Abstract
Wind-generated ocean waves are key inputs for several studies and applications, both near the coast (coastal vulnerability assessment, coastal structures design, harbor operativity) and off-shore (a.o. oil and gas production, ship routes, and navigation safety). As such, the evaluation of trends in future wave climate is fundamental for the development of efficient policies in the framework of climate change adaptation and mitigation measures. This study focuses on the Mediterranean Sea, an area of primary interest, since it plays a crucial role in the worldwide maritime transport and it is highly populated along all its coasts. We perform an analysis of wave climate changes using an ensemble of 7 models under emission scenario RCP8.5, over the entire Mediterranean basin. Future projections of wave climate and their variability are analyzed taking into account annual statistics of wave parameters, such as significant wave height, mean period, and mean direction. The results show, on average, a decreasing trend of significant wave height and mean period, while the wave directions may be characterized by a slight eastward shift.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Since the dawn of human history, many civilizations thrived along the shores of the Mediterranean Sea (MS), deriving sustenance from its resources, and trading and spreading across its waters. Until present times, this basin retained a prominent role in the development of human culture and economy. Today, about half billion people live along the Mediterranean shores, with consequent concentration of critical infrastructures and sites of cultural heritage. About 20% of the world’s seaborne commerce, and 10% of the container traffic pass through the MS, making it one of the busiest seas in the world (Leone 2017). Therefore, a detailed knowledge and monitoring of oceanographic variables in this basin is of foremost importance. In particular, gravity waves play a relevant role on several aspects of ocean and coastal dynamics. They are one of the main drivers of coastal erosion and accretion (De Leo et al. 2016; Harley et al. 2017; Mentaschi et al. 2018). Extreme and multi-modal sea states can pose a threat to the safety of navigation and to coastal structures (Soares and Teixeira 2001; de Osés and Castells 2008; Ventikos et al. 2018). Wave setup and runup contribute to the extreme sea levels that drive coastal floods (Didier et al. 2015; De Leo et al. 2019) and coastal erosion (Shih et al. 1995; Ruggiero et al. 2001), together with storm surges and tides (e.g., Cazenave and Cozannet 2014; Melet et al.2018).
According to projections of future climate, the ongoing sea level rise (SLR) will increase the magnitude and frequency of coastal hazard worldwide (Hinkel et al. 2014; Vousdoukas et al. 2018). However, local increases/decreases in wave height and periods or directional shifts of waves could exacerbate or mitigate this tendency. The important question of understanding how the wave climate will evolve in view of future climate changes has been tackled by a number of research groups worldwide, which in the last decade started coordinating their efforts within the Coordinated Ocean Waves Climate Project (COWCLIP, www.cowclip.org). Among the existing global and large-scale studies, it is worth mentioning the joint COWCLIP analyses (Hemer et al. 2013; Morim et al. 2019; Morim et al. 2020a), as well as the publications of individual research groups on mean wave climate and on the extremes (e.g., Mori et al. 2010; Semedo et al.2012; Hemer et al. 2013; Wang et al. 2014; Perez et al. 2015; Shimura et al. 2016; Aarnes et al. 2017; Mentaschi et al. 2017; Bricheno and Wolf 2018). On the basis of global altimetry Young and Ribal (2019), and earlier Young et al. (2011), produced analyses of the global historical trends of significant wave height (Hs). Other authors estimated how changes in wave climate will translate into wave setup and wave runup along the world’s coasts (Vousdoukas et al. 2018; Melet et al. 2019). These studies shed light on the present and future changes of wave climate and on their consequences; however, they lack the spatial resolution for a comprehensive analysis in smaller basins or at a regional scale. Few studies were developed specifically for the MS or its sub-basins, notably the work of De Leo et al. (2020), the pioneering work by Lionello et al. (2008), based on a single model with a resolution of 50 km, and the study by Casas-Prat and Sierra (2013), limited to the northwestern Mediterranean. The advancement of our knowledge of local basins is the objective of a specific task of the COWCLIP initiative, dedicated to the development and intercomparison of comprehensive regional projections.
This contribution aims to improve our understanding of the future changes of wave climate in the MS, within the framework of the regional projection task of the COWCLIP initiative. We carried out wave simulations with the model Wavewatch III (WW3DG 2019) with a resolution of about 10 km in longitude and latitude, forced by an ensemble of 7 Euro-CORDEX regional models (Jacob et al. 2014) in Representative Concentration Pathway (RCP) scenario RCP8.5 (Van Vuuren et al. 2011). Then, we computed some annual statistics of the expected future significant wave height {Hs}, mean period {Tm}, and mean direction {θm}, and studied the relative trends. Section 2 describes the regional climate models (RCM) and wave model used to derive the projections of future wave climate in the Mediterranean, along with the analysis employed to characterize trends in wave parameters. Results are outlined and discussed in Section 3, followed by conclusions in Section 4.
