Abstract
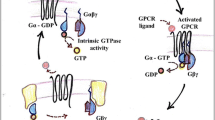
Heterotrimeric G-proteins are key transducers for signal transfer from outside the cell, mediating signals emanating from cell-surface G-protein coupled receptors (GPCR). Many, if not all, subtypes of heterotrimeric G-proteins are also regulated by accessory proteins that influence guanine nucleotide binding, guanosine triphosphate (GTP) hydrolysis, or subunit interactions. One subgroup of such accessory proteins (activators of G-protein signaling; AGS proteins) refer to a functionally defined group of proteins that activate selected G-protein signaling systems in the absence of classical G-protein coupled receptors. AGS and related proteins provide unexpected insights into the regulation of the G-protein activation–deactivation cycle. Different AGS proteins function as guanine nucleotide exchange factors or guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors and may also influence subunit interactions by interaction with Gβγ. These proteins play important roles in the generation or positioning of signaling complexes and of the regulation of GPCR signaling, and as alternative binding partners for G-protein subunits. Perhaps of even broader impact is the discovery that AGS proteins provide a foundation for the concept that heterotrimeric G-protein subunits are processing signals within the cell involving intrinsic cues that do not involve the classical signal input from a cell surface GPCR.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGS:
-
Activator of G-protein signaling
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- GAP:
-
GTPase-activating protein
- GDI:
-
Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor
- GEF:
-
Guanine nucleotide exchange factor
- GPCR:
-
G-protein coupled receptor
- GPR:
-
G-protein regulatory
- GPSM:
-
G-protein signaling modulator
- GTPγS:
-
Guanosine 5′-3-O-(thio)triphosphate
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- NMDA:
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate
- nNOS:
-
Neuronal nitric oxide synthase
- PDZ:
-
PSD95/DLG/ZO-1 domain
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase
- PLC:
-
Phospholipase C
- PTB:
-
Phosphotyrosine binding
- RBD:
-
Ras binding domain
- RGS:
-
Regulator of G-protein signaling
- TPR:
-
Tetratricopeptide repeat
References
Abba MC, Drake JA, Hawkins KA, Hu Y, Sun H, Notcovich C, Gaddis S, Sahin A, Baggerly K, Aldaz CM (2004) Transcriptomic changes in human breast cancer progression as determined by serial analysis of gene expression. Breast Cancer Res 6:R499–R513
Adhikari A, Sprang SR (2003) Thermodynamic characterization of the binding of activator of G protein signaling 3 (AGS3) and peptides derived from AGS3 with G alpha i1. J Biol Chem 278:51825–51832
Afshar K, Willard FS, Colombo K, Johnston CA, McCudden CR, Siderovski DP, Gonczy P (2004) RIC-8 is required for GPR-1/2-dependent Galpha function during asymmetric division of C. elegans embryos. Cell 119:219–230
Agell N, Bachs O, Rocamora N, Villalonga P (2002) Modulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by Ca(2+), and calmodulin. Cell Signal 14:649–654
Ahnert-Hilger G, Schafer T, Spicher K, Grund C, Schultz G, Wiedenmann B (1994) Detection of G-protein heterotrimers on large dense core and small synaptic vesicles of neuroendocrine and neuronal cells. Eur J Cell Biol 65:26–38
Ahringer J (2003) Control of cell polarity and mitotic spindle positioning in animal cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:73–81
Aronin N, DiFiglia M (1992) The subcellular localization of the G-protein Gi alpha in the basal ganglia reveals its potential role in both signal transduction and vesicle trafficking. J Neurosci 12:3435–3444
Barbacid M (1987) Ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem 56:779–827
Bellaiche Y, Radovic A, Woods DF, Hough CD, Parmentier ML, O’Kane CJ, Bryant PJ, Schweisguth F (2001) The Partner of Inscuteable/Discs-large complex is required to establish planar polarity during asymmetric cell division in Drosophila. Cell 106:355–366
Berman DM, Gilman AG (1998) Mammalian RGS proteins: barbarians at the gate. J Biol Chem 273:1269–1272
Bernard ML, Peterson YK, Chung P, Jourdan J, Lanier SM (2001) Selective interaction of AGS3 with G-proteins and the influence of AGS3 on the activation state of G-proteins. J Biol Chem 276:1585–1593
Blackmer T, Larsen EC, Takahashi M, Martin TF, Alford S, Hamm HE (2001) G protein betagamma subunit-mediated presynaptic inhibition: regulation of exocytotic fusion downstream of Ca2+ entry. Science 292:293–297
Blatch GL, Lassle M (1999) The tetratricopeptide repeat: a structural motif mediating protein-protein interactions. Bioessays 21:932–939
Blumer JB, Lanier SM (2003) Accessory proteins for G protein-signaling systems: activators of G protein signaling and other nonreceptor proteins influencing the activation state of G proteins. Receptors Channels 9: 195–204
