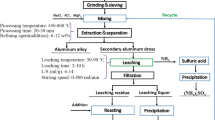
Abstract
Recycling plays an important role in today's world due to its considerable contributions to mitigating energy concerns and environmental challenges. One of them is dross recycling from aluminum (Al) cast houses. Unlike other recyclable materials, dross has an abundance of components, including rare earth elements, heavy metals, ferrous, and recycled Al. These features make dross a useful commodity within the recycling sector. It is harmful to the ecology and human health to land fill the dross. Recycling dross is economically advantageous and yields products with added worth. This article consolidates the current methods for extracting alumina from dross. The processes of plasma dross processing, acidic and alkaline leaching are critically examined. Dross is used in numerous applications, including the production of hydrogen as a renewable energy source, the manufacture of refractories, composites, ceramics, reductants, catalysts, and absorption agents, as a result of its multi-utility advantages. In construction applications, dross serves a unique purpose by Providing greater strength, thermal insulation and less water absorption increased the desirability of materials in this industry. This study explores the applications that maximize the utilization of dross and the associated advantages.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsakiridis PE (2012) Aluminium salt slag characterization and utilization—a review. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.03.052
Verma SK, Dwivedi VK, Dwivedi SP (2020) Utilization of aluminium dross for the development of valuable product—A review. Mater Today Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.045
Shinzato MC, Hypolito R (2016) Effect of disposal of aluminum recycling waste in soil and water bodies. Environ Earth Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-5438-3
Attia N, Hassan KM, Hassan MI (2018) Environmental Impacts of Aluminum Dross After Metal Extraction. Minerals Metals and Materials Series. Springer International Publishing, pp 1155–1161
Bruckard WJ, Woodcock JT (2007) Characterisation and treatment of Australian salt cakes by aqueous leaching. Miner Eng 20:1376–1390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2007.08.020
Huang XL, el Badawy A, Arambewela M et al (2014) Characterization of salt cake from secondary aluminum production. J Hazard Mater 273:192–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02.035
Xiao Y, Reuter MA (2002) Recycling of distributed aluminium turning scrap. Miner Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0892-6875(02)00137-1
Lavoie S, Dubé G (1991) A salt-free treatment of aluminum dross using plasma heating. JOM 43:54–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220144
Wajima T (2020) A novel process for recycling of aluminum dross using alkali fusion. Mater Trans 61:2208–2215. https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans.M-M2020849
Solem CKW, Deledda S, Tranell G, Aune RE (2023) Sampling procedure, characterization, and quantitative analyses of industrial aluminum white dross. J Sustain Metall 9(1):95–106
Peng, Zhiwei ,Hwang, Jiann-Yang, Downey, Jerome P. et al(2022). 10th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing. Springer.
Gomez A, NBJA LT (2008) Quantitative analysis of aluminum dross by the Rietveld method. Mater transa 49(4):728–732
Wang C, Li S, Guo Y, He Y, Liu J, Liu H (2023) Comprehensive treatments of aluminum dross in China: a critical review. J Environ Manage 345:118575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118575
Murayama N, Maekawa I, Ushiro H, Miyoshi T, Shibata J, Valix M (2012) Synthesis of various layered double hydroxides using aluminum dross generated in aluminum recycling process. Int J Miner Process 110:46–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2012.03.011
López-Delgado A, Tayibi H, Pérez C, Alguacil FJ, López FA (2009) A hazardous waste from secondary aluminium metallurgy as a new raw material for calcium aluminate glasses. J Hazard Mater 165(1–3):180–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.09.124
Abdulkadir A, Ajayi A, Hassan MI (2015) Evaluating the chemical composition and the molar heat capacities of a white aluminum dross. Energy Procedia 75:2099–2105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2015.07.326
Bruckard WJ, Woodcock JT (2009) Recovery of valuable materials from aluminium salt cakes. Int J Miner Process 93(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2009.05.002
Yoshimura HN, Abreu AP, Molisani AL, De Camargo AC, Portela JCS, Narita NE (2008) Evaluation of aluminum dross waste as raw material for refractories. Ceram Int 34(3):581–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2006.12.007
Kudyba A, Akhtar S, Johansen I, Safarian J (2021) Aluminum recovery from white aluminum dross by a mechanically activated phase separation and remelting process. JOM 73:2625–2634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-021-04730-x
Hiraki T, Nagasaka T (2015) An easier upgrading process of aluminum dross residue by screening technique. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 17:566–573. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-014-0283-5