2 Data and methods
2.1 CORDEX-Forced regional wave model
Simulations for future wave climate conditions in the MS were performed employing the third-generation wave model WavewatchIII v5.16 with a resolution of 0.127∘ in longitude and 0.09∘ in latitude, corresponding to about 10 km, and a time output for all the wave bulk variables equal to 3 h. The model was implemented with the ST4 source term (Ardhuin et al. 2010), and a setup similar to that employed by Mentaschi et al. (2015) for the implementation and validation of a wave hindcast in the MS.
The future projections of wave climate were forced by seven different Euro-CORDEX climate projections under scenario RCP8.5 (see Table 1). These RCM were chosen due to their relatively high resolution (11 km), which is needed to resolve adequately the complex orography and geography of the MS. A similar assumption motivated the studies of Bricheno et al. (2013) and Menendez et al. (2014), who showed that an improved accuracy is achieved in coastal waters and in the MS owing to the regional downscaling of wind forcing. Due to the uncertainties inherent in modeling future climate, we opted to develop an ensemble approach employing seven different RCM in order to exhaustively investigate the variability of future projections of wave climate. Simulations available for control (historical) period and RCP8.5 scenario were carried out for the time slices 1970–2005 and 2006–2100, respectively, saving the maps (i.e., gridded fields) of Hs, Tm, and θm every 3 h along with other variables over the entire MS. The historical output of each ensemble member, for each of the analyzed variables, was compared with hindcast values (Mentaschi et al. 2013, 2015) to assess the performance of the models. The hindcast was developed on the same computational grid used for the RCM projections, and provides hourly data of wave parameters in the 1979–2019 period. The common time slice 1979–2005 was used for the comparison: first, the time series of Hs and Tm were averaged over the whole period, resulting in a single data point for each node. Then, for each ensemble member, we computed the maps of the bias and the spatial correlation among the nodes between the hindcast and the RCM data.
2.2 Trend analysis
The annual means, annual 90th percentiles, and annual maxima of Hs and Tm were computed for each grid point using the COWCLIP utility getStat. The annual means of θm were computed instead with the utility getStatDir (Morim et al. 2020b). For the sake of brevity, the series of annual mean Hs, annual 90th percentile Hs, and annual maxima Hs are hereon referred to as \(H_{s}^{mean}\), \(H_{s}^{p90}\), and \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), respectively. A similar notation is used for the time series of Tm statistics. The yearly ensemble values were then computed as the mean over the seven models. As for θm, the arithmetic mean was first computed on the components projected into Cartesian coordinates, then it was subsequently converted back to polar coordinates (Fisher 1995). Such an approach allows to account for the discontinuity in the 0/2π space: given a series of n directions \(\theta _{m_{j}}\), the circular mean can be defined as:
In case of the θm time series, the computation of the ensenmble mean values took advantage of the CircStat Matlab toolbox (Berens et al. 2009).
Then, analyses of wave climate changes were performed on the 2006–2100 time series, that is, for the future time slice. First, trends on the time series of Hs and Tm annual statistics were quantified through the slope of the respective best linear fit. In this work, we employed the Theil-Sen’s slope (Sen 1968, Theil 1992), henceforth referred to as b. Given a series of xi data (i = 1...n, n being the number of samples), its computation reads:
where xj and xl are the jth and lth data of the series, respectively. Then, the (1-α) confidence interval of b was computed according to Hollander et al. (2013):
where Φ denotes the inverse of the standard normal distribution, and N is the number of slopes related to the n(n − 1)/2 possible pairs of sample points; this computation was performed through the Matlab built-in function provided by Burkey (2006). The confidence interval of b allows assessing whether the computed trend is significant or not. Namely, if a change of sign occurs between b+ (the upper confidence level) and b− (the lower confidence level), this may indicate that the data are too dispersed to compute a reliable linear trend.
As a second step, the estimates of b were analyzed in the context of the Mann-Kendall test (Mann 1945; Kendall 1955). This test allows to check whether an either upward or downward monotonic trend is present within a dataset on the basis of the test p value, computed as:
said pMK the p value related to the Mann-Kendall test, and ZMK being the test statistic, that depends on the ranks of the data within the series they belong to. The values of pMK can be used to evaluate whether the data behave consistently with the hypothesis that there is no trend (pMK close to 1) or, at the opposite, that a trend affects the data (pMK close to 0). Such a combined use of b and pMK was already used by De Leo et al. (2020) that showed how to use these information jointly to strengthen the analysis of long-term trends on time series of Hs data.
