanking (downstream) of BrGL1, differed considerably between Mizuna (Kyo-mizore) and Mibuna (Kyo-nishiki). These results indicate that BrGL1 on LG A9 is one of the candidate genes responsible for the difference in trichome number between Mizuna and Mibuna. Detecting genes that are responsible for morphological variations allows us to better understand the breeding history of Mizuna and Mibuna.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artemyeva AM, Budahn H, Klocke E, Chesnokov YV (2011) Use of CACTA mobile genetic elements for revision of phylogenetic relationships in Brassica rapa L. species. Russian J Genet Appl Res 1:577–586. doi:10.1134/S2079059711060025
Bischoff V et al (2010) TRICHOME BIREFRINGENCE and its homolog AT5G01360 encode plant-specific DUF231 proteins required for cellulose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 153:590–602. doi:10.1104/pp.110.153320
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Catchen J, Hohenlohe PA, Bassham S, Amores A, Cresko WA (2013) Stacks: an analysis tool set for population genomics. Mol Ecol 22:3124–3140. doi:10.1111/mec.12354
Chen AL et al (2014) Reassessment of QTLs for late blight resistance in the tomato accession L3708 using a restriction site associated DNA (RAD) linkage map and highly aggressive isolates of Phytophthora infestans. PLoS One 9:e96417. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0096417
Choi S et al (2007) The reference genetic linkage map for the multinational Brassica rapa genome sequencing project TAG Theoretical and applied genetics. Theoretische und angewandte Genetik 115:777–792
Gan Y, Liu C, Yu H, Broun P (2007) Integration of cytokinin and gibberellin signalling by Arabidopsis transcription factors GIS, ZFP8 and GIS2 in the regulation of epidermal cell fate. Development 134:2073–2081 doi:10.1242/dev.005017
Herman PL, Marks MD (1989) Trichome development in Arabidopsis thaliana. II. Isolation and complementation of the GLABROUS1 gene. Plant Cell 1:1051–1055. doi:10.1105/tpc.1.11.1051
Ishida T et al (2007) Arabidopsis TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2 is directly regulated by R2R3 MYB transcription factors and is involved in regulation of GLABRA2 transcription in epidermal differentiation. Plant Cell Online 19:2531–2543. doi:10.1105/tpc.107.052274
Iwata H, Ninomiya S (2006) AntMap: constructing genetic linkage maps using an ant colony optimization algorithm. Breed Sci 56:371–377. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.56.371
Johnson CS, Kolevski B, Smyth DR (2002). TRANSPARENT TESTA GLABRA2, a trichome and seed coat development gene of Arabidopsis, encodes a WRKY transcription factor. Plant Cell Online 14:1359–1375 doi:10.1105/tpc.001404
Kawamura K et al (2016) Genetic distance of inbred lines of Chinese cabbage and its relationship to heterosis. Plant Gene 5:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.plgene.2015.10.003
Kim H et al (2009) Sequenced BAC anchored reference genetic map that reconciles the ten individual chromosomes of Brassica rapa. BMC Genom 10:432
Kirik V, Simon M, Huelskamp M, Schiefelbein J (2004) The ENHANCER OF TRY AND CPC1 gene acts redundantly with TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE in trichome and root hair cell patterning in Arabidopsis. Dev Biol 268:506–513. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.12.037
Kubo N, Saito M, Tsukazaki H, Kondo T, Matsumoto S, Hirai M (2010) Detection of quantitative trait loci controlling morphological traits in Brassica rapa L. Breeding. Science 60:164–171. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.60.164
Kumar R et al (2012) A high-throughput method for Illumina RNA-Seq library preparation. Front Plant Sci 3:202
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol. doi:10.1093/molbev/msw054
Larkin JC, Oppenheimer DG, Pollock S, Marks MD (1993) Arabidopsis GLABROUS1 gene requires downstream sequences for function. Plant Cell 5:1739–1748. doi:10.1105/tpc.5.12.1739
Li F, Kitashiba H, Inaba K, Nishio T (2009) A Brassica rapa linkage map of EST-based SNP markers for identification of candidate genes controlling flowering time and leaf morphological traits. DNA Res 16:311–323. doi:10.1093/dnares/dsp020
Li F, Kitashiba H, Nishio T (2011) Association of sequence variation in Brassica GLABRA1 orthologs with leaf hairiness. Mol Breed 28:577–584. doi:10.1007/s11032-010-9508-z
Li X et al (2013) Quantitative trait loci mapping in Brassica rapa revealed the structural and functional conservation of genetic loci governing morphological and yield component traits in the A, B, and C subgenomes of Brassica species. DNA Res 20:1–16. doi:10.1093/dnares/dss029
Ling AE et al (2007) Characterization of simple sequence repeat markers derived in silico from Brassica rapa bacterial artificial chromosome sequences and their application in Brassica napus. Mol Ecol Notes 7:273–277. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01578.x
Lou P et al (2007) Quantitative trait loci for flowering time and morphological traits in multiple populations of Brassica rapa. J Exp Bot 58:4005–4016. doi:10.1093/jxb/erm255
Lowe AJ, Moule C, Trick M, Edwards KJ (2004) Efficient large-scale development of microsatellites for marker and mapping applications in Brassica crop species. Theor Appl Genet 108:1103–1112. doi:10.1007/s00122-003-1522-7
Morohashi K, Zhao M, Yang M, Read B, Lloyd A, Lamb R, Grotewold E (2007) Participation of the Arabidopsis bHLH factor GL3 in trichome initiation regulatory events. Plant Physiol 145:736–746. doi:10.1104/pp.107.104521
Oppenheimer DG, Herman PL, Sivakumaran S, Esch J, Marks MD (1991) A myb gene required for leaf trichome differentiation in Arabidopsis is expressed in stipules. Cell 67:483–493. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90523-2
