Abstract
Objectives
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic multi-systemic inflammatory rheumatic disorder. Several studies have suggested that the interval from the peak to the end of the electrocardiographic T wave (Tp-e) may correspond to the transmural dispersion of repolarization and that increased Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio are associated with malignant ventricular arrhythmias. The aim of this study was to evaluate ventricular repolarization by using Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio in patients with AS, and to assess the relation with inflammation.
Methods
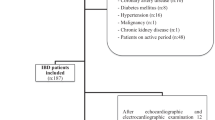
Sixty-two patients with AS and 50 controls were included. Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio were measured from a 12-lead electrocardiogram, and the Tp-e interval corrected for heart rate. The plasma level of high sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) was measured. These parameters were compared between groups.
Results
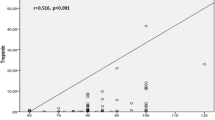
In electrocardiographic parameters analysis, QT dispersion (QTd) and corrected QTd were significantly increased in AS patients compared to the controls (31.7 ± 9.6 vs 28.2 ± 7.4 and 35.8 ± 11.5 vs 30.6 ± 7.9 ms, P = 0.03 and P = 0.007, respectively). cTp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio were also significantly higher in AS patients (92.1 ± 10.2 vs 75.8 ± 8.4 and 0.22 ± 0.02 vs 0.19 ± 0.02 ms, all P values <0.001). cTp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio were significantly correlated with hsCRP (r = 0.63, P < 0.001 and r = 0.49, P < 0.001, respectively).
Conclusions
Our study revealed that Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio were increased in AS patients. These electrocardiographic ventricular repolarization indexes were significantly correlated with the plasma level of hsCRP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lehtinen K. Mortality and causes of death in 398 patients admitted to hospital with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993;52:174–6.
Mathieu S, Gossec L, Dougados M, Soubrier M. Cardiovascular profile in ankylosing spondylitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2011;63:557–63.
Yildirir A, Aksoyek S, Calguneri M, Aytemir K, Kabakci G, Ovunc K, et al. QT dispersion as a predictor of arrhythmic events in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatology. 2000;39:875–9.
Acar G, Sayarlioglu M, Akcay A, Sokmen A, Sokmen G, Altun B, et al. Assessment of atrial electromechanical coupling characteristics in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Echocardiography. 2009;26:549–57.
Antzelevitch C, Shimizu W, Yan GX, Sicouri S. Cellular basis for QT dispersion. J Electrocardiol. 1998;30:168–75.
Kors JA, Ritsema van Eck HJ, van Herpen G. The meaning of the Tp-Te interval and its diagnostic value. J Electrocardiol. 2008;41:575–80.
Antzelevitch C, Sicouri S, Di Diego JM, Burashnikov A, Viskin S, Shimizu W, et al. Does Tpeak-Tend provide an index of transmural dispersion of repolarization? Heart Rhythm. 2007;4:1114–6.
Castro Hevia J, Antzelevitch C, Tornés Bárzaga F, Dorantes Sánchez M, Dorticós Balea F, Zayas Molina R, et al. Tpeak-Tend and Tpeak-Tend dispersion as risk factors for ventricular tachycardia/ventricular fibrillation in patients with the Brugada syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:1828–34.
Smetana P, Schmidt A, Zabel M, Hnatkova K, Franz M, Huber K, et al. Assessment of repolarization heterogeneity for prediction of mortality in cardiovascular disease: peak to the end of the T wave interval and nondipolar repolarization components. J Electrocardiol. 2011;44:301–8.
Erikssen G, Liestøl K, Gullestad L, Haugaa KH, Bendz B, Amlie JP. The terminal part of the QT interval (T peak to T end): a predictor of mortality after acute myocardial infarction. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2012;17:85–94.
Watanabe N, Kobayashi Y, Tanno K, Miyoshi F, Asano T, Kawamura M, et al. Transmural dispersion of repolarization and ventricular tachyarrhythmias. J Electrocardiol. 2004;37:191–200.
Gupta P, Patel C, Patel H, Narayanaswamy S, Malhotra B, Green JT, et al. T(p-e)/QT ratio as an index of arrhythmogenesis. J Electrocardiol. 2008;41:567–74.
Zhao X, Xie Z, Chu Y, Yang L, Xu W, Yang X, et al. Association between Tp-e/QT ratio and prognosis in patients undergoing primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Clin Cardiol. 2012;35:559–64.
Gunes Y, Tuncer M, Guntekin U, Sahin M, Yazmalar L. Effects of ankylosing spondylitis on the heart. Acta Cardiol. 2009;64:385–92.
Kazmierczak J, Peregud-Pogorzelska M, Biernawska J, Przepiera-Bedzak H, Goracy J, Brzosko I, Plonska E, et al. Cardiac arrhythmias and conduction disturbances in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Angiology. 2007;58:751–6.
Van Der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A. Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum. 1984;27:361–8.
Day CP, McComb JM, Campbell RW. QT dispersion: an indication of arrhythmia risk in patients with long QT intervals. Br Heart J. 1990;63:342–4.
Caliskan M, Erdogan D, Gullu H, Yilmaz S, Gursoy Y, Yildirir A, et al. Impaired coronary microvascular and left ventricular diastolic functions in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Atherosclerosis. 2008;196:306–12.
Kaya EB, Okutucu S, Aksoy H, Karakulak UN, Tulumen E, Ozdemir O, et al. Evaluation of cardiac autonomic functions in patients with ankylosing spondylitis via heart rate recovery and heart rate variability. Clin Res Cardiol. 2010;99:803–8.
Lagrand WK, Visser CA, Hermens WT, Niessen HW, Verheugt FW, Wolbink GJ, et al. C-reactive protein as a cardiovascular risk factor: more than an epiphenomenon? Circulation. 1999;100:96–102.
Mountantonakis S, Deo R. Biomarkers in atrial fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. Cardiovasc Ther. 2012;30:e74–80.
Kobayashi Y, Giles JT, Hirano M, Yokoe I, Nakajima Y, Bathon JM, et al. Assessment of myocardial abnormalities in rheumatoid arthritis using a comprehensive cardiac magnetic resonance approach: a pilot study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12:R171.
Akcay A, Acar G, Sayarlioglu M, Sokmen A, Kaya H, Ispiroglu M, et al. QT dispersion and transmural dispersion of repolarization in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Mod Rheumatol. 2009;19:550–5.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Acar, G., Yorgun, H., İnci, M.F. et al. Evaluation of Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QT ratio in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Mod Rheumatol (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-013-0881-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-013-0881-4