Furthermore, the present work referred to the innovative trend analysis (referred to as ITA, Şen 2011, 2013), a simple and intuitive graphical analysis. Given a time series of data, the ITA implies selecting two subsets of equal length belonging to successive time periods. These subsets are subsequently sorted in ascending order, and plotted versus each other in a common range. If the resulting scatters lie entirely above (below) the 45∘ straight line, the existence of a positive (negative) trend can be deduced. An example of the ITA for three synthetic datasets characterized by different trends is shown in Fig. 1. In this case, the sorted subsets are referred to as x1 (belonging to the earlier time slice) and x2 (belonging to the later time slice).
Here, the annual statistics of Hs and Tm were averaged across all the computational nodes, leading to the regional mean annual statistics of the parameters at hand. Then, the data of 2010–2040 and 2070–2100 time slices were selected and compared according to the ITA, to get further indications on the future trends of Hs and Tm. Similarly to De Leo et al. (2020), the trend magnitude resulting from the ITA was assessed computing the distances (hereinafter referred to as δ) of the scatters with respect to the 45∘ straight line (which identifies the absence of trend). Positive and negative trends can be therefore discussed in terms of the empirical cumulative distribution function (ecdf) of delta, and of its position relative to the 45∘ line. The ITA should be carefully used, as to rely only on this test could lead to wrong conclusions (Serinaldi et al. 2020). However, in this work, the outcomes related to three different tests were compared, in order to discuss and strengthen the outcomes related to each single method.
Besides the statistical significance of the trend, in a study on climate projections it is important to assess the consistency of the projected changes across the ensemble (Knutti and Sedláček 2013). In this work, this has been accomplished by evaluating the number of ensemble members indicating either positive or negative trends at each point of the computational grid. Finally, \(\theta _{m}^{mean}\) was investigated by means of polar plots of the time series at six locations, selected in different sub-basins of the MS.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Analysis of historical wave climate simulations
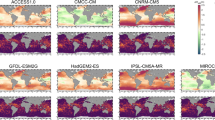
First, the historical wave climate in the MS driven by each of the RCM was compared to the hindcast data developed and validated by Mentaschi et al. (2013) and Mentaschi et al. (2015). Attached in the A are the comparison maps for Hs (Figs. 19, 20, and 21) and Tm (Figs. 22, 23, and 24), which show the different spatial patterns of the biases models-hindcast. The maps also show the mean biases averaged over the MS. In case of the Hs statistics, the mean biases are between [− 15.3%,− 1.8%], [− 6.8%,7.7%], and [− 15.9%,3.8%] for \(H_{s}^{mean}\), \(H_{s}^{p90}\), and \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), respectively. When the annual statistics of Tm are considered, the mean biases attain values between [− 0.9%,6%] (\(T_{m}^{mean}\)), [− 2.7%,5.6%] (\(T_{m}^{p90}\)), and [− 5.6%,6%] (\(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\)). Table 2 reports the spatial correlations between the hindcast and the RCM data, computed through Pearson’s coefficient. The high values of the spatial correlation indicate that the spatial patterns are adequately captured by each model, for all the examined parameters and statistics. Altogether, these results show the ability of the models to reproduce reasonably well the wave dynamics on the historical period.
3.2 Analysis of trends on the future wave climate
First, the trends were computed on the ensemble time series of each wave parameter for each grid point. Trend analysis could be also performed directly on the series related to each single ensemble member, averaging the trend metrics at a second time. Such approach will be discussed in the second part of this section.
Figure 2 summarizes the values of b related to Hs and Tm. First of all, it can be noticed how for all the examined statistics the vast majority of highlighted trends is negative, indicating an average reduction in the expected future wave parameters. According to the boxplots, positive values of b (i.e., upward trends) lie always above the upper bars, which denote the 75th percentile of the whole series. Moreover, the highest positive trends are generally less pronounced than the negative ones, especially as far as annual maxima data are concerned. Besides, the boxplots of Fig. 2 also reveal that the variability of b among the grid nodes increases with the order (mean, p90, and maxima) of the annual statistic considered. This can be clearly noticed by looking at the whiskers outside the upper and lower quartiles of the boxes, and leaves room for a further consideration: annual maxima data are more dispersed with respect to the annual lower percentiles, since the latter are influenced by mild sea states which, being more frequent, matter the most. This affects the estimations of b which show a higher variability for the annual maxima than for the other two statistics.
The aforementioned considerations are confirmed by the spatial distribution of b in the MS, as reported in Fig. 3. In this case, positive and negative values of b were linearly scaled in the [0,1] and [− 1,0] ranges, respectively, to better compare the trends location rather than the trends magnitude. To this end, we used the general formula:
where U and L denote the upper and lower values of the desired range, respectively; \(b_{\min \limits }\) and \(b_{\max \limits }\) indicate the minimum and the maximum values in the dataset of b, respectively.