Blumer JB, Chandler LJ, Lanier SM (2002) Expression analysis and subcellular distribution of the two G-protein regulators AGS3 and LGN indicate distinct functionality. Localization of LGN to the midbody during cytokinesis. J Biol Chem 277:15897–15903
Blumer JB, Bernard ML, Peterson YK, Nezu J, Chung P, Dunican DJ, Knoblich JA, Lanier SM (2003) Interaction of activator of G-protein signaling 3 (AGS3) with LKB1, a serine/threonine kinase involved in cell polarity and cell cycle progression: phosphorylation of the G-protein regulatory (GPR) motif as a regulatory mechanism for the interaction of GPR motifs with Gi alpha. J Biol Chem 278:23217–23220
Bomsel M, Mostov K (1992) Role of heterotrimeric G proteins in membrane traffic. Mol Biol Cell 3:1317–1328
Bonacci TM, Ghosh M, Malik S, Smrcka AV (2005) Regulatory interactions between the amino terminus of G-protein betagamma subunits and the catalytic domain of phospholipase Cbeta2. J Biol Chem 280:10174–10181
Bowers MS, McFarland K, Lake RW, Peterson YK, Lapish CC, Gregory ML, Lanier SM, Kalivas PW (2004) Activator of G protein signaling 3: a gatekeeper of cocaine sensitization and drug seeking. Neuron 42:269–281
Brogan MD, Behrend EN, Kemppainen RJ (2001) Regulation of Dexras1 expression by endogenous steroids. Neuroendocrinology 74:244–250
Bueb JL, Mousli M, Bronner C, Rouot B, Landry Y (1990) Activation of Gi-like proteins, a receptor-independent effect of kinins in mast cells. Mol Pharmacol 38:816–822
Burde R, Dippel E, Seifert R (1996) Receptor-independent G protein activation may account for the stimulatory effects of first-generation H1-receptor antagonists in HL-60 cells, basophils, and mast cells. Biochem Pharmacol 51:125–131
Burstein ES, Spalding TA, Brann MR (1998) Structure/function relationships of a G-protein coupling pocket formed by the third intracellular loop of the m5 muscarinic receptor. Biochemistry 37:4052–4058
Campbell KS, Cooper S, Dessing M, Yates S, Buder A (1998) Interaction of p59fyn kinase with the dynein light chain, Tctex-1, and colocalization during cytokinesis. J Immunol 161:1728–1737
Cao X, Cismowski MJ, Sato M, Blumer JB, Lanier SM (2004) Identification and characterization of AGS4: a protein containing three G-protein regulatory motifs that regulate the activation state of Gialpha. J Biol Chem 279:27567–27574
Chandler LJ, Sutton G, Dorairaj NR, Norwood D (2001) N-methyl D-aspartate receptor-mediated bidirectional control of extracellular signal-regulated kinase activity in cortical neuronal cultures. J Biol Chem 276:2627–2636
Chatterjee TK, Fisher RA (2000a) Cytoplasmic, nuclear, and golgi localization of RGS proteins. Evidence for N-terminal and RGS domain sequences as intracellular targeting motifs. J Biol Chem 275:24013–24021
Chatterjee TK, Fisher RA (2000b) Novel alternative splicing and nuclear localization of human RGS12 gene products. J Biol Chem 275:29660–29671
Cheng HY, Obrietan K, Cain SW, Lee BY, Agostino PV, Joza NA, Harrington ME, Ralph MR, Penninger JM (2004) Dexras1 potentiates photic and suppresses nonphotic responses of the circadian clock. Neuron 43:715–728
Cho H, Kozasa T, Takekoshi K, De Gunzburg J, Kehrl JH (2000) RGS14, a GTPase-activating protein for Gialpha, attenuates Gialpha- and G13alpha-mediated signaling pathways. Mol Pharmacol 58:569–576
Cho H, Kim DU, Kehrl JH (2005) RGS14 is a centrosomal and nuclear cytoplasmic shuttling protein that traffics to promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies following heat shock. J Biol Chem 280:805–814
Cismowski MJ, Takesono A, Ma C, Lizano JS, Xie X, Fuernkranz H, Lanier SM, Duzic E (1999) Genetic screens in yeast to identify mammalian nonreceptor modulators of G-protein signaling. Nat Biotechnol 17:878–883
Cismowski MJ, Ma C, Ribas C, Xie X, Spruyt M, Lizano JS, Lanier SM, Duzic E (2000) Activation of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling by a ras-related protein: implications for signal integration. J Biol Chem 275:23421–23424
Cismowski MJ, Takesono A, Ma C, Lanier SM, Duzic E (2002) Identification of modulators of mammalian G-protein signaling by functional screens in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol 344:153–168
Colombo K, Grill SW, Kimple RJ, Willard FS, Siderovski DP, Gonczy P (2003) Translation of polarity cues into asymmetric spindle positioning in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos. Science 300:1957–1961
Couwenbergs C, Spilker AC, Gotta M (2004) Control of embryonic spindle positioning and Galpha activity by C. elegans RIC-8. Curr Biol 14:1871–1876
Cox AD, Der CJ (2003) The dark side of ras: regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 22:8999–9006
Crouch MF, Simson L (1997) The G-protein G(I) regulates mitosis but not DNA synthesis in growth factor-activated fibroblasts: a role for the nuclear translocation of G(I). FASEB J 11:189–198
