Abstract
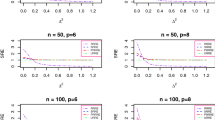
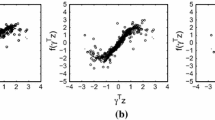
A consistent test via the partial penalized empirical likelihood approach for the parametric hypothesis testing under the sparse case, called the partial penalized empirical likelihood ratio (PPELR) test, is proposed in this paper. Our results are demonstrated for the mean vector in multivariate analysis and regression coefficients in linear models, respectively. And we establish its asymptotic distributions under the null hypothesis and the local alternatives of order n−1/2 under regularity conditions. Meanwhile, the oracle property of the partial penalized empirical likelihood estimator also holds. The proposed PPELR test statistic performs as well as the ordinary empirical likelihood ratio test statistic and outperforms the full penalized empirical likelihood ratio test statistic in term of size and power when the null parameter is zero. Moreover, the proposed method obtains the variable selection as well as the p-values of testing. Numerical simulations and an analysis of Prostate Cancer data confirm our theoretical findings and demonstrate the promising performance of the proposed method in hypothesis testing and variable selection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breheny, P., Huang, J. Coordinate descent algorithms for nonconvex penalized regression, with applications to biological feature selection. Ann. App. Statist., 5: 232–253 (2011)
Bühlmann, P., Van De Geer, S. Statistics for High-dimensional Data: Methods, Theory and Applications. Springer-Verlag, 2011
Chen, S.X., Cui, H.J. On Bartlett correction of empirical likelihood in the presence of nuisance parameters. Bimetrika, 16: 1101–1115 (2006)
Chen, S.X., Peng, L., Qin, Y.L. Effects of data dimension on empirical likelihood. Bimetrika, 96 (3): 711–722 (2009)
Diciccio, T.J., Hall, P., Romano, J.P. Empirical likelihood is Bartlett-correctable. Ann. statist., 19: 1053–1061 (1991)
Fan, J., Li, R. Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J. Am. Statist. Assoc., 96: 1348–1360 (2001)
Fan, J., Lv, J. A selective overview of variable selection in high dimensional feature space. Statistica Sinica, 20: 101–148 (2010)
Fan, J., Peng, H. Nonconcave penalized likelihood with a diverging number of parameters. Ann. Statist., 32: 928–961 (2004)
Friedman, J., Hastie, T., Höfling, H., Tibshirani, R. Pathwise coordinate optimization. Ann. App. Statist., 1: 302–332 (2007)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference and Prediction, 2nd ed., Springer, New York, 2009
Hjort, N.L., Mckeague, I.W., Keilegom, I.V. Extending the scope of empirical likelihood. Ann. Statist., 37 (3): 1079–1111 (2009)
Leng, C.L., Tang, C.Y. Penalized empirical likelihood and growing dimensional general estimating equations. Biometrika, 99 (3): 703–716 (2012)
Lockhart, R., Taylor, J., Tibshirani, R.J., Tibshirani, R. A significance test for the Lasso. Ann. Statist., 42 (2): 413–468 (2014)
Owen, A. B. Empirical likelihood ratio confidence regions. Ann. Statist., 18: 90–120 (1990)
Owen, A.B. Empirical Likelihood. Chapman & Hall-CRC, New York, 2001
Stamey, T., Kabalin, J., McNeal, J., Johnstone, I., Freiha, F., Redwine, E., Yang, N. Prostate specific antigen in the diagnosis and treatment of adenocarcinoma of the prostate, II,Radical prostatectomy treated patients. Journal of Urology, 16: 1076–1083 (1989)
Tang, C.Y., Leng, C.L. Penalized high-dimensional empirical likelihood. Biometrika, 97 (4): 905–920 (2010)
Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the Lasso. J. R. Statist. Soc. B, 58: 267–288 (1996)
Wang, H.S., Li, B., Leng, C.L. Shrinkage tuning parameter selection with a divergent number of parameters. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B, 71: 671–683 (2009)
Wang, S.S., Cui, H.J. Partial penalized likelihood ratio test under sparse case. URL: http://arxiv.org/abs/1312.3723 (2013)
Wu, T.T., Lange, K. Coordinate descent algorithms for Lasso penalized regression. Ann. App. Statist., 2: 224–244 (2008)
Zhang, C.H. Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann. Statist., 38: 894–942 (2010)
Zou, H. The adaptive lasso and its oracle properties. J. Am. Statist. Assoc., 101: 1418–1429 (2006)
Zou, H., Hastie, T. Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. Roy. Statist. Soc. Ser. B, 67: 301–320 (2005)
Zou, H., Li, R. One-step sparse estimates in nonconcave penalized likelihood models (with discussion). Ann. Statist., 36: 1509–1566 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the editor, the editorial committee and the referees for their valuable comments and suggestions which would lead to great improvements of the presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11471223, 11231010, 11028103, 11071022, 11501586, 71420107025), the Key project of Beijing Municipal Education Commission (Grant No. KZ201410028030) and the Foundation of Beijing Center for Mathematics and Information Interdisciplinary Sciences.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Ss., Cui, Hj. Partial penalized empirical likelihood ratio test under sparse case. Acta Math. Appl. Sin. Engl. Ser. 33, 327–344 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10255-017-0663-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10255-017-0663-4