Similarities can be appreciated in the spatial distribution of upward trends for \(H_{s}^{mean}\) and \(H_{s}^{p90}\) (panels A and C) and \(T_{m}^{mean}\) and \(T_{m}^{p90}\) (panels B and D), where positive values of b mainly characterize two areas in the Aegean Sea and close to the strait of Gibraltar. On the other hand, the most negative trends for \(H_{s}^{mean}\) and \(H_{s}^{p90}\) are located around the Balearic islands, in the southern part of the Ionian Sea and in the South-East Mediterranean basin around Cyprus. As for Tm, the lowest values of b (i.e., the strongest downward trends) are found in the west coast of Greece and Crete. The weakest trends for annual mean and annual 90th percentile series of both Hs and Tm are located in the Adriatic Sea, the North Tyrrhenian Sea, the Aegean Sea (but a small area characterized by positive trends, as previously highlighted) and east of the Tunisia coastline. When annual maxima are taken into account, the spatial distribution of expected trends becomes much more irregular (panels E and F for \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\) and \(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\), respectively). Positive trends are scattered over isolated spots in the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian Sea and off the south coast of Tunisia, while no broad areas uniformly characterized by significantly low values of b can be detected.
Figure 3 allows assessing where trends characterized by different magnitude are most likely expected to take place, but it does not provide any information about their significance. To this end, the reliability of the b estimates was further evaluated looking at their 90% confidence interval, and coupling this information with the values of pMK computed on the respective time series, as explained in Sect. 2. Results related to the Hs annual statistics are presented in Fig. 4, while results related to the Tm annual statistics are presented in Fig. 5. The locations showing a change of sign between the upper and the lower confidence intervals of b are underlined in the leftmost side of the figures.
Significance of trends for the time slice 2006–2100. Panels A, C, and E highlight the grid nodes where b+ and b− show opposite sign for \(H_{s}^{mean}\), \(H_{s}^{p90}\), and \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), respectively; panels B, D, and F show the values of pMK for each grid node and \(H_{s}^{mean}\), \(H_{s}^{p90}\), and \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), respectively
Significance of trends for the time slice 2006–2100. Panels A, C, and E highlight the grid nodes where b+ and b− show opposite sign for \(T_{m}^{mean}\), \(T_{m}^{p90}\), and \(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\), respectively; panels B, D, and F show the values of pMK for each grid node and \(T_{m}^{mean}\), \(T_{m}^{p90}\), and \(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\), respectively
As regards \(H_{s}^{mean}\) and \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), the areas characterized by non-significant trends are similarly located. In particular, attention is posed to the strait of Gibraltar and the Aegean Sea, being characterized by widespread marked areas (panels A and C of Fig. 4). A majority of the time series within such areas are in turn characterized by close-to-1 values of pMK, indicating the absence of a significant trend. A similar result characterizes the upward trends of \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\) (panels E and F of Fig. 4). In fact, positive values of b in the Adriatic and in broad areas to the east of Tunisia and the Ionian Sea, are associated to change of sign between the respective b− and b+. A clear correlation exists also when negative trends are considered, that is, the values of b closest to 0 occur jointly with high values of pMK and no significant trends (e.g., in the southeast Mediterranean basin, the areas to the east of the Balearic islands, and in the North Tyrrhenian Sea).
As regards the time series of Tm (Fig. 5), most of the positive trends in the Aegean Sea are still found to be not significant in case of annual mean (panels A and B) and annual 90th percentile (panels C and D). An exception is the area close to the Strait of Gibraltar, where positive trends of \(T_{m}^{mean}\) are significant, while in case of \(T_{m}^{p90}\) a majority of the locations are characterized by negligible trends. For both the statistics considered, trends in the North-Tyrrhenian east of Corsica and Sardinia are generally not relevant, and these are indeed related to low values of b (reference is made to panels B and D of Fig. 3). When the time series of \(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\) are considered (panels E and F), the locations showing not significant trends are concentrated in the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian Sea, the Aegean Sea, and the southeast basin of the Mediterranean Sea.
Given that the wave model was only forced by the RCM wind data, the trends previously highlighted are to be related to expected variations in the atmospheric circulation patterns. The MS is an enclosed basin at the mid-latitudes; thus, there is no environmental forcing affecting the wave climate as much as the wind (for instance, swells generated elsewhere or variation in the ice coverage). Overall, the results presented so far indicate a widespread decrease in the future wave heights and periods over the MS, and this seems to be consistent with expected decreases in the surface wind speed in this area, as shown for example by Mori et al. (2013) and Casas-Prat et al. (2018) (even though the latter considered a shorter period for the future projection, i.e., 2081–2100).