Crouch MF, Osborne GW, Willard FS (2000) The GTP-binding protein G(ialpha) translocates to kinetochores and regulates the M-G(1) cell cycle transition of Swiss 3T3 cells. Cell Signal 12:153–163
D’Andrea LD, Regan L (2003) TPR proteins: the versatile helix. Trends Biochem Sci 28:655–662
Denker SP, McCaffery JM, Palade GE, Insel PA, Farquhar MG (1996) Differential distribution of alpha subunits and beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins on Golgi membranes of the exocrine pancreas. J Cell Biol 133:1027–1040
Detert H, Seifert R, Schunack W (1996) Cationic amphiphiles with G-protein-stimulatory activity: studies on the role of the basic domain in the activation process. Pharmazie 51:67–72
DeVries L, Farquhar MG (1999) RGS proteins: more than just GAPs for heterotrimeric G proteins. Trends Cell Biol 9:138–144
DeVries L, Fischer T, Tronchere H, Brothers GM, Strockbine B, Siderovski DP, Farquhar MG (2000) Activator of G protein signaling 3 is a guanine dissociation inhibitor for Galpha I subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:14364–14369
Dohlman HG, Thorner J (1997) RGS proteins and signaling by heterotrimeric G proteins. J Biol Chem 272:3871–3874
Du Q, Macara IG (2004) Mammalian Pins is a conformational switch that links NuMA to heterotrimeric G proteins. Cell 119:503–516
Du Q, Stukenberg PT, Macara IG (2001) A mammalian partner of inscuteable binds NuMA and regulates mitotic spindle organization. Nat Cell Biol 3:1069–1075
Duzic E, Lanier SM (1992) Factors determining the specificity of signal transduction by guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled receptors. III. Coupling of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtypes in a cell type-specific manner. J Biol Chem 267:24045–24052
Falk JD, Vargiu P, Foye PE, Usui H, Perez J, Danielson PE, Lerner DL, Bernal J, Sutcliffe JG (1999) Rhes: a striatal-specific Ras homolog related to Dexras1. J Neurosci Res 57:782–788
Fang M, Jaffrey SR, Sawa A, Ye K, Luo X, Snyder SH (2000) Dexras1: a G protein specifically coupled to neuronal nitric oxide synthase via CAPON. Neuron 28:183–193
Feig LA, Cooper GM (1988) Relationship among guanine nucleotide exchange, GTP hydrolysis, and transforming potential of mutated ras proteins. Mol Cell Biol 8:2472–2478
Fiordalisi JJ, Holly SP, Johnson RL II, Parise LV, Cox AD (2002) A distinct class of dominant negative Ras mutants: cytosolic GTP-bound Ras effector domain mutants that inhibit Ras signaling and transformation and enhance cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 277:10813–10823
Franzoni L, Nicastro G, Pertinhez TA, Oliveira E, Nakaie CR, Paiva AC, Schreier S, Spisni A (1999) Structure of two fragments of the third cytoplasmic loop of the rat angiotensin II AT1A receptor: implications with respect to receptor activation and G-protein selection and coupling. J Biol Chem 274:227–235
Freissmuth M, Waldhoer M, Bofill-Cardona E, Nanoff C (1999) G protein antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci 20:237–245
Gaetz J, Kapoor TM (2004) Dynein/dynactin regulate metaphase spindle length by targeting depolymerizing activities to spindle poles. J Cell Biol 166:465–471
Ghosh M, Peterson YK, Lanier SM, Smrcka AV (2003) Receptor and nucleotide independent mechanisms for promoting G-protein subunit dissociation. J Biol Chem 278:34747–34750
Gotta M, Dong Y, Peterson YK, Lanier SM, Ahringer J (2003) Asymmetrically distributed C. elegans homologs of AGS3/PINS control spindle position in the early embryo. Curr Biol 13:1029–1037
Goubaeva F, Ghosh M, Malik S, Yang J, Hinkle PM, Griendling KK, Neubig RR, Smrcka AV (2003) Stimulation of cellular signaling and G protein subunit dissociation by G protein betagamma subunit-binding peptides. J Biol Chem 278:19634–19641
Graham TE, Key TA, Kilpatrick K, Dorin RI (2001) Dexras1/AGS-1, a steroid hormone-induced guanosine triphosphate-binding protein, inhibits 3’,5’-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-stimulated secretion in AtT-20 corticotroph cells. Endocrinology 142:2631–2640
Graham TE, Prossnitz ER, Dorin RI (2002) Dexras1/AGS-1 inhibits signal transduction from the Gi-coupled formyl peptide receptor to Erk-1/2 MAP kinases. J Biol Chem 277:10876–10882
Graham TE, Qiao Z, Dorin RI (2004) Dexras1 inhibits adenylyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:307–312
Harrison A, Olds-Clarke P, King SM (1998) Identification of the t complex-encoded cytoplasmic dynein light chain tctex1 in inner arm I1 supports the involvement of flagellar dyneins in meiotic drive. J Cell Biol 140:1137–1147
Helms JB (1995) Role of heterotrimeric GTP binding proteins in vesicular protein transport: indications for both classical and alternative G protein cycles. FEBS Lett 369:84–88
Herrmann C (2003) Ras-effector interactions: after one decade. Curr Opin Struct Biol 13:122–129
