Abstract
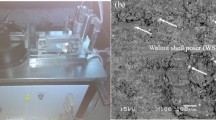
In this experiment banana fly ash (BA) at 1, 3 and 4 wt% was mixed with the hybrid natural fiber combination of sisal/pineapple at 30, 40 and 50 wt%. Grey relational analysis (GRA) coupled with Taguchi method is followed to find the common optimal parameter combination that yields lesser specific wear rate (SWR) and coefficient of friction while testing the developed novel polymer matrix composites against steel ball. The multi-response optimization using GRA pointed out that minimal addition of BA filler (1 wt%), hybrid fibre content (30 wt%), higher sliding distance (1500 m) and lesser loading (5 N) results in good overall tribological properties. The addition of filler materials and hybrid fibres with the polymer matrix results in increased friction. The SEM results showed high adding up of fiber results in pull out of fibers in the epoxy resin resulting in high wear rate of natural composites. Good fiber/filler/epoxy bonding created a tribolayer surface in the combination and that reduces the surface contact between counter specimen and work piece with reduced SWR.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sukudom N, Jariyasakoolroj P, Jarupan L, Tansin K (2019) Mechanical, thermal, and biodegradation behaviors of poly(vinyl alcohol) biocomposite with reinforcement of oil palm frond fiber. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0773-y
Bhogayata AC, Arora NK (2019) Utilization of metalized plastic waste of food packaging articles in geopolymer concrete. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:1014–1026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00859-9
Balaji A, Karthikeyan B, Swaminathan J, Sundar RC (2017) Mechanical behavior of short bagasse fiber reinforced cardanol-formaldehyde composites. Fibers Polym 18:1193–1199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-7009-y
Keskisaari A, Karki T (2017) Raw material potential of recyclable materials for fiber composites: a review study. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 19:1136–1143. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-016-0511-2
De Paiva FFG, de Maria VPK, Torres GB et al (2019) Sugarcane bagasse fiber as semi-reinforcement filler in natural rubber composite sandals. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:326–335. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0801-y
Grause G, Mochizuki T, Kameda T, Yoshioka T (2013) Recovery of glass fibers from glass fiber reinforced plastics by pyrolysis. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 15:122–128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-012-0101-x
Chen W, Zhang S, He F et al (2019) Porosity and surface chemistry development and thermal degradation of textile waste jute during recycling as activated carbon. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:315–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-018-0792-8
Mittal V, Saini R, Sinha S (2016) Natural fiber-mediated epoxy composites—a review. Compos B 99:425–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.06.051
Nguyen H, Jamali Moghadam M, Moayedi H (2019) Agricultural wastes preparation, management, and applications in civil engineering: a review. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 21:1039–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-019-00872-y
Oushabi A (2019) The pull-out behavior of chemically treated lignocellulosic fibers/polymeric matrix interface (LF/PM ): a review. Compos B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107059
Jaafar J, Parlaungan J, Mohd S et al (2018) Influence of selected treatment on tensile properties of short pineapple leaf fiber reinforced tapioca resin biopolymer composites. J Polym Environ 26:4271–4281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1296-2
Todkar SS, Patil SA (2019) Review on mechanical properties evaluation of pineapple leaf fibre (PALF) reinforced polymer composites. Compos B. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.106927
Aslan M, Tufan M, Küçükömeroğlu T (2018) Tribological and mechanical performance of sisal-filled waste carbon and glass fibre hybrid composites. Compos B 140:241–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.12.039
Maurya HO, Jha K, Tyagi YK (2017) Tribological behavior of short sisal fiber reinforced epoxy composite. Polym Polym Compos 25:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1177/096739111702500306
Nirmal U, Hashim J, Low KO (2012) Adhesive wear and frictional performance of bamboo fibres reinforced epoxy composite. Tribol Int 47:122–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.10.012
Shuhimi FF, Bin AMF, Kalam MA et al (2016) Tribological characteristics comparison for oil palm fibre/epoxy and kenaf fibre/epoxy composites under dry sliding conditions. Tribol Int 101:247–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.04.020
Singha AS, Thakur VK (2008) Mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced polymer composites. Bull Mater Sci 31:791–799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-008-0126-x
Joseph J, Munda PR, Kumar M et al (2020) Sustainable conducting polymer composites: study of mechanical and tribological properties of natural fiber reinforced PVA composites with carbon nanofillers. Polym Plast Technol Mater. https://doi.org/10.1080/25740881.2020.1719144
Nanda BP, Satapathy A (2020) An analysis of the sliding wear characteristics of epoxy-based hybrid composites using response surface method and neural computation. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2020.1722781
Fei J, Zhang C, Luo D et al (2018) Vertically aligned TiO2 nanorods-woven carbon fiber for reinforcement of both mechanical and anti-wear properties in resin composite. Appl Surf Sci 435:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.10.182
Kumar MNS, Yaakob Z, Mohan N, Babu SPK (2010) Mechanical and abrasive wear studies on biobased jatropha oil cake incorporated glass–epoxy composites. J Am Oil Chem Soc 87:929–936. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11746-010-1575-0