It can be clearly noticed that, when annual maxima are taken into account, the number of locations where trends are not significant increases dramatically (panels E and F in Figs. 4 and 5). This is due to the fact that the most negative trends are concentrated in isolated spots (as shown in panels E and F of Fig. 3); thus, it is difficult to detect homogeneous behaviors at basin level, compared with \(T_{m}^{mean}\) and \(T_{m}^{p90}\). Moreover, annual maxima refer to single instantaneous values per year, resulting in noisier datasets. Even though the methodology of Sen (1968) and Theil (1992) is sound with respect to possible outliers, this affects the computation of the confidence intervals, often leading to not significant trends.
In addition to the analysis so far described, as a compulsory step in the evaluation of the significance of the projected changes, we looked at the consistency of the trends related to the each single ensemble member. To this end, we computed the number of members resulting in concordant/discordant values of b for all the time series analyzed. Such number ranges from 7−, meaning that all the models present negative trends, to 7+ (all the models presenting positive trends). Results are shown in Fig. 6.
A small stripe of fully consistent positive trends is found in the South Aegean Sea for \(H_{s}^{mean}\) and \(H_{s}^{p90}\), which exactly overlap with the locations characterized by significant upward trends according to panels A, B, C, and D of Fig. 4. When annual maxima are considered, there are instead no locations characterized by positive trends according to all the members. On the contrary, broad areas of fully consistent negative trends are placed in the South Tyrrhenian, and off the southern coastlines of Spain up to the westmost side of the Mediterranean Sea, consistent with results reported in panels E and F of Fig. 4. In case of \(T_{m}^{mean}\), a remarkable correlation can be noticed between the areas close to the Strait of Gibraltar, being characterized by significant positive trends according to both the approaches. Extending the analysis to \(T_{m}^{p90}\), a wide area east of Sardinia shows poor agreement among the ensemble members (panels C and D of Fig. 6), and this is exactly corresponding to the areas characterized by not significant trends underlined in panels A, B, C, and D of Fig. 5. Again, results related to the time series of annual maxima show a much more irregular spatial distribution (see panels E and F of Fig. 6).
As a further step, b was computed on the series of the 2006–2100 annual statistics averaged over the entire MS (i.e., across all the hindcast nodes taken into account), to derive an insight on the expected variation in the regional future wave climate. The ensemble values of regional b were carried out in 2 ways: (a) computing the slope of the ensemble values of the wave parameters. This estimate is hereinafter referred to as br1; (b) computing the slope separately for each ensemble member, and then averaging on the ensemble members. This estimate is hereinafter referred to as br2.
Figures 7, 8, and 9 show the time series of the regional Hs statistics, while Figs. 10, 11, and 12 show the regional statistics relative to Tm. In all the panels, the whole period covered by the models (1970–2100) is shown, along with the historical series computed from the hindcast developed and validated by Mentaschi et al. (2015). It can be seen from the orange lines in Figs. 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12 that the hindcast series fall within the envelopes of the simulated ensembles for both Hs and Tm. Accordingly, the trends computed on the hindcast series are within the ranges provided by the estimates of b related to the ensemble members and summarized in Table 4 (see the Appendix), and serve to confirm the validity of the simulation models in producing reliable future wave climate projections. Results of br1 and br2 are reported in Table 3.
From Figs. 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12, it is clear at a glance that the regional time series of the investigated parameters are characterized by a downward trend. This finding can be also verified by the ITA, performed over the mean data of the regional averaged statistics (i.e., the black lines in Figs. 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, and 12) for two different time periods, 2010–2040 and 2070–2100. Results are shown in Figs. 13 and 14. The ITA on the regional \(T_{m}^{mean}\), \(T_{m}^{p90}\), and \(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\) series reveals negative trends, as the scatters of the 2010–2040 period lie below the no-trend line. Similarly, the series of regional \(H_{s}^{mean}\) and \(H_{s}^{p90}\) show negative trends. As for the series of regional \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), the ITA seems to be noisier, with a couple of data being above the no-trend line, though a clear negative trend can be pointed out also in this case.
Differences in the trends according to the ITA can be better appreciated by looking at the ecdf of δ, as shown in Fig. 15. Here, it can be noticed how the δ related to the annual maxima are generally farther from the zero line with respect to the other statistics, indicating a stronger negative trend. Similarly, the 90th percentile series are characterized by a trend more negative than the mean data. This particularly applies to the series of regional Hs (panel A), while in case of Tm the ITA trends are more similar among the investigated statistics (panel B). Such finding is further supported by the results of br1 and br2, which show values increasing from the annual mean to the annual maxima.
These results show also that the differences between br1 (trends computed on the parameters averaged across the models) and br2 (trends computed as mean of the single model trends) are small. Indeed, the highest difference is observed for the time series of regional \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\), where using br1 (br2) would result in a variation of − 24.4 cm (− 27.3 cm) between 2006 and 2100.