Kevorkijan V (2002) Evaluating the aluminum content of pressed dross. JOM 54:34–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02701070
Hwang J, Huang X, Xu Z (2006) Recovery of metals from aluminum dross and saltcake. J Miner Mater Charact Eng. https://doi.org/10.4236/jmmce.2006.51003
Capuzzi S, Timelli G (2018) Preparation and melting of scrap in aluminum recycling: a review. Metals (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/MET8040249
Alberto J, Tenorio S, Carboni MC et al (2001) Recycling of aluminium-effect of fluoride additions on the salt viscosity and on the alumina dissolution. J light met. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1471-5317(01)00013-X
Majidi O, Shabestari SG, Aboutalebi MR (2007) Study of fluxing temperature in molten aluminum refining process. J Mater Process Technol 182:450–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.09.003
Masson DB, Taghiei MM (1989) interfacial reaction between aluminum alloys and salt flux during melting. Mater transactions JIM. https://doi.org/10.2320/MATERTRANS1989.30.411
Markus R, Yanping X, Boin U (2004) Recycling and environmental issues of metallurgical slags and salt fluxes. VII Int Conf Molten Slags Fluxes Salts. 2004:349–356
Wibner S, Antrekowitsch H, Meisel TC (2021) Studies on the formation and processing of aluminium dross with particular focus on special metals. Metals (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071108
Burkhard R, Hoffelner W, Eschenbach RC (1994) Recycling of metals from waste with thermal plasma. Resour conserve recycl 10:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/0921-3449(94)90033-7
Drouet M, Handfield MD, Meunier J, Laflamme CB (1994) Dross treatment in a rotary arc furnace with graphite electrodes. JOM 46:26–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03220691
Tzonev T, Lucheva B (2007) Recovering aluminum from aluminum dross in a DC electric rotary furnace. JOM J Miner Met Mater Soc 59(11):64–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-007-0143-z
Ünlü N, Drouet M (2002) Comparison of salt-free aluminum dross treatment processes. Resour Conserv Recycl 36:61–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-3449(02)00010-1
Beheshti R, Moosberg-Bustnes J, Akhtar S, Aune RE (2014) Black dross: processing salt removal from black dross by thermal treatment. JOM 66:2243–2252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1178-6
Khoei AR, Masters I, Gethin DT (2003) Numerical modelling of the rotary furnace in aluminium recycling processes. J Mater Process Technol 139:567–572. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00538-7
Carmona M, Cortés C (2014) Numerical simulation of a secondary aluminum melting furnace heated by a plasma torch. J Mater Process Technol 214:334–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2013.09.024
Syvertsen M, Øye B (2018) Recycling of Oxide from Dross into Aluminum Electrolysis Cells. In: Martin O (ed) Light Metals 2018 The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series. Springer, Cham
Tsakiridis PE, Oustadakis P, Agatzini-Leonardou S (2013) Aluminium recovery during black dross hydrothermal treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 1:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.03.004
Shen H, Forssberg E (2003) An overview of recovery of metals from slags. Waste Manage 23:933–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0956-053X(02)00164-2
Jafari NH, Asce SM, Stark TD et al (2014) Classification and reactivity of secondary aluminum production. J Hazard Toxic Radioact Waste 8(4). https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HZ.2153-5515.0000223
Bowen P, Highfield J, Mocellin A, Ring TA (1990) Degradation of aluminum nitride powder in an aqueous environment. ChemInform. https://doi.org/10.1002/CHIN.199024021
Fukumoto S, Hookabe T, Tsubakino H (2000) Hydrolysis behavior of aluminum nitride in various solutions. J Mater Sci 35:2743–2748. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004718329003
Zauzi NS, Zakaria MZ, Baini R, Rahman MR, Mohamed Sutan N, Hamdan S (2016) Influence of alkali treatment on the surface area of aluminium dross. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6306304
Shi M, Li Y, Ni P (2022) Recycling valuable elements from aluminum dross. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03925-2
David E, Kopac J (2018) The assessment of the recycling process of aluminum hazardous waste and a new route of development. Mater Proc. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2018.10.415
Gao Q, Guo Q, Li Y et al (2021) Innovative technology for defluorination of secondary aluminum dross by alkali leaching. Miner Eng. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107134
Meshram A, Gautam D, Singh KK (2020) Recycling of white aluminium dross: production of potash alum. Trans Indian Inst Met 73:1239–1248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-020-01973-1
Hu K, Reed D, Robshaw TJ et al (2021) Characterisation of aluminium black dross before and after stepwise salt-phase dissolution in non-aqueous solvents. J Hazard Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123351