Sumesh KR, Kanthavel K (2019) Synergy of fiber content, Al2O3 nanopowder, NaOH treatment and compression pressure on free vibration and damping behavior of natural hybrid-based epoxy composites. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-019-02823-x
Sumesh KR, Kanthavel K (2020) Effect of TiO2 nano - filler in mechanical and free vibration damping behavior of hybrid natural fiber composites. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40430-020-02308-3
Sumesh KR, Kavimani V, Rajeshkumar G, Ravikumar P (2020) An investigation into the mechanical and wear characteristics of hybrid composites: influence of different types and content of biodegradable reinforcements. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2020.1821297
Mahesh V, Joladarashi S, Kulkarni SM (2019) Physio-mechanical and wear properties of novel jute reinforced natural rubber based flexible composite. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab0164
Chegdani F, El Mansori M, Bukkapatnam STS, El Amri I (2019) Thermal effect on the tribo-mechanical behavior of natural fiber composites at micro-scale. Tribol Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2019.06.024
Correa CE, Betancourt S, Vázquez A, Gañan P (2017) Wear performance of vinyl ester reinforced with Musaceae fiber bundles sliding against different metallic surfaces. Tribol Int 109:447–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.01.009
Kumar S, Patel VK, Mer KKS et al (2019) Himalayan natural fiber-reinforced epoxy composites: effect of Grewia optiva/Bauhinia vahlii fibers on physico-mechanical and dry sliding wear behavior. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2019.1612814
Yousif BF, Lau STW, McWilliam S (2010) Polyester composite based on betelnut fibre for tribological applications. Tribol Int 43:503–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2009.08.006
Akpan EI, Wetzel B, Friedrich K (2018) A fully biobased tribology material based on acrylic resin and short wood fibres. Tribol Int 120:381–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.01.010
Vivek S, Kanthavel K (2019) Effect of bagasse ash filled epoxy composites reinforced with hybrid plant fibres for mechanical and thermal properties. Compos B Eng 160:170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.10.038
Sumesh KR, Kanthavel K (2020) Abrasive water jet machining of sisal/pineapple epoxy hybrid composites with the addition of various fly ash filler. Mater Res Express. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab7865
Sumesh KR, Saikrishnan G, Pandiyan P, Prabhu L, Gokulkumar S, Priya AK et al (2021) The influence of different parameters in tribological characteristics of pineapple/sisal/TiO2 filler incorporation. J Ind Text. https://doi.org/10.1177/15280837211022614
Rajeshkumar G (2020) An experimental study on the interdependence of mercerization, moisture absorption and mechanical properties of sustainable Phoenix sp. fibre-reinforced epoxy composites. J Ind Text 49:1233–1251. https://doi.org/10.1177/1528083718811085
Rodríguez-díaz JM, Omar J, García P, Ramón L, Sánchez B, Gurgel M et al (2015) Comprehensive characterization of sugarcane bagasse ash for its use as an adsorbent. Bioenergy Res 8:1885–1895. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-015-9646-6
Castaldelli VN, Akasaki JL, Melges JLP et al (2013) Use of slag/sugar cane bagasse ash (SCBA) blends in the production of alkali-activated materials. Materials 6:3108–3127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma6083108
Pereira AM, Moraes JCB, Moraes MJB et al (2018) Valorisation of sugarcane bagasse ash (SCBA) with high quartz content as pozzolanic material in Portland cement mixtures. Mater Constr 68:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3989/mc.2018.00617
Sumesh KR, Kavimani V, Rajeshkumar G, Indran S, Saikrishnan G (2021) Effect of banana, pineapple and coir fly ash filled with hybrid fiber epoxy based composites for mechanical and morphological study. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 23:1277–1288. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-021-01196-6
Balaji A, Purushothaman R, Udhayasankar R, Vijayaraj S, Karthikeyan B (2020) Study on mechanical, thermal and morphological properties of banana fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. J Bio Tribo Corros. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40735-020-00357-8
Udhayasankar R, Karthikeyan B, Balaji A (2020) Comparative mechanical, thermal properties and morphological study of untreated and NaOH-treated coconut shell-reinforced cardanol environmental friendly green composites. J Adhes Sci Technol 34:1720–1740. https://doi.org/10.1080/01694243.2020.1727643
Rajeshkumar G (2020) A new study on tribological performance of Phoenix sp. fiber-reinforced epoxy composites. J Nat Fibers. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2020.1724235
Nirmal U, Hashim J, Megat Ahmad MMH (2015) A review on tribological performance of natural fibre polymeric composites. Tribol Int 83:77–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2014.11.003
Liu Y, Xie J, Wu N et al (2019) Influence of silane treatment on the mechanical, tribological and morphological properties of corn stalk fiber reinforced polymer composites. Tribol Int 131:398–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.11.004
Chang BP, Chan WH, Zamri MH et al (2019) Investigating the effects of operational factors on wear properties of heat-treated pultruded kenaf fiber-reinforced polyester composites using Taguchi method. J Nat Fibers 16:702–717. https://doi.org/10.1080/15440478.2018.1432001
Funding
The research work was funded by European Social Fund Project,” International Mobility of Researchers in CTU” (CZ.02.2.69/0.0/0.0/16_027/0008465).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keerthiveettil Ramakrishnan, S., Vijayananth, K., Pudhupalayam Muthukutti, G. et al. The effect of various composite and operating parameters in wear properties of epoxy-based natural fiber composites. J Mater Cycles Waste Manag 24, 667–679 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-022-01357-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10163-022-01357-1