Finally, the mean direction \(\theta _{m}^{mean}\) was considered. The trend analysis was carried out on the time series averaged over the whole MS, as shown in Fig. 16. Here, all the ensemble members agree on a slight clockwise shift.
A more detailed analysis was performed on six locations selected among different sub-basins of the MS, plotting the \(\theta _{m}^{mean}\) series versus the respective years on a polar plot, along with the best linear fit. The investigated locations and the correspondent polar plots are shown in Figs. 17 and 18, respectively.
Polar plots of 2006–2100 time series of \(\theta _{m}^{mean}\) in the test locations. The red line represents the linear fit of \(\theta _{m}^{mean}\) series with respect to the corresponding years. Panels are labeled according to the letters reported in Fig. 17
On average, an eastward trend seems to characterize the wave directions at locations A, D, and E, corresponding to the Gibraltar, South Mediterranean, and the Aegean basin, respectively. Conversely, no trends can be highlighted at location B (North Tyrrhenian Sea) and F (in front of the Nile Delta), while at location C scatters seem to be too dispersed to derive a reliable trend analysis, even though an anti-clockwise shift can be pointed out. This is most likely due to the local climatology of the Adriatic Sea, which is influenced by several local circulation patterns, resulting in no prevailing fetches for the point at hand.
4 Conclusion
In this work, we performed a trend analysis on time series of wave parameters projected up to the end of the twenty-first century in the MS. To this end, we used wave simulations driven by seven RCM over the 1970–2100 period under the RCP8.5 emission scenario. The future trends on time series of annual mean, annual 90th percentile, and annual maxima wave heights and periods were assessed through the Theil-Sen slope and the Mann-Kendall test, while the analysis of the wave directions relied on the use of polar plots. As for Hs and Tm, the results show that the trend metrics employed are generally consistent with each other, indicating the robustness of the projected changes. Such consideration is further confirmed by the similarities in the spatial patterns of the b estimates computed either on the parameters averaged across the models, and as the mean of the trends resulting from each single model.
Overall, the analysis revealed that the wave climate of the MS will be mainly characterized by downward trends, implying a progressive reduction in the magnitude of wave heights and periods. These results are in line with previous studies developed under the same emission scenario at larger scale, both for annual mean (Perez et al. 2015) and annual maxima (Wang et al. 2014). The trends computed on the time series of annual mean and annual 90th percentile are characterized by similar magnitudes and similar spatial distributions. On the other hand, the trends of annual maxima are more uncertain and irregularly distributed through the basin, despite the fact that the slope generally attains higher values. This suggests that the annual maxima should be used with caution, as they could result in dispersed time series, and lead to unreliable estimations of future trends.
Finally, as far as wave direction is concerned, a slight eastward trend is expected, but such behavior is not homogeneous across the different sub-basins.
References
Aarnes OJ, Reistad M, Breivik Ø, Bitner-Gregersen E, Ingolf Eide L, Gramstad O, Magnusson AK, Natvig B, Vanem E (2017) Projected changes in significant wave height toward the end of the 21st century: Northeast Atlantic. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 122(4):3394–3403
Ardhuin F, Rogers E, Babanin AV, Filipot JF, Magne R, Roland A, Van Der Westhuysen A, Queffeulou P, Lefevre JM, Aouf L et al (2010) Semiempirical dissipation source functions for ocean waves. Part I: definition, calibration, and validation. J Phys Oceanogr 40(9):1917–1941
Berens P et al (2009) Circstat: a Matlab toolbox for circular statistics. J Stat Softw 31(10):1–21
Bricheno LM, Soret A, Wolf J, Jorba O, Baldasano JM (2013) Effect of high-resolution meteorological forcing on nearshore wave and current model performance. J Atmos Ocean Technol 30(6):1021–1037
Bricheno LM, Wolf J (2018) Future wave conditions of Europe, in response to high-end climate change scenarios. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 123(12):8762–8791
Burkey J (2006) A non-parametric monotonic trend test computing Mann-Kendall tau, tau-b, and Sen’s slope written in Mathworks-Matlab implemented using matrix rotations. King County, Department of Natural Resources and Parks, Science and Technical Services Section: Seattle WA
Casas-Prat M, Sierra J (2013) Projected future wave climate in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 118(7):3548–3568