Amer A (2002) Extracting aluminum from dross tailings. JOM 54:72–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02709754
Dash B, Das BR, Tripathy BC et al (2008) Acid dissolution of alumina from waste aluminium dross. Hydrometallurgy 92:48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2008.01.006
Das BR, Dash B, Tripathy BC et al (2007) Production of η-alumina from waste aluminium dross. Miner Eng 20:252–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2006.09.002
Sarker MSR, Alam MZ, Qadir MR et al (2015) Extraction and characterization of alumina nanopowders from aluminum dross by acid dissolution process. Int J Miner Metall Mater 22:429–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-015-1090-2
David E, Kopac J (2013) Aluminum recovery as a product with high added value using aluminum hazardous waste. J Hazard Mater 261:316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.07.042
Uehara K, Takeshita H, Kotaka H (2002) Hydrogen gas generation in the wet cutting of aluminum and its alloys. J Mater Process Technol 127:174–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00121-8
Hurtubise DW, Klosterman DA, Morgan AB (2018) Development and demonstration of a deployable apparatus for generating hydrogen from the hydrolysis of aluminum via sodium hydroxide. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43:6777–6788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.087
David E, Kopac J (2012) Hydrolysis of aluminum dross material to achieve zero hazardous waste. J Hazard Mater 209–210:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.01.064
Elsarrag E, Elhoweris A, Alhorr Y (2017) The production of hydrogen as an alternative energy carrier from aluminium waste. Energy Sustain Soc. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13705-017-0110-7
Li P, Wang J, Zhang X et al (2017) Molten salt-enhanced production of hydrogen by using skimmed hot dross from aluminum remelting at high temperature. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42:12956–12966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.046
Meshram A, Jain A, Rao MD, Singh KK (2019) From industrial waste to valuable products: preparation of hydrogen gas and alumina from aluminium dross. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00856-y
Nakajima K, Osuga H, Yokoyama K, Nagasaka T (2007) Material flow analysis of aluminum dross and environmental assessment for its recycling process. Mater Trans 48:2219–2224. https://doi.org/10.2320/MATERTRANS.MRA2007070
Elseknidy MH, Salmiaton A, Shafizah IN, Saad AH (2020) A study on mechanical properties of concrete incorporating aluminum dross, fly ash, and quarry dust. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12219230
Ewais EMM, Khalil NM, Amin MS et al (2009) Utilization of aluminum sludge and aluminum slag (dross) for the manufacture of calcium aluminate cement. Ceram Int 35:3381–3388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2009.06.008
Javali S, Chandrashekar AR, Naganna SR et al (2017) Eco-concrete for sustainability: utilizing aluminium dross and iron slag as partial replacement materials. Clean Technol Environ Policy 19:2291–2304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-017-1419-9
Panditharadhya BJ, Mulangi RH, Shankar AU, Amulya S (2019) Performance of concrete mix with secondary aluminium dross as a partial replacement for Portland pozzolana cement. Airfld Highw Pavements. https://doi.org/10.1061/9780784482469041
Elinwa AU, Mbadike EM (2011) The use of aluminum waste for concrete production. J Asian Archit Build Eng 10:217–220. https://doi.org/10.3130/jaabe.10.217
Nduka DO, Joshua O, Ajao AM et al (2019) Influence of secondary aluminum dross (SAD) on compressive strength and water absorption capacity properties of sandcrete block. Cogent Eng. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311916.2019.1608687
Nduka DO, Ede AN, Olofinnade OM, Ajao AM (2020) Mechanical and water absorption properties of normal strength concrete (NSC) containing secondary aluminum dross (SAD). Int J Eng Res Afr 47:1–13. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/JERA.47.1
Reddy MS, Neeraja D (2016) Mechanical and durability aspects of concrete incorporating secondary aluminium slag. Resour Effic Technol 2:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reffit.2016.10.012
Pereira DA, Aguiar B, Castro F, Almeida M, Labrincha JA (2000) Mechanical behaviour of Portland cement mortars with incorporation of Al-containing salt slags. Cem Concr Res 30:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(00)00272-6
Taha MA, Zawrah MF, Abomostafa HM (2022) Fabrication of Al/Al2O3/ SiC/graphene hybrid nanocomposites from Al-dross by powder metallurgy: sinterability, mechanical and electrical properties. Ceram Int 48:20923–20932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.04.084
Taha MA, Nassar AH, Zawrah MF (2020) In-situ formation of composite having hard outer layer based on aluminum dross reinforced by SiC and TiO2. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118638
Yurtbasi Z, Kuyumcu M, Kurt G, Kasgoz A (2022) Evaluation of morphological, rheological, mechanical, and dielectric properties of aluminum dross filled polyoxymethylene (POM) composites. Polym Compos. https://doi.org/10.1002/pc.26778
