Abstract
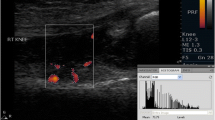
Synovial vascularization was analyzed by power Doppler and spectral Doppler sonography in 42 knee joints of 28 patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The synovial vessels with greater intensity of color flow signals demonstrated significantly lower indicators of vascular resistance – resistive index (P < 0.01) and pulsatility index (P < 0.01) – than those with lesser intensity. Consequently, an inverse correlation was observed between intensity of color flow signals and both resistive index (P < 0.01) and pulsatility index (P < 0.01).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, A., Takahashi, A., Yamadera, Y. et al. Doppler sonographic analysis of synovial vascularization in knee joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis: increased color flow signals and reduced vascular resistance. Mod Rheumatol 15, 33–36 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-004-0353-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10165-004-0353-y