Casas-Prat M, Wang X, Swart N (2018) Cmip5-based global wave climate projections including the entire Arctic Ocean. Ocean Model 123:66–85
Cazenave A, Cozannet GL (2014) Sea level rise and its coastal impacts. Earth’s Future 2 (2):15–34
De Leo F, Besio G, Zolezzi G, Bezzi M (2019) Coastal vulnerability assessment: through regional to local downscaling of wave characteristics along the bay of Lalzit (Albania). Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 19(1):287–298
De Leo F, Besio G, Zolezzi G, Bezzi M, Floqi T, Lami I (2016) Coastal erosion triggered by political and socio-economical abrupt changes: the case of Lalzit Bay, Albania. Coastal Engineering Proceedings 35:13
De Leo F, De Leo A, Besio G, Briganti R (2020) Detection and quantification of trends in time series of significant wave heights: an application in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Eng 202:107155
de Osés FXM, Castells M (2008) Heavy weather in European short sea shipping: its influence on selected routes. Journal of Navigation 61(1):165–176. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0373463307004468. https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0373463307004468/type/journal_article
Didier D, Bernatchez P, Boucher-Brossard G, Lambert A, Fraser C, Barnett RL, Van-Wierts S (2015) Coastal flood assessment based on field debris measurements and wave runup empirical model. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 3(3):560–590
Fisher NI (1995) Statistical analysis of circular data. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Harley MD, Turner IL, Kinsela MA, Middleton JH, Mumford PJ, Splinter KD, Phillips MS, Simmons JA, Hanslow DJ, Short AD (2017) Extreme coastal erosion enhanced by anomalous extratropical storm wave direction. Scientific Reports 7(1):1–9
Hemer MA, Fan Y, Mori N, Semedo A, Wang XL (2013) Projected changes in wave climate from a multi-model ensemble. Nature Climate Change 3(5):471–476
Hemer MA, Katzfey J, Trenham CE (2013) Global dynamical projections of surface ocean wave climate for a future high greenhouse gas emission scenario. Ocean Model 70:221–245
Hinkel J, Lincke D, Vafeidis AT, Perrette M, Nicholls RJ, Tol RS, Marzeion B, Fettweis X, Ionescu C, Levermann A (2014) Coastal flood damage and adaptation costs under 21st century sea-level rise. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111(9):3292–3297
Hollander M, Wolfe DA, Chicken E (2013) Nonparametric statistical methods, vol 751. Wiley, New York
Jacob D, Petersen J, Eggert B, Alias A, Christensen OB, Bouwer LM, Braun A, Colette A, Déqué M, Georgievski G et al (2014) Euro-cordex: new high-resolution climate change projections for european impact research. Regional Environmental Change 14(2):563–578
Kendall MG (1955) Rank correlation methods
Knutti R, Sedláček J (2013) Robustness and uncertainties in the new cmip5 climate model projections. Nat Clim Chang 3(4):369
Leone G (2017) Mediterranean quality status report un environment programme
Lionello P, Cogo S, Galati M, Sanna A (2008) The Mediterranean surface wave climate inferred from future scenario simulations. Glob Planet Chang 63(2-3):152–162
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica. Journal of the Econometric Society 13:245–259
Melet A, Almar R, Hemer M, Le Cozannet G, Meyssignac B, Ruggiero P (2019) Contribution of wave setup to projected coastal sea level changes. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans 125 (8):e2020JC016078
Melet A, Meyssignac B, Almar R, Le Cozannet G (2018) Under-estimated wave contribution to coastal sea-level rise. Nat Clim Chang 8(3):234–239
Menendez M, García-Díez M, Fita L, Fernández J, Méndez F, Gutiérrez JM (2014) High-resolution sea wind hindcasts over the Mediterranean area. Climate dynamics 42(7-8):1857–1872
Mentaschi L, Besio G, Cassola F, Mazzino A (2013) Developing and validating a forecast/hindcast system for the Mediterranean Sea. Journal of Coastal Research 65:1551–1556
Mentaschi L, Besio G, Cassola F, Mazzino A (2015) Performance evaluation of Wavewatch III in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Model 90:82–94
Mentaschi L, Vousdoukas MI, Pekel JF, Voukouvalas E, Feyen L (2018) Global long-term observations of coastal erosion and accretion. Scientific Reports 8(1):1–11
Mentaschi L, Vousdoukas MI, Voukouvalas E, Dosio A, Feyen L (2017) Global changes of extreme coastal wave energy fluxes triggered by intensified teleconnection patterns. Geophys Res Lett 44(5):2416–2426
Mori N, Shimura T, Yasuda T, Mase H (2013) Multi-model climate projections of ocean surface variables under different climate scenarios—future change of waves, sea level and wind. Ocean Eng 71:122–129
Mori N, Yasuda T, Mase H, Tom T, Oku Y (2010) Projection of extreme wave climate change under global warming. Hydrological Research Letters 4:15–19
