Abstract
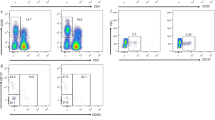
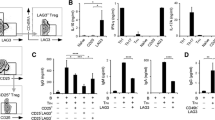
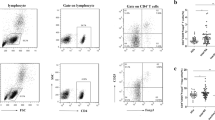
Regulatory subsets of B cells (Bregs) modulate immune responses in autoimmunity, cancer, and other inflammation diseases. In the present study, we investigated the numbers of circulating Breg cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We evaluated 59 RA patients and 25 healthy controls. CD19+CD5+CD1dhi B cells and granzyme B-secreting B cells (CD19+CD5+GzmB+) were analyzed by flow cytometry in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. We detected serum interleukin 10 (IL-10), interleukin 21 (IL-21), granzyme B (GzmB) using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Compared to control subjects, we found a decreased proportion of CD19+CD5+CD1dhi B cells in RA patients. The number of CD19+CD5+CD1dhi B cells negatively correlated with DAS28 (P < 0.05). Moreover, serum IL-10 and IL-21 concentrations were significantly lower in RA patients compared to healthy controls (P < 0.05). Conversely, the number of CD19+CD5+GzmB+ B cells was significantly higher in RA patients (P < 0.05), and the number of CD19+CD5+GzmB+ B cells did not correlate with DAS28, IL-21, or GzmB (P > 0.05, all). Interestingly, IL-21 and GzmB levels positively correlated in RA patients (P < 0.05). Our data indicate that CD19+CD5+CD1dhi B cells influence RA disease activity. CD19+CD5+GzmB+ B cells may be involved in RA development and progression. Our data strongly suggest a role for Bregs in RA, and Bregs may be a viable therapeutic strategy for RA disease.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feldmann M, Brennan FM, Maini RN. Rheumatoid arthritis. Cell. 1996;85:307–10.
Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–61.
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TW. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376:1094–108.
Mizoguchi A, Bhan AK. A case for regulatory B cells. J Immunol. 2006;176:705–10.
Iwata Y, Matsushita T, Horikawa M, et al. Characterization of a rare IL-10 competent B cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells. Blood. 2011;117:530–41.
Flores-Borja F, Bosma A, Mauri C, et al. CD19 + CD24hiCD38hi B cells Maintain Regulatory T Cells While Limiting TH1 and TH17 differentiation. Sci Transl Med. 2013;V5N173:173ra23.
Lee JH, Noh J, Noh G, et al. Allergen-specific transforming growth factor-β-producing CD19(+)CD5(+)regulatory B cell(Br 3) responses in human late eczematous allergic reactions to cow’s milk. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2011;31:441–9.
Noh J, Choi WS, Noh S, et al. Presence of Foxp3-expressing CD19(+)CD5(+) B cells in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: human CD19(+)CD5(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory B cell (Breg). Immune Netw. 2010;10:247–9.
Lundy SK. Killer B lymphocytes: the evidence and the potential. Inflamm Res. 2009;58(7):345–57.
Yang M, Den J, Liu J, et al. IL-10-producing regulatory B10 cells sameliorate collagen induced arthritis via suppressing Th17 cell generation. Am J Pathol. 2012;180(6):2375–85.
Hagn M, Ebel V, Sontheimer K, et al. CD5 + B cells from individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus express granzyme B. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40(7):2060–9.
Jahrsdörfer B, Blackwell SE, Wooldridge JE, et al. B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and other B cells can produce granzyme B and gain cytotoxic potential after interleukin-21-based activation. Blood. 2006;108(8):2712–9.
Lindner S, Dahlke K, Sontheimer K, et al. Interleukin 21-induced granzyme B-expressing B cells infiltrate tumors and regulate T cells. Cancer Res. 2013;73(8):2468–9.
Goldbach-Mansky R, Suson S, et al. Raised granzyme B levels are associated with erosions in patients with early rheumatoid factor positive rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(5):715–21.
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, et al. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988;31(3):315–24.
Prevoo ML, Van’t Hof MA, Kuper HH, et al. Modified disease activity scores that includes twenty-eight joint counts development and validation in a prospective longitudinal study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38(1):44–8.
Kalampokis I, Yoshizaki A, Tedder TF. IL-10-producing regulatory B cells(B10 cells) in autoimmune disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(Suppl 1):S1.
Yang M, Rui K, Wang S, et al. Regulatory B cells in autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol Immunol. 2013;10(2):122–32.
Mauri C, Bosma A. Immune regulatory function of B cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:221–41.
Ma L, Liu B, Jiang Z, et al. Reduced numbers of regulatory B cells are negatively correlated with disease activity in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(2):187–95.
Daien CI, Gailhac S, et al. (2014) Regulatory B10 cels are decreased in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and inversely correlated with disease activity.Arthritis Rheumatol. [Epup ahead of print].
DiLillo DJ, Matsushita T, Tedder TF. B10 cells and regulatory B cells balance immune responses during inflammation, autoimmunity, and cancer. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1183:38–57.
Tian G, Li JL, Wang DG, et al. (2014) Targeting IL-10 in Auto-immune Diseases. Cell Biochem Biophys s12013-14-9903-x.
Chen R, Tao Y, Qiu K, et al. Association of circulating Treg cells with disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2012;32(6):886–9.
Hagn M, Sontheimer K, Dahlke K, et al. Human B cells differentiate into granzyme B-secreting cytotoxic B lymphocytes upon incomplete T-cell help. Immunol Cell Biol. 2012;90(4):457–67.
Ozaki K, Spolski R, Feng CG, et al. A critical role for IL-21 in regulating immunoglobulin production. Science. 2002;298:1630–4.
Konforte D, Simard N, Paige CJ. IL-21: an executor of B cell fate. J Immunol. 2009;182:1781–7.
Yoshizaki A, Miyagaki T, Tedder TF. Regulatory B cells control T-cell autoimmunity through IL-21-dependent cognate interactions. Nature. 2012;491(7423):264–8.
Trapani JA, Sutton VR. Granzyme B: pro-apoptotic, antiviral and antitumor functions. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15(5):533–43.
Tak PP, Spaeny-Dekking, et al. The levels of soluble granzyme A and B are elevated in plasma and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Clin Exp Immunol 1999; 116(2): 366–70.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the Zhejiang Province Natural Science Fund (LY12H10002). We thank Prof. Jahrsdörfer, Thamara Beyer for helpful advice.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, D., Zhang, L., Chen, J. et al. Changes in regulatory B cells and their relationship with rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Clin Exp Med 15, 285–292 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-014-0310-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10238-014-0310-9