Herrmann C, Horn G, Spaargaren M, Wittinghofer A (1996) Differential interaction of the ras family GTP-binding proteins H-Ras, Rap1A, and R-Ras with the putative effector molecules Raf kinase and Ral-guanine nucleotide exchange factor. J Biol Chem 271:6794–6800
Herzog H, Hort YJ, Ball HJ, Hayes G, Shine J, Selbie LA (1992) Cloned human neuropeptide Y receptor couples to two different second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5794–5798
Hess HA, Roper JC, Grill SW, Koelle MR (2004) RGS-7 completes a receptor-independent heterotrimeric G protein cycle to asymmetrically regulate mitotic spindle positioning in C. elegans. Cell 119:209–218
Higashijima T, Burnier J, Ross EM (1990) Regulation of Gi and Go by mastoparan, related amphiphilic peptides, and hydrophobic amines: mechanism and structural determinants of activity. J Biol Chem 265:14176–14186
Hollinger S, Hepler JR (2002) Cellular regulation of RGS proteins: modulators and integrators of G protein signaling. Pharmacol Rev 54:527-559
Hollinger S, Taylor JB, Goldman EH, Hepler JR (2001) RGS14 is a bifunctional regulator of Galphai/o activity that exists in multiple populations in brain. J Neurochem 79:941–949
Hollinger S, Ramineni S, Hepler JR (2003) Phosphorylation of RGS14 by protein kinase A potentiates its activity toward G alpha I. Biochemistry 42:811–819
Hughes JR, Bullock SL, Ish-Horowicz D (2004) Inscuteable mRNA localization is dynein-dependent and regulates apicobasal polarity and spindle length in Drosophila neuroblasts. Curr Biol 14:1950–1956
Ja WW, Roberts RW (2004) In vitro selection of state-specific peptide modulators of G protein signaling using mRNA display. Biochemistry 43:9265–9275
Jaffrey SR, Fang M, Snyder SH (2002) Nitrosopeptide mapping: a novel methodology reveals s-nitrosylation of dexras1 on a single cysteine residue. Chem Biol 9:1329–1335
Jordan JD, Carey KD, Stork PJ, Iyengar R (1999) Modulation of rap activity by direct interaction of Galpha(o) with Rap1 GTPase-activating protein. J Biol Chem 274:21507–21510
Kaushik R, Yu F, Chia W, Yang X, Bahri S (2003) Subcellular localization of LGN during mitosis: evidence for its cortical localization in mitotic cell culture systems and its requirement for normal cell cycle progression. Mol Biol Cell 14:3144–3155
Kavelaars A, Jeurissen F, von Frijtag Drabbe Kunzel J, Herman van Roijen J, Rijkers GT, Heijnen CJ (1993) Substance P induces a rise in intracellular calcium concentration in human T lymphocytes in vitro: evidence of a receptor-independent mechanism. J Neuroimmunol 42:61–70
Kemppainen RJ, Behrend EN (1998) Dexamethasone rapidly induces a novel ras superfamily member-related gene in AtT-20 cells. J Biol Chem 273:3129–3131
Kemppainen RJ, Cox E, Behrend EN, Brogan MD, Ammons JM (2003) Identification of a glucocorticoid response element in the 3′-flanking region of the human Dexras1 gene. Biochim Biophys Acta 1627:85–89
Kerov VS, Natochin M, Artemyev NO (2005) Interaction of transducin-alpha with LGN, a G-protein modulator expressed in photoreceptor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 28:485–495
Kimple RJ, DeVries L, Tronchere H, Behe CI, Morris RA, Gist Farquhar M, Siderovski DP (2001) RGS12 and RGS14 GoLoco motifs are Galpha(I) interaction sites with guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor activity. J Biol Chem 276:29275–29281
Kimple RJ, Kimple ME, Betts L, Sondek J, Siderovski DP (2002) Structural determinants for GoLoco-induced inhibition of nucleotide release by Galpha subunits. Nature 416:878–881
Kimple RJ, Willard FS, Hains MD, Jones MB, Nweke GK, Siderovski DP (2004) Guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitor activity of the triple GoLoco motif protein G18: alanine-to-aspartate mutation restores function to an inactive second GoLoco motif. Biochem J 378:801–808
Kinoshita-Kawada M, Oberdick J, Xi Zhu M (2004) A Purkinje cell specific GoLoco domain protein, L7/Pcp-2, modulates receptor-mediated inhibition of Cav2.1 Ca2+ channels in a dose-dependent manner. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 132:73–86
Klein C, Paul JI, Sauve K, Schmidt MM, Arcangeli L, Ransom J, Trueheart J, Manfredi JP, Broach JR, Murphy AJ (1998) Identification of surrogate agonists for the human FPRL-1 receptor by autocrine selection in yeast. Nat Biotechnol 16:1334–1337
Klinker JF, Seifert R (1997) Morphine and muscle relaxants are receptor-independent G-protein activators and cromolyn is an inhibitor of stimulated G-protein activity. Inflamm Res 46:46–50
Klinker JF, Seifert R, Damm H, Rommelspacher H (1997) Activation by beta-carbolines of G-proteins in HL-60 membranes and the bovine retinal G-protein transducin in a receptor-independent manner. Biochem Pharmacol 53:1621–1626
Knoblich JA (2001) Asymmetric cell division during animal development. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:11–20
Kroslak T, Koch T, Kahl E, Hollt V (2001) Human phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein facilitates heterotrimeric G protein-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem 276:39772–39778
