Abstract
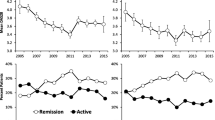
We aimed to clarify the degree of improvement in disease control following early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in daily clinical practice in 2006 compared to that in 2001. Using a large observational Japanese RA cohort (IORRA), we analyzed changes in clinical parameters, including disease activity assessed by the disease activity score 28 (DAS28) and physical disability assessed by the Japanese version of the Health Assessment Questionnaire (J-HAQ), which occurred within 2 years of cohort inception. All patients had enrolled in the IORRA cohort within 1 year of RA onset, in either 2001 (2001-cohort) or 2006 (2006-cohort). For both cohorts, changes in clinical features over 2 years were compared by Fisher’s exact test or the Wilcoxon test. The 2001-cohort included 71 patients and the 2006-cohort included 56 patients. Over the 2-year period for each cohort, DAS28 significantly decreased from 3.9 to 3.5 in the 2001-cohort (p < 0.001) and from 4.1 to 3.1 in the 2006-cohort (p < 0.0001), and J-HAQ significantly decreased from 0.62 to 0.49 (p < 0.02) in the 2001-cohort and from 0.71 to 0.41 (p < 0.001) in the 2006-cohort. Greater improvement in disease activity over 2 years occurred in the 2006-cohort than in the 2001-cohort (p < 0.05). Better disease control was obtained following changes in RA treatment strategy that occurred in Japan between 2001 and 2006.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sokka T, Abelson B, Pincus T. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: 2008 update. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2008;26:S35–61.
Peltomaa R, Paimela L, Kautiainen H, et al. Mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated actively from the time of diagnosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61:889–94.
Young A, Koduri G, Batley M, et al. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis. Increased in the early course of disease, in ischaemic heart disease and in pulmonary fibrosis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46:350–7.
Welsing PM, Fransen J, van Riel PL. Is the disease course of rheumatoid arthritis becoming milder? Time trends since 1985 in an inception cohort of early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:2616–24.
Uhlig T, Heiberg T, Mowinckel P, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis is milder in the new millennium: health status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 1994–2004. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1710–5.
Sokka T, Kautiainen H, Hakkinen A, et al. Radiographic progression is getting milder in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Results of 3 cohorts over 5 years. J Rheumatol. 2004;31:1073–82.
Verstappen SM, Jacobs JW, Bijlsma JW, et al. Five-year followup of rheumatoid arthritis patients after early treatment with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs versus treatment according to the pyramid approach in the first year. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:1797–807.
van Riel PL, Taggart AJ, Sany J, et al. Efficacy and safety of combination etanercept and methotrexate versus etanercept alone in patients with rheumatoid arthritis with an inadequate response to methotrexate: the ADORE study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1478–83.
Emery P, Keystone E, Tony HP, et al. IL-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab improves treatment outcomes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumour necrosis factor biologicals: results from a 24-week multicentre randomised placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:1516–23.
Nakajima A, Kamitsuji S, Saito A, et al. Disability and patient’s appraisal of general health contribute to depressed mood in rheumatoid arthritis in a large clinical study in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:151–7.
Yamanaka H, Inoue E, Singh G, et al. Improvement of disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis patients from 2000 to 2006 in a large observational cohort study IORRA in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2007;17:283–9.
Yamada T, Nakajima A, Inoue E, et al. Increased risk of tuberculosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65:1661–3.
Tanaka E, Singh G, Saito A, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of upper gastrointestinal ulcer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. Mod Rheumatol. 2005;15:340–5.
Furuya T, Kotake S, Inoue E, et al. Risk factors associated with incident fractures in Japanese men with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective observational cohort study. J Bone Miner Metab. 2008;26:499–505.
Momohara S, Ikari K, Mochizuki T, et al. Declining use of synovectomy surgery for patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Japan. Ann Rheum Dis. 2009;68:291–2.
Nakajima A, Inoue E, Tanaka E, et al. Mortality and cause of death in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis based on a large observational cohort, IORRA. Scand J Rheumatol. 2010;39:360–7.
Matsuda Y, Singh G, Yamanaka H, et al. Validation of a Japanese version of the Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire in 3, 763 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:784–8.
Wells GA, Tugwell P, Kraag GR, et al. Minimum important difference between patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the patient’s perspective. J Rheumatol. 1993;20:557–60.
Young A, Dixey J, Cox N, et al. How does functional disability in early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) affect patients and their lives? Results of 5 years of follow-up in 732 patients from the Early RA Study (ERAS). Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39:603–11.
Acknowledgments
The IORRA cohort was supported by non-restricted research grants from 36 pharmaceutical companies; Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Asahikasei Kuraray Medical Co., Ltd., Asahikasei Pharma Corporation, Astellas Pharma Inc., AstraZeneca K.K., Banyu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Fine Chemical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., GlaxoSmithKline K.K., Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Japan Tobacco Inc., Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Chemical Medience Corporation, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Nippon Chemiphar Co., Ltd., Nippon Shinyaku Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Sanofi-Aventis K.K., Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Sekisui Medical Co., Ltd., Taisho Toyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Teijin Pharma Limited, Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd., UCB Japan Co., Ltd., Wyeth K.K., and Zeria Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Conflict of interest
Hisashi Yamanaka: Research grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Wyeth K.K., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Banyu Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Abbott Japan Co., Ltd., Eisai Co., Ltd., Santen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Taishotoyama Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. Lecture fees and/or consulting fees from Abbott, Eisai Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., Hoffmann-La Roche, Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Pfizer Inc. The other authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Nakajima, A., Inoue, E., Shidara, K. et al. Standard treatment in daily clinical practice for early rheumatoid arthritis improved disease activity from 2001 to 2006. Mod Rheumatol 21, 594–597 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0457-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-011-0457-0