Abstract
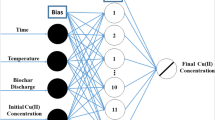
Two models were evaluated as alternative methods for predicting pyrite oxidation in the Alborz Sharghi coal washing waste pile (in northeastern Iran). The first model applies a ‘feed-forward artificial neural network (ANN) with 4-7-1 structure’. The model uses depth, initial remaining pyrite fraction, mole fraction of oxygen, and annual precipitation as input parameters and returns the remaining pyrite fraction in the related depth of the pile as its output. In the second model, an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS), which uses generalised bell membership functions and the Takagi–Sugeno-type fuzzy inference system, was applied with the same input–output parameters. The correlation coefficient, root mean squared error, and average absolute relative error for the training stage of the ANNs were 0.81, 0.169, and 0.12, respectively, while the values for ANFIS were 0.91, 0.091, and 0.078, respectively. Comparison of the correlation coefficients and the error parameters revealed that both models successfully predicted remaining pyrite fraction from various depths of the pile. However, ANFIS was found to be more reliable and more accurate.
Zusammenfassung
Zwei Modelle werden am Beispiel der Alborz-Shargi Kohlenwaschhalde als alternative Methoden zur Vorhersage von Pyritoxidationsprozessen beurteilt. Im ersten Modell werden vorwärtsbetriebene künstliche neurale Netze (ANN, „artificial neural network“) mit 4-7-1 Strukturen verwendet. Als Eingangsparameter gehen Tiefenangaben, die Anfangsmenge der Pyritfraktion, die Stoffmenge an Sauerstoff und der Jahresniederschlag in die Modelle ein. Berechnet wird die verbleibende Pyritmenge in verschiedenen Tiefen der Halde. Im zweiten Modell wird das ANFIS-Modell (Adaptives netzbasiertes Fuzzy Interface System) mit verallgemeinerter Glockenkurvenfunktion und dem Fuzzy System vom Takagi–Sugeno-Typ als Eingangs- bzw. Ausgangsparameter verwendet. Die zuerst genutzten Korrelationskoeffizienten, mittleren quadratischen Abweichungen und mittleren relativen Fehler betrugen für das ANN-Modell 0,81, 0,169 sowie 0,12 und für das ANFIS-Modell 0,91, 0,091 sowie 0,078. Der Vergleich der Korrelationskoeffizienten und der Fehlerparameter zeigt, dass beide Modelle die verbleibende Pyritfraktion in den jeweiligen Tiefen zufriedenstellend berechnen können. Die Ergebnisse des ANFIS Modells erscheinen jedoch verlässlicher.
Resúmen
Dos modelos fueron evaluados como métodos alternativos para predecir la oxidación de pirita en la pila de residuos del proceso de lavado de carbón Alborz Sharghi (en el noreste de Irán). El primer modelo aplica a red neuronal artificial pre-alimentada (ANN) con estructura 4-7-1. El modelo usa la profundidad, la fracción remanente de pirita, la fracción molar de oxígeno y la precipitación anual como parámetros de entrada y la fracción remanente de pirita en la profundidad requerida como salida de la red. En el segundo modelo, un sistema de inferencia neuro-difusa adaptado (ANFIS), que usa funciones generalizadas con forma de campana y el sistema de interferencia difusa Takagi–Sugeno, se aplicó con los mismos parámetros de entrada y salida. El coeficiente de correlación, la raíz del error cuadrático medio y el error relativo promedio para la etapa de entrenamiento del ANNs fueron 0,81, 0,169 y 0,12, respectivamente, mientras que los valores para ANFIS fueron 0,91, 0,091 y 0,078, respectivamente. La comparación de los coeficientes de correlación y los errores en los parámetros revelaron que ambos modelos predicen exitosamente la fracción remanente de pirita a diferentes profundidades de la pila. Sin embargo, ANFIS fue más preciso y confiable.
抽象
利用两种模型预测了伊朗东北部Alborz Sharghi洗煤厂废石堆中黄铁矿的氧化过程。第一个模型运用前馈人工神经网络(feed-forward artificial neural network,ANN)4-7-1模型,以黄铁矿埋深、黄铁矿初始残余量、氧摩尔浓度和降水量为输入参数,以废石堆内相应埋深的残余黄铁矿量为输出值。第二个模型采用自适应神经模糊推理系统(adaptive neuro- fuzzy inference system,ANFIS)的钟形隶属函数和Takagi–Sugeno型模糊推理系统,选用同样的输入和输出参数。ANNS方法学习阶段的相关系数、均方根误差、平均相对误差绝对值分别为0.81、0.169和 0.12,而ANFIS方法学习阶段的上述检验值分别为0.91、0.09和0.078。比较两个模型的相关系数和误差值发现,两个模型都成功地预测了废石堆中不同埋深残余黄铁矿含量,而且ANFIS方法更可靠和准确。






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cathles LM, Apps JA (1975) A model of the dump leaching process that incorporates oxygen balance, heat balance and air convection. Metall Trans B 6:617–624
Cheng CH, Wei LY (2010) One step-ahead ANFIS time series model for forecasting electricity loads. Optim Eng 11:303–307
Davis GB, Ritchie AIM (1986) A model of oxidation in pyritic mine wastes. Part 1: equations and approximate solution. Appl Math Model 10(5):314–322
Demuth H, Beale M (2002) Neural network toolbox for use with Matlab. The Mathworks, Inc., Natick, MA
Doulati Ardejani F, Singh RN, Baafi EY (2004) Use of PHOENICS for solving one-dimensional mine pollution problems. J Comput Fluid Dyn Appl 16:1–23
Doulati Ardejani F, Jodeiri Shokri B, Moradzadeh A, Soleimani E, Ansari Jafari M (2008) A combined mathematical geophysical model for prediction of pyrite oxidation and pollutant leaching associated with a coal washing waste dump. Int J Environ Sci Tech 5(4):517–526
Doulati Ardejani F, Jodeiri Shokri B, Bagheri M, Soleimani E (2010) Investigation of pyrite oxidation and acid mine drainage characterization associated with Razi active coal mine and coal washing waste dumps in the Azad shahr–Ramian region, northeast Iran. Environ Earth Sci 61:1547–1560