Lankford K, Cypher C, Letourneau P (1990) Nerve growth cone motility. Curr Opin Cell Biol 2:80–85
Law GJ, Northrop AJ, Mason WT (1993) Rab3-peptide stimulates exocytosis from mast cells via a pertussis toxin-sensitive mechanism. FEBS Lett 333:56–60
Leschke C, Storm R, Breitweg-Lehmann E, Exner T, Nurnberg B, Schunack W (1997) Alkyl-substituted amino acid amides and analogous di- and triamines: new non-peptide G protein activators. J Med Chem 40:3130–3139
Lova P, Paganini S, Hirsch E, Barberis L, Wymann M, Sinigaglia F, Balduini C, Torti M (2003) A selective role for phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in the Gi-dependent activation of platelet Rap1B. J Biol Chem 278:131–138
Luo Y, Denker BM (1999) Interaction of heterotrimeric G protein Galphao with Purkinje cell protein-2: evidence for a novel nucleotide exchange factor. J Biol Chem 274:10685–10688
Maier O, Ehmsen E, Westermann P (1995) Trimeric G protein alpha subunits of the Gs and Gi families localized at the Golgi membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 208:135–143
Malbon CC (1997) Heterotrimeric G-proteins and development. Biochem Pharmacol 53:1–4
Marjamaki A, Sato M, Bouet-Alard R, Yang Q, Limon-Boulez I, Legrand C, Lanier SM (1997) Factors determining the specificity of signal transduction by guanine nucleotide-binding protein-coupled receptors. Integration of stimulatory and inhibitory input to the effector adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem 272:16466–16473
Martin ME, Hidalgo J, Vega FM, Velasco A (1999) Trimeric G proteins modulate the dynamic interaction of PKAII with the Golgi complex. J Cell Sci 112:3869–3878
Martin-McCaffrey L, Willard FS, Oliveira-dos-Santos AJ, Natale DR, Snow BE, Kimple RJ, Pajak A, Watson AJ, Dagnino L, Penninger JM, Siderovski DP, D’Souza SJ (2004) RGS14 is a mitotic spindle protein essential from the first division of the mammalian zygote. Dev Cell 7:763–769
Marty C, Browning DD, Ye RD (2003) Identification of tetratricopeptide repeat 1 as an adaptor protein that interacts with heterotrimeric G proteins and the small GTPase Ras. Mol Cell Biol 23:3847–3858
McCormick F (1995) Ras-related proteins in signal transduction and growth control. Mol Reprod Dev 42:500–506
Meng J, Casey PJ (2002) Activation of Gz attenuates Rap1-mediated differentiation of PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 277:43417–43424
Meng J, Glick JL, Polakis P, Casey PJ (1999) Functional interaction between Galpha(z) and Rap1GAP suggests a novel form of cellular cross-talk. J Biol Chem 274:36663–36669
Merdes A, Heald R, Samejima K, Earnshaw WC, Cleveland DW (2000) Formation of spindle poles by dynein/dynactin-dependent transport of NuMA. J Cell Biol 149:851–862
Miller KG, Rand JB (2000) A role for RIC-8 (Synembryn) and GOA-1 (G(o)alpha) in regulating a subset of centrosome movements during early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 156:1649–1660
Mittal V, Linder ME (2004) The RGS14 GoLoco domain discriminates among Galphai isoforms. J Biol Chem 279:46772–46778
Mochizuki N, Cho G, Wen B, Insel PA (1996) Identification and cDNA cloning of a novel human mosaic protein, LGN, based on interaction with G alpha i2. Gene 181:39–43
Mochizuki N, Ohba Y, Kiyokawa E, Kurata T, Murakami T, Ozaki T, Kitabatake A, Nagashima K, Matsuda M (1999) Activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway by an isoform of rap1GAP associated with G alpha(I). Nature 400:891–894
Mousli M, Bueb JL, Bronner C, Rouot B, Landry Y (1990) G protein activation: a receptor-independent mode of action for cationic amphiphilic neuropeptides and venom peptides. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:358–362
Mueller S, Cao X, Welker R, Wimmer E (2002) Interaction of the poliovirus receptor CD155 with the dynein light chain Tctex-1 and its implication for poliovirus pathogenesis. J Biol Chem 277:7897–7904
Nagano F, Orita S, Sasaki T, Naito A, Sakaguchi G, Maeda M, Watanabe T, Kominami E, Uchiyama Y, Takai Y (1998) Interaction of Doc2 with tctex-1, a light chain of cytoplasmic dynein. Implication in dynein-dependent vesicle transport. J Biol Chem 273:30065–30068
Nair KS, Mendez A, Blumer JB, Rosenzweig DH, Slepak VZ (2005) The presence of a Leu-Gly-Asn repeat enriched protein (LGN), a putative binding partner of transducin, in ROD photoreceptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:383–389
Nanoff C, Kudlacek O, Freissmuth M (2002) Development of Gs-selective inhibitory compounds. Methods Enzymol 344:469–480
Natochin M, Lester B, Peterson YK, Bernard ML, Lanier SM, Artemyev NO (2000) AGS3 inhibits GDP dissociation from Gα subunits of Gi family and rhodopsin-dependent activation of transducin. J Biol Chem 275:40981-40985