Kevorkijan VM (1999) The quality of aluminum dross particles and cost-effective reinforcement for structural aluminum-based composites. Compos Sci Technol 59:1745–1751. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0266-3538(99)00034-2
Ibarra Castro MN, Almanza Robles JM, Cortés Hernández DA et al (2009) Development of mullite/zirconia composites from a mixture of aluminum dross and zircon. Ceram Int 35:921–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2008.03.006
Aj O, Ts I, Hs B et al (2014) The development and characterisation of aluminium dross-epoxy resin composite materials. J Mater Sci Res. https://doi.org/10.5539/jmsr.v3n2p23
Li W, Zhang X, Zhang J et al (2022) Porous ceramics with near-zero shrinkage and low thermal conductivity from hazardous secondary aluminum dross. J Am Ceram Soc 105:3197–3210. https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.18322
Ewais EMM, Besisa NHA (2018) Tailoring of magnesium aluminum titanate based ceramics from aluminum dross. Mater Des 141:110–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.12.027
Sassi M, Simon A (2022) Waste-to-reuse foam glasses produced from soda-lime-silicate glass, cathode ray tube glass, and aluminium dross. Inorganics (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10010001
Xu L, Liu Y, Chen M, Wang N (2022) Efficient recycling of valuable metals from waste copper slag by using secondary aluminum dross as a novel reductant. Metall Mater Trans B. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-022-02567-6
Zhang G, Wang N, Chen M, Cheng Y (2020) Comprehensive recovery of multisource metallurgical wastes: recycling nickel slag by aluminum dross with converter-slag addition. ISIJ Int 60:1863–1871. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-670
Zhang G, Wang N, Chen M, Cheng Y (2020) Recycling nickel slag by aluminum dross: Iron-extraction and secondary slag stabilization. ISIJ Int 60:602–609. https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-173
Heo JH, Park JH (2017) Thermochemical analysis for the reduction behavior of FeO in EAF slag via aluminothermic smelting reduction (ASR) process: Part II. effect of aluminum dross and lime fluxing on Fe and Mn recovery. Calphad 58:229–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.calphad.2017.02.004
Fotovat F, Kazemian H, Kazemeini M (2009) Synthesis of Na-A and faujasitic zeolites from high silicon fly ash. Mater Res Bull 44:913–917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.08.008
Sánchez-Hernández R, López-Delgado A, Padilla I et al (2016) One-step synthesis of NaP1, SOD and ANA from a hazardous aluminum solid waste. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 226:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2016.01.037
Takehito HIRAKI ANNO and TA (2009) Synthesis of zeolite-X from waste materials. volume 49:1644–1648: https://doi.org/10.2355/isijinternational.49.1644
Yoldi M, Fuentes-Ordoñez EG, Korili SA, Gil A (2020) Zeolite synthesis from aluminum saline slag waste. Powder Technol 366:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.02.069
Kuroki S, Hashishin T, Morikawa T et al (2019) Selective synthesis of zeolites A and X from two industrial wastes: crushed stone powder and aluminum ash. J Environ Manage 231:749–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.082
Kang Y, Swain B, Im B et al (2019) Synthesis of zeolite using aluminum dross and waste LCD glass powder: a waste to waste integration valorization process. Metals (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/met9121240
Ghassemi Kakroudi M, Yeugo-Fogaing E, Huger M et al (2009) Influence of the thermal history on the mechanical properties of two alumina based castables. J Eur Ceram Soc 29:3197–3204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2009.05.052
Su N, Li Z, Ding Y et al (2021) Waste to wealth strategy: preparation and properties of lightweight Al2O3-SiO2-rich castables using aluminum dross waste. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247803
Yoshimura HN, Abreu AP, Molisani AL et al (2008) Evaluation of aluminum dross waste as raw material for refractories. Ceram Int 34:581–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2006.12.007
Chobtham C, Kongkarat S (2020) Synthesis of hercynite from aluminium dross at 1550°C: Implication for industrial waste recycling. Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech Publications Ltd., pp 223–228
Funding
The project was funded by the Indian Ministry of Mines (project No.: SNTMOM/156/2020), for which the authors are grateful.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kishor Modalavalasa: original manuscript writing, literature review, analysis and critical discussions; Dr. Kameswari Prasada Rao Ayyagari: conceptualization, overall guidance and final draft correction.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Modalavalasa, K., Ayyagari, K.P.R. Aluminum dross: aluminum metal recovery and emerging applications. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-024-01948-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-024-01948-0