Payne CT, Zhang F, Lloyd AM (2000) GL3 encodes a bHLH protein that regulates trichome development in Arabidopsis through interaction with GL1 and TTG1. Genetics 156:1349–1362
Potikha T, Delmer DP (1995) A mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana displaying altered patterns of cellulose deposition. Plant J 7:453–460
Schellmann S et al (2002) TRIPTYCHON and CAPRICE mediate lateral inhibition during trichome and root hair patterning in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21:5036–5046. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf524
Schiefelbein J (2003) Cell-fate specification in the epidermis: a common patterning mechanism in the root and shoot. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:74–78. doi:10.1016/S136952660200002X
Sen Ś, Churchill GA (2001) A statistical framework for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 159:371–387
Song K, Slocum MK, Osborn TC (1995) Molecular marker analysis of genes controlling morphological variation in Brassica rapa (syn. campestris). Theor Appl Genet 90:1–10. doi:10.1007/BF00220989
Stracke R, Werber M, Weisshaar B (2001) The R2R3-MYB gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:447–456. doi:10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00199-0
Suo B, Seifert S, Kirik V (2013) Arabidopsis GLASSY HAIR genes promote trichome papillae development. J Exp Bot. doi:10.1093/jxb/ert287
Suwabe K, Iketani H, Nunome T, Kage T, Hirai M (2002) Isolation and characterization of microsatellites in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 104:1092–1098. doi:10.1007/s00122-002-0875-7
Suwabe K, Iketani H, Nunome T, Ohyama A, Hirai M, Fukuoka H (2004) Characteristics of microsatellites in Brassica rapa genome and their potential utilization for comparative genomics in Cruciferae. Breed Sci 54:85–90. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.54.85
Suwabe K et al (2006) Simple sequence repeat-based comparative genomics between Brassica rapa and Arabidopsis thaliana: the genetic origin of clubroot resistance. Genetics 173:309–319. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.038968
Takuno S, Kawahara T, Ohnishi O (2006) Phylogenetic relationships among cultivated types of Brassica rapa L. em. Metzg. as revealed by AFLP analysis. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:279–285. doi:10.1007/s10722-005-4260-7
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729. doi:10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tominaga R, Iwata M, Sano R, Inoue K, Okada K, Wada T (2008). Arabidopsis CAPRICE-LIKE MYB 3 (CPL3) controls endoreduplication and flowering development in addition to trichome and root hair formation. Development 135:1335–1345 doi:10.1242/dev.017947
Traw MB, Bergelson J (2003) Interactive effects of jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, and gibberellin on induction of trichomes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1367–1375. doi:10.1104/pp.103.027086
Tsuro M, Suwabe K, Kubo N, Matsumoto S, Hirai M (2005) Construction of a molecular linkage map of radish (Raphanus sativus L.), based on AFLP and Brassica-SSR markers. Breed Sci 55:107–111. doi:10.1270/jsbbs.55.107
Wagner GJ, Wang E, Shepherd RW (2004) New approaches for studying and exploiting an old protuberance, the plant trichome. Ann Bot (Lond) 93:3–11. doi:10.1093/aob/mch011
Wang S, Basten C, Zeng Z (2007) Windows QTL cartographer 2.5 Department of Statistics. North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Wester K, Digiuni S, Geier F, Timmer J, Fleck C, Hulskamp M (2009). Functional diversity of R3 single-repeat genes in trichome development. Development 136:1487–1496 doi:10.1242/dev.021733
Wu K et al (2014) High-density genetic map construction and QTLs analysis of grain yield-related traits in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) based on RAD-Seq techonology. BMC Plant Biol 14:1–14. doi:10.1186/s12870-014-0274-7
Yang C, Ye Z (2013) Trichomes as models for studying plant cell differentiation. CMLS Cell Mol Life Sci 70:1937–1948. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1147-6
Yu X, Wang H, Zhong W, Bai J, Liu P, He Y (2013) QTL mapping of leafy heads by genome resequencing in the RIL population of Brassica rapa. PLoS One 8:e76059
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Ferjani Ali for taking Scanning Electron Microscope pictures and Takahiro Kawanabe and Kaoru O. Yoshiyama for helpful discussion throughout our study. This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (JP16H01472) and MEXT-Supported Program for the Strategic Research Foundation at Private Universities (2015–2019: S1511023) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science & Technology of Japan to SK. This work was financially supported by grants-in-aid from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (KAKENHI Grant Numbers JP2287003 and JP24770047) and research grants from Kyoto Sangyo University to S.K, and the Sasakawa Scientific Research Grant from The Japan Science Society to Y.K.
Author contributions
YK, HN, NK, and SK conceived and designed the project. YK, KK, KI, MY, HK, AN, KY, and SK performed the experiments. YK, HN, AN, and SK wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Members of the Botanical Society of Japan: Seisuke Kimura, Hokuto Nakayama and Yaichi Kawakatsu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawakatsu, Y., Nakayama, H., Kaminoyama, K. et al. A GLABRA1 ortholog on LG A9 controls trichome number in the Japanese leafy vegetables Mizuna and Mibuna (Brassica rapa L. subsp. nipposinica L. H. Bailey): evidence from QTL analysis. J Plant Res 130, 539–550 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-017-0917-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-017-0917-5