Natochin M, Gasimov KG, Artemyev NO (2001) Inhibition of GDP/GTP exchange on G alpha subunits by proteins containing G-protein regulatory motifs. Biochemistry 40:5322–5328
Ngsee JK, Miller K, Wendland B, Scheller RH (1990) Multiple GTP-binding proteins from cholinergic synaptic vesicles. J Neurosci 10:317–322
Nurnberg B, Ahnert-Hilger G (1996) Potential roles of heterotrimeric G proteins of the endomembrane system. FEBS Lett 389:61–65
Ogier-Denis E, Couvineau A, Maoret JJ, Houri JJ, Bauvy C, De Stefanis D, Isidoro C, Laburthe M, Codogno P (1995) A heterotrimeric Gi3-protein controls autophagic sequestration in the human colon cancer cell line HT-29. J Biol Chem 270:13–16
Ogier-Denis E, Houri JJ, Bauvy C, Codogno P (1996) Guanine nucleotide exchange on heterotrimeric Gi3 protein controls autophagic sequestration in HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem 271:28593–28600
Ogier-Denis E, Petiot A, Bauvy C, Codogno P (1997) Control of the expression and activity of the Galpha-interacting protein (GAIP) in human intestinal cells. J Biol Chem 272:24599–24603
Pacold ME, Suire S, Perisic O, Lara-Gonzalez S, Davis CT, Walker EH, Hawkins PT, Stephens L, Eccleston JF, Williams RL (2000) Crystal structure and functional analysis of Ras binding to its effector phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma. Cell 103:931–943
Parmentier ML, Woods D, Greig S, Phan PG, Radovic A, Bryant P, O’Kane CJ (2000) Rapsynoid/partner of inscuteable controls asymmetric division of larval neuroblasts in Drosophila. J Neurosci 20:RC84
Pattingre S, DeVries L, Bauvy C, Chantret I, Cluzeaud F, Ogier-Denis E, Vandewalle A, Codogno P (2003) The G-protein regulator AGS3 controls an early event during macroautophagy in human intestinal HT-29 cells. J Biol Chem 278:20995–21002
Pattingre S, Petiot A, Codogno P (2004) Analyses of Galpha-interacting protein and activator of G-protein-signaling-3 functions in macroautophagy. Methods Enzymol 390:17–31
Perez DM, DeYoung MB, Graham RM (1993) Coupling of expressed alpha 1B- and alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor to multiple signaling pathways is both G protein and cell type specific. Mol Pharmacol 44:784–795
Peterson YK, Bernard ML, Hong Z, Graber SG, Lanier SM (2000) Stabilization of the GDP-bound conformation of Giα by a peptide derived from the G-protein regulatory motif of AGS3. J Biol Chem 275:33193–33196
Peterson YK, Hazard S III, Graber SG, Lanier SM (2002) Identification of structural features in the G-protein regulatory motif required for regulation of heterotrimeric G-proteins. J Biol Chem 277:6767–6770
Pinxteren JA, O’Sullivan AJ, Tatham PE, Gomperts BD (1998) Regulation of exocytosis from rat peritoneal mast cells by G protein beta gamma-subunits. EMBO J 17:6210–6218
Pizzinat N, Takesono A, Lanier SM (2001) Identification of a truncated form of the G-protein regulator AGS3 in heart that lacks the tetratricopeptide repeat domains. J Biol Chem 276:16601–16610
Repke H, Bienert M (1987) Mast cell activation—a receptor-independent mode of substance P action? FEBS Lett 221:236–240
Reynolds NK, Schade MA, Miller KG (2005) Convergent, RIC-8-dependent G{alpha} signaling pathways in the caenorhabditis elegans synaptic signaling network. Genetics 169:651–670
Ribas C, Takesono A, Sato M, Hildebrandt JD, Lanier SM (2002) Pertussis toxin-insensitive activation of the heterotrimeric G-proteins Gi/Go by the NG108-15 G-protein activator. J Biol Chem 277:50223–50225
Ross EM, Higashijima T (1994) Regulation of G-protein activation by mastoparans and other cationic peptides. Methods Enzymol 237:26–37
Ross EM, Wilkie TM (2000) GTPase-activating proteins for heterotrimeric G proteins: regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) and RGS-like proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 69:795–827
Rupnik M, Law GJ, Mason WT, Zorec R (1997) Mastoparan and Rab3AL peptide potentiation of calcium-independent secretory activity in rat melanotrophs is inhibited by GDPβS. FEBS Lett 411:356–358
Saraste M, Sibbald PR, Wittinghofer A (1990) The P-loop—a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 15:430–434
Sato M, Kataoka R, Dingus J, Wilcox M, Hildebrandt J, Lanier SM (1995) Factors determining specificity of signal transduction by G-protein-coupled receptors. IV. Regulation of signal transfer from receptor to G-protein. J Biol Chem 270:15269–15276
Sato M, Ribas C, Hildebrandt JD, Lanier SM (1996) Characterization of a G-protein activator in the neuroblastoma-glioma cell hybrid NG108-15. J Biol Chem 271:30052–30060
Sato M, Gettys TW, Lanier SM (2004) AGS3 and signal integration by Galpha(s)- and Galpha(i)-coupled receptors: AGS3 blocks the sensitization of adenylyl cyclase following prolonged stimulation of a Galpha(i)-coupled receptor by influencing processing of Galpha(i). J Biol Chem 279:13375–13382
