Abstract
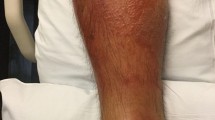
Two cases of subcutaneous soft tissue infection in 30 RA patients treated with tocilizumab are reported. In both patients, local redness, swelling, and heat were observed around the affected site. WBC spikes and such local findings were suggested to be clinically useful for the early detection of low-grade subcutaneous infection in RA patients whose disease is tightly controlled with tocilizumab. Of note, the C-reactive protein (CRP) level and temperature lacked clinical utility for such detection.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ellerin T, Rubin RH, Weinblatt ME. Infections and anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:3013–22.
Strangfeld A, Listing J. Infection and musculoskeletal conditions: bacterial and opportunistic infections during anti-TNF therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006;20:1181–95.
Arnett EC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, et al. The American Rheumatology Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31:315–24.
Ohzato H, Yoshizaki K, Nishimoto N, Ogata A, Tagoh H, Monden M, et al. Interleukin-6 as a new indicator of inflammatory status: detection of serum levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein after surgery. Surgery. 1992;111:201–9.
Mackiewicz A, Speroff T, Ganapathi MK, Kushner I. Effects of cytokine combinations on acute phase protein production in two human hepatoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1991;146:3032–7.
Nishimoto N, Terao K, Mima T, Nakahara H, Takagi N, Kakehi T. Mechanisms and pathologic significances in increase in serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) and soluble IL-6 receptor after administration of an anti-IL-6 receptor antibody, tocilizumab, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and Castleman disease. Blood. 2008;112:3959–64.
Hirao M, Hashimoto J, Tsuboi H, Nampei A, Nakahara H, Yoshio N, et al. Laboratory and febrile features after joint surgery in patients with tocilizumab. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:654–7.
Niimi M, Wada Y, Sato M, Takahara J, Kawanishi K. Effect of continuous intravenous injection of interleukin-6 and pretreatment with cyclooxygenase inhibitor on brain c-fos expression in the rat. Neuroendocrinology. 1997;66:47–53.
Wang JP, Dunn AJ. Mouse interleukin-6 stimulates the HPA axis and increases brain tryptophan and serotonin metabolism. Neurochem Int. 1998;33:143–54.
Besedovsky HO, Del Ray A, Futukawa H, Arditi GM, Kabiersch A. Cytokines as modulators of the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40:613–8.
Van der Meer MJM, Sweep CGJ, Rijnkels CEM, Pesman GJ, Tilders FJH, Kloppenborg PWC, Hermus ARMM. Acute stimulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by IL-1β, TNFα and IL-6: a dose response study. J Endocrinol Invest. 1996;19:175–82.
Nouri AME, Panayi GS, Goodman SM. Cytokines and the chronic inflammation of rheumatic disease: I. The presence of interleukin-1 in synovial fluids. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984;55:295.
Di Giovine FS, Nuki G, Duff GW. Tumour necrosis factor in synovial exudates. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988;47:768–72.
Newcombe DS, Fahey JV, Ishikawa Y. Hydrocortisone inhibition of the bradykinin activation of human synovial fibroblasts. Prostaglandins. 1977;13:235.
Oguogho A, Alomaka CP, Ereigbre AB. Depressed endothelium-dependent relaxation responses to acetylcholine and histamine in isolated human epigastric arteries from pre-eclamptic women. Clin Auton Res. 1996;6:153–5.
Suzuki Y, Yamamoto T, Suzumori K, Kajikuri J, Itoh T. Modified histamine-induced NO-mediated relaxation in resistance arteries in pre-eclampsia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;410:7–13.
Cockell AP, Poston L. Flow-mediated vasodilatation is enhanced in normal pregnancy but reduced in preeclampsia. Hypertension. 1997;30:247–51.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hirao, M., Nampei, A., Shi, K. et al. Diagnostic features of mild cellulitis phlegmon in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tocilizumab: a report of two cases. Mod Rheumatol 21, 673–677 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0459-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0459-y