Morim J, Hemer M, Wang XL, Cartwright N, Trenham C, Semedo A, Young I, Bricheno L, Camus P, Casas-Prat M et al (2019) Robustness and uncertainties in global multivariate wind-wave climate projections. Nat Clim Chang 9(9):711–718
Morim J, Trenham C, Hemer M, Wang XL, Mori N, Casas-Prat M, Semedo A, Shimura T, Timmermans B, Camus P et al (2020) A global ensemble of ocean wave climate projections from cmip5-driven models. Scientific Data 7(1):1–10
Morim J, Trenham C, Hemer M, Wang XL, Mori N, Casas-Prat M, Semedo A, Shimura T, Timmermans B, Camus P et al (2020) A global ensemble of ocean wave climate projections from cmip5-driven models. Scientific Data 7(1):1–10
Perez J, Menendez M, Camus P, Mendez FJ, Losada IJ (2015) Statistical multi-model climate projections of surface ocean waves in Europe. Ocean Model 96:161–170
Ruggiero P, Komar PD, McDougal WG, Marra JJ, Beach RA (2001) Wave runup, extreme water levels and the erosion of properties backing beaches. Journal of Coastal Research 17(2):407–419
Semedo A, Weisse R, Behrens A, Sterl A, Bengtsson L, Günther H (2012) Projection of global wave climate change toward the end of the twenty-first century. J Clim 26(21):8269–8288
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63(324):1379–1389
Şen Z (2011) Innovative trend analysis methodology. J Hydrol Eng 17(9):1042–1046
Şen Z (2013) Trend identification simulation and application. J Hydrol Eng 19(3):635–642
Serinaldi F, Chebana F, Kilsby CG (2020) Dissecting innovative trend analysis. Stoch Env Res Risk A 34:1–22
Shih SM, Komar P, Tillotson K, McDougal W, Ruggiero P (1995) Wave run-up and sea-cliff erosion. In: Coastal engineering 1994, pp 2170–2184
Shimura T, Mori N, Hemer MA (2016) Variability and future decreases in winter wave heights in the Western North Pacific. Geophys Res Lett 43(6):2716–2722
Soares C, Teixeira A (2001) Risk assessment in maritime transportation. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 74(3):299–309. DOI10.1016/S0951-8320(01)00104-1. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0951832001001041
Theil H (1992) A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis. In: Henri Theil’s contributions to economics and econometrics, pp 345–381. Springer
Van Vuuren DP, Edmonds J, Kainuma M, Riahi K, Thomson A, Hibbard K, Hurtt GC, Kram T, Krey V, Lamarque JF et al (2011) The representative concentration pathways: an overview. Climatic Change 109(1-2):5
Ventikos N, Papanikolaou A, Louzis K, Koimtzoglou A (2018) Statistical analysis and critical review of navigational accidents in adverse weather conditions. Ocean Engineering 163 :502–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.06.001. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0029801818310011
Vousdoukas MI, Mentaschi L, Voukouvalas E, Verlaan M, Jevrejeva S, Jackson LP, Feyen L (2018) Global probabilistic projections of extreme sea levels show intensification of coastal flood hazard. Nature Communications 9(1):1–12
Wang XL, Feng Y, Swail VR (2014) Changes in global ocean wave heights as projected using multimodel cmip5 simulations. Geophys Res Lett 41(3):1026–1034
WW3DG TWIDG (2019) User manual and system documentation of Wavewatch III version 6.07. tech note 333. Tech. rep., NOAA/NWS/NCEP/MMAB
Young I, Zieger S, Babanin AV (2011) Global trends in wind speed and wave height. Science 332(6028):451–455
Young IR, Ribal A (2019) Multiplatform evaluation of global trends in wind speed and wave height. Science 364(6440):548–552
Acknowledgments
Numerical simulations of future wave climate projection have been partially supported by Iscra Class-C Project WACCS (project n. HP10CNB26B).
Funding
Open access funding provided by Università degli Studi di Genova within the CRUI-CARE Agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Val Swail
This article is part of the Topical Collection on the 16th International Workshop on Wave Hindcasting and Forecasting in Melbourne, AU, November 10–15, 2019
Appendix
Appendix
Mean of the 1979–2005 \(H_{s}^{mean}\) series according to the hindcast of Mentaschi et al. (2015) (panel A), and differences of the latter with the means of the ensemble members: panel B, CanESM2; panel C, MIROC5; panel D, MPI-ESM-LR; panel E, NorESM1-M; panel F, CNRM-CM5; panel G, IPSL-CM5A-MR; panel H, HadGEM2-ES
As in Fig. 19, for \(H_{s}^{p90}\)
As in Fig. 19, for \(H_{s}^{\max \limits }\)
As in Fig. 19, for \(T_{m}^{mean}\)
As in Fig. 19, for \(T_{m}^{p90}\)
As in Fig. 19, for \(T_{m}^{\max \limits }\)
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
De Leo, F., Besio, G. & Mentaschi, L. Trends and variability of ocean waves under RCP8.5 emission scenario in the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Dynamics 71, 97–117 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-020-01419-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10236-020-01419-8