Schade MA, Reynolds NK, Dollins CM, Miller KG (2005) Mutations that rescue the paralysis of caenorhabditis elegans ric-8 (Synembryn) mutants activate the G{alpha}s pathway and define a third major branch of the synaptic signaling network. Genetics 169:631–649
Schaefer M, Shevchenko A, Shevchenko A, Knoblich JA (2000) A protein complex containing Inscuteable and the Galpha-binding protein Pins orients asymmetric cell divisions in Drosophila. Curr Biol 10:353–362
Schaefer M, Petronczki M, Dorner D, Forte M, Knoblich JA (2001) Heterotrimeric G proteins direct two modes of asymmetric cell division in the Drosophila nervous system. Cell 107:183–194
Scott JK, Huang SF, Gangadhar BP, Samoriski GM, Clapp P, Gross RA, Taussig R, Smrcka AV (2001) Evidence that a protein-protein interaction ‘hot spot’ on heterotrimeric G protein betagamma subunits is used for recognition of a subclass of effectors. EMBO J 20:767–776
Seifert R, Hageluken A, Hoer A, Hoer D, Grunbaum L, Offermanns S, Schwaner I, Zinge V, Schunack W, Schultz G (1994) The H1 receptor agonist 2-(3-chlorophenyl) histamine activates Gi proteins in HL-60 cells through a mechanism that is independent of known histamine receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol 45:578–586
Siderovski DP, Diverse-Pierluissi M, De Vries L (1999) The GoLoco motif: a Galphai/o binding motif and potential guanine-nucleotide exchange factor. Trends Biochem Sci 24:340–341
Smine A, Xu X, Nishiyama K, Katada T, Gambetti P, Yadav SP, Wu X, Shi YC, Yasuhara S, Homburger V, Okamoto T (1998) Regulation of brain G-protein Go by Alzheimer’s disease gene presenilin-1. J Biol Chem 273:16281–16288
Snow BE, Hall RA, Krumins AM, Brothers GM, Bouchard D, Brothers CA, Chung S, Mangion J, Gilman AG, Lefkowitz RJ, Siderovski DP (1998) GTPase activating specificity of RGS12 and binding specificity of an alternatively spliced PDZ (PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1) domain. J Biol Chem 273:17749–17755
Spicer J, Ashworth A (2004) LKB1 kinase: master and commander of metabolism and polarity. Curr Biol 14:R383–R385
Srinivasan DG, Fisk RM, Xu H, van den Heuvel S (2003) A complex of LIN-5 and GPR proteins regulates G protein signaling and spindle function in C. elegans. Genes Dev 17:1225–1239
St Croix B, Rago C, Velculescu V, Traverso G, Romans KE, Montgomery E, Lal A, Riggins GJ, Lengauer C, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (2000) Genes expressed in human tumor endothelium. Science 289:1197–1202
Stow JL, de Almeida JB, Narula N, Holtzman EJ, Ercolani L, Ausiello DA (1991) A heterotrimeric G protein, G alpha i-3, on Golgi membranes regulates the secretion of a heparan sulfate proteoglycan in LLC-PK1 epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 114:1113–1124
Strader CD, Sigal IS, Dixon RA (1989) Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J 3:1825–1832
Strittmatter SM, Valenzuela D, Sudo Y, Linder ME, Fishman MC (1991) An intracellular guanine nucleotide release protein for Go. GAP-43 stimulates isolated alpha subunits by a novel mechanism. J Biol Chem 266:22465–22471
Sugai M, Saito M, Sukegawa I, Katsushima Y, Kinouchi Y, Nakahata N, Shimosegawa T, Yanagisawa T, Sukegawa J (2003) PTH/PTH-related protein receptor interacts directly with Tctex-1 through its COOH terminus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:24–31
Tai AW, Chuang JZ, Bode C, Wolfrum U, Sung CH (1999) Rhodopsin’s carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic tail acts as a membrane receptor for cytoplasmic dynein by binding to the dynein light chain Tctex-1. Cell 97:877–887
Takahashi H, Umeda N, Tsutsumi Y, Fukumura R, Ohkaze H, Sujino M, van der Horst G, Yasui A, Inouye ST, Fujimori A, Ohhata T, Araki R, Abe M (2003) Mouse dexamethasone-induced RAS protein 1 gene is expressed in a circadian rhythmic manner in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 110:1–6
Takasaki J, Saito T, Taniguchi M, Kawasaki T, Moritani Y, Hayashi K, Kobori M (2004) A novel Galphaq/11-selective inhibitor. J Biol Chem 279:47438–47445
Takesono A, Cismowski MJ, Ribas C, Bernard M, Chung P, Hazard S III, Duzic E, Lanier SM (1999) Receptor-independent activators of heterotrimeric G-protein signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 274:33202–33205
Takesono A, Nowak MW, Cismowski M, Duzic E, Lanier SM (2002) Activator of G-protein signaling 1 blocks GIRK channel activation by a G-protein-coupled receptor: apparent disruption of receptor signaling complexes. J Biol Chem 277:13827–13830
Tall GG, Krumins AM, Gilman AG (2003) Mammalian Ric-8A (synembryn) is a heterotrimeric Galpha protein guanine nucleotide exchange factor. J Biol Chem 278:8356–8362
Tomita U, Takahashi K, Ikenaka K, Kondo T, Fujimoto I, Aimoto S, Mikoshiba K, Ui M, Katada T (1991) Direct activation of GTP-binding proteins by venom peptides that contain cationic clusters within their alpha-helical structures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 178:400–406