Doulati Ardejani F, Rooki R, Jodeiri Shokri B, Eslam Kish T, Aryafar A, Tourani P (2013) Prediction of rare earth elements in neutral alkaline mine drainage from Razi Coal Mine, Golestan Province, northeast Iran, using general regression neural network. J Environ Eng 139(6):896–907
Elberling B, Nicholson RV, Scharer JM (1994) A combined kinetic and diffusion model for pyrite oxidation in tailings: a change in controls with time. J Hydro 157(1):47–60
Gerke HH, Molson JW, Frind EO (2001) Modelling the impact of physical and chemical heterogeneity on solute leaching in pyritic overburden mine spoils. Ecol Eng 17:91–101
Gladfelter WL, Dickerhoof DW (1976) Use of atomic absorption spectrometry for iron determinations in coals. Fuel 55(4):360–361
Haykin S (1991) Neural networks: a comprehensive foundation. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Heddam S, Bermad A, Dechemi N (2012) ANFIS-based modelling for coagulant dosage in drinking water treatment plant: a case study. Environ Monit Assess 184:1953–1971
Jang JSR (1992) Neuro-fuzzy modeling: architecture, analyses and applications, PhD Dissertation, University of California, Berkeley
Jang JSR (1993) ANFIS: adaptive-network-based fuzzy inference system. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 23(3):665–685
Jang JSR, Sun CT (1997) Neuro-fuzzy and soft computing: a computational approach to learning and machine intelligence. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Jaynes DB, Rogowski AS, Pionke HB (1984) Acid mine drainage from reclaimed coal strip mines 2. Simulation results of model. Water Res Res 20(2):243–250
Ju J, Ryu H (2006) A study on subjective assessment of knit fabric by ANFIS. Fiber Polym 7(2):203–212
Karimpouli S, Fathianpour N, Roohi J (2010) A new approach to improve neural networks’ algorithm in permeability prediction of petroleum reservoirs using supervised committee machine neural network (SCMNN). J Petrol Sci Eng 73:227–232
Lo SP (2002) The application of an ANFIS and grey system method in turning tool-failure detection. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 19:564–572
Mamdani EH (1974) Applications of fuzzy algorithm for control of a simple dynamic plant. Proc IEEE 121(12):1585–1588
Mamdani EH, Assilian S (1975) An experiment in linguistic synthesis with a fuzzy logic controller. Int J Man Mach Study 7(1):1–13
Montgomery DC, Peck EA (1992) Introduction to linear regression analysis, 2nd edit. Wiley-Interscience, NYC
Nagendra S, Mukesh Khare SM (2006) Artificial neural network approach for modelling nitrogen dioxide dispersion from vehicular exhaust emissions. Ecol Model 190:99–115
Nikravesh M (2004) Soft computing-based computational intelligent for reservoir characterization. Exp Sys Appl 26:19–38
Rainfall Data of Semnan Province (2012) Semnan Regional Water Co, Research and Lab Centre
Sadeghiamirshahidi M, Eslam Kish T, Doulati Ardejani F (2013) Application of artificial neural networks to predict pyrite oxidation in a coal washing refuse pile. Fuel 104:163–169
Shahhoseiny M, Doulati Ardejani F, Shafaei SZ, Noaparast M, Hamidi D (2013) Geochemical and mineralogical characterization of a pyritic waste pile at the Anjir Tangeh coal washing plant, Zirab, northern Iran. Mine Water Environ 32(2):84–96
Sheoran AS, Sheoran V (2006) Heavy metal removal mechanism of acid mine drainage in wetlands: a critical review. Miner Eng 19:105–116
Singh RN, Doulati Ardejani F (2004) Finite volume discretisation for solving acid mine drainage problems. Arch Min Sci 49(4):531–556
Sugeno M, Kang GT (1988) Structure identification of fuzzy model. Fuzzy Sets Syst 28(1):15–33
Sugeno M, Tanaka K (1991) Successive identification of a fuzzy model and its application to prediction of complex systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst 42:315–334
Tahmasebi P, Hezarkhani A (2010) Application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for grade estimation; case study, sarcheshmeh porphyry copper deposit, Kerman, Iran. Aus J Basic Appl Sci 4(3):408–420
Tahmasebi P, Hezarkhani A (2012) A hybrid neural networks-fuzzy logic-genetic algorithm for grade estimation. Comput Geosci 42:18–27
Takagi T, Sugeno M (1985) Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 15(1):116–132
Yao HM, Vuthaluru HB, Tade MO, Djukanovic D (2005) Artificial neural network-based prediction of hydrogen content of coal in power station boilers. Fuel 84:1535–1542
Young VR (1996) Insurance rate changing: a fuzzy logic approach. J Risk Insur 63:461–483
Zadeh LA (1965) Fuzzy sets. Inform Control 8:338–353
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the technical support of both Amirkabir University of Technology and Shahrood University of Technology. We also thank the Alborz Sharghi Coal Company for their support of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jodeiri Shokri, B., Ramazi, H., Doulati Ardejani, F. et al. Prediction of Pyrite Oxidation in a Coal Washing Waste Pile Applying Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Inference Systems (ANFIS). Mine Water Environ 33, 146–156 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-013-0247-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-013-0247-3