Abstract
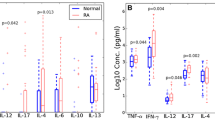
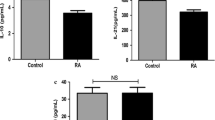
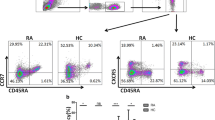
We had a rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patient resistant to multiple drugs and who developed panniculitis due to etanercept treatment, then responded fairly well to rituximab. Intracellular staining of cytokines in the peripheral blood mononuclear cells before and after rituximab administration revealed that the cytokine production, representative of T-helper (Th)1-, Th2-, and Th17-type responses, decreased abruptly after the treatment. Interestingly, this timing coincided with that of the manifestation of the beneficial effect. This relationship may provide useful insight into the mechanism of action of the drug and hence about the pathogenesis of RA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elliott MJ, Maini RN, Feldmann M, Kalden JR, Antoni C, Smolen JS, et al. Randomised double-blind comparison of chimeric monoclonal antibody to tumour necrosis factor alpha (cA2) versus placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1994;344:1105–10.
Moreland LW, Baumgartner SW, Schiff MH, Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Weaver AL, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion protein. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:141–7.
Nishimoto N, Yoshizaki K, Miyasaka N, Yamamoto K, Kawai S, Takeuchi T, et al. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with humanized anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody: a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:1761–9.
Smolen JS, Beaulieu A, Rubbert-Roth A, Ramos-Remus C, Rovensky J, Alecock E, et al. Effect of interleukin-6 receptor inhibition with tocilizumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (OPTION study): a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised trial. Lancet. 2008;371:987–97.
Kremer JM, Genant HK, Moreland LW, Russell AS, Emery P, Abud-Mendoza C, et al. Effects of abatacept in patients with methotrexate-resistant active rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144:865–76.
Genovese MC, Kaine JL, Lowenstein MB, Giudice JD, Baldassare A, Schechtman J, et al. Ocrelizumab, a humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, in the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a phase I/II randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58:2652–61.
Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2572–81.
Finckh A, Ciurea A, Brulhart L, Kyburz D, Moller B, Dehler S, et al. B cell depletion may be more effective than switching to an alternative anti-tumor necrosis factor agent in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate response to anti-tumor necrosis factor agents. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:1417–23.
Sato K. Th17 cells and rheumatoid arthritis––from the standpoint of osteoclast differentiation. Allergol Int. 2008;57:109–14.
Weaver CT, Hatton RD, Mangan PR, Harrington LE. IL-17 family cytokines and the expanding diversity of effector T cell lineages. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:821–52.
Lipsky PE, van der Heijde DM, St Clair EW, Furst DE, Breedveld FC, Kalden JR, et al. Infliximab and methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Trial in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Concomitant Therapy Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:1594–602.
Cambridge G, Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein MR, Salden M, Bodman-Smith M, et al. Serologic changes following B lymphocyte depletion therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48:2146–54.
Harris J, Vaughan JH. Transfusion studies in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1961;4:47–55.
Cohen SB, Emery P, Greenwald MW, Dougados M, Furie RA, Genovese MC, et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:2793–806.
Manzo A, Pitzalis C. Lymphoid tissue reactions in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2007;7:30–4.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, A., Sato, K., Miyoshi, F. et al. Analysis of cytokine production patterns of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from a rheumatoid arthritis patient successfully treated with rituximab. Mod Rheumatol 20, 183–187 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0244-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-009-0244-3