Toutant M, Aunis D, Bockaert J, Homburger V, Rouot B (1987) Presence of three pertussis toxin substrates and Go alpha immunoreactivity in both plasma and granule membranes of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett 215:339–344
Traver S, Splingard A, Gaudriault G, De Gunzburg J (2004) The RGS (regulator of G-protein signalling) and GoLoco domains of RGS14 co-operate to regulate Gi-mediated signalling. Biochem J 379:627–632
Tu Y, Wu C (1999) Cloning, expression and characterization of a novel human Ras-related protein that is regulated by glucocorticoid hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta 1489:452–456
Vaidyanathan G, Cismowski MJ, Wang G, Vincent TS, Brown KD, Lanier SM (2004) The Ras-related protein AGS1/RASD1 suppresses cell growth. Oncogene 23:5858–5863
Vargiu P, Morte B, Manzano J, Perez J, de Abajo R, Gregor Sutcliffe J, Bernal J (2001) Thyroid hormone regulation of rhes, a novel Ras homolog gene expressed in the striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 94:1–8
Vargiu P, De Abajo R, Garcia-Ranea JA, Valencia A, Santisteban P, Crespo P, Bernal J (2004) The small GTP-binding protein, Rhes, regulates signal transduction from G protein-coupled receptors. Oncogene 23:559–568
Vos MD, Ellis CA, Bell A, Birrer MJ, Clark GJ (2000) Ras uses the novel tumor suppressor RASSF1 as an effector to mediate apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275:35669–35672
Voss T, Wallner E, Czernilofsky AP, Freissmuth M (1993) Amphipathic alpha-helical structure does not predict the ability of receptor-derived synthetic peptides to interact with guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem 268:4637–4642
Watts VJ (2002) Molecular mechanisms for heterologous sensitization of adenylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 302:1–7
Webb CK, McCudden CR, Willard FS, Kimple RJ, Siderovski DP, Oxford GS (2005) D2 dopamine receptor activation of potassium channels is selectively decoupled by Galpha-specific GoLoco motif peptides. J Neurochem 92:1408–1418
Weissman JT, Ma JN, Essex A, Gao Y, Burstein ES (2004) G-protein-coupled receptor-mediated activation of rap GTPases: characterization of a novel Galphai regulated pathway. Oncogene 23:241–249
Willard FS, Kimple RJ, Siderovski DP (2004) Return of the GDI: the GoLoco motif in cell division. Annu Rev Biochem 73:925–951
Winkler DG, Johnson JC, Cooper JA, Vojtek AB (1997) Identification and characterization of mutations in Ha-Ras that selectively decrease binding to cRaf-1. J Biol Chem 272:24402–24409
Yamaguchi T, Nagahama M, Itoh H, Hatsuzawa K, Tani K, Tagaya M (2000) Regulation of the golgi structure by the alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. FEBS Lett 470:25–28
Yamaguchi Y, Katoh H, Mori K, Negishi M (2002) Galpha(12) and Galpha(13) interact with Ser/Thr protein phosphatase type 5 and stimulate its phosphatase activity. Curr Biol 12:1353–1358
Yao L, McFarland K, Fan P, Jiang Z, Inoue Y, Diamond I (2005) Activator of G protein signaling 3 regulates opiate activation of protein kinase A signaling and relapse of heroin-seeking behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:8746–8751
Yen KM (1998) Mammalian blood loss-induced gene, kd312. US Patent #6,462,177
Yu F, Morin X, Cai Y, Yang X, Chia W (2000) Analysis of partner of inscuteable, a novel player of Drosophila asymmetric divisions, reveals two distinct steps in inscuteable apical localization. Cell 100:399–409
Zarling AL, Ficarro SB, White FM, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Engelhard VH (2000) Phosphorylated peptides are naturally processed and presented by major histocompatibility complex class I molecules in vivo. J Exp Med 192:1755–1762
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by MH90531 (S.M.L.) and NS24821 (S.M.L.). S.M.L. is greatly appreciative for this support and that provided by the David R. Bethune/Lederle Laboratories Professorship in Pharmacology and the Research Scholar Award from Yamanouchi Pharmaceutical Company. The authors acknowledge the ongoing discussions with Dr. Emir Duzic (Cephalon) and the continuous input provided for this endeavor over the years by the many fellows and students who have spent time in the laboratory and the many colleagues with whom we have had the pleasure of working and publishing. We thank Yuri Peterson for allowing us to adapt Figs. 6 and 7 from his thesis. We also express our thanks to Dr. Offermans and the editorial board of the Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology for the opportunity to make this contribution to the journal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cismowski, M.J., Lanier, S.M. Activation of heterotrimeric G-proteins independent of a G-protein coupled receptor and the implications for signal processing. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10254-005-0042-